The state of the world nuclear technology
Learning and studying from nuclear countries in the world that have developed for many years, especially civil nuclear powers, is necessary for a country that has just started on the path of building nuclear power technology like Vietnam.
Historical milestones
The 1950s saw the birth and widespread development of the first commercial nuclear power plants across continents.
 |
| Figure 1- Experimental Breeder Reactor EBR-I, Arco, Idaho, USA. |
First of all, we should also mention the EBR-I Nuclear Power Experimental Reactor, in Arco, Idaho, USA. This reactor, as early as December 20, 1951, conducted its first test of electricity production and lit four light bulbs.
Second, the APS-1 Nuclear Power Plant in Obninsk, Russia, was the first plant in the world to generate commercial electricity on June 26, 1954, connecting to the grid despite its very small total capacity of 5 MW. The reactor operated for nearly half a century until it was shut down on April 30, 2002.
Two years later, the Calder Hall 1 nuclear power plant in the UK was started up on July 27, 1956, connected to the national grid with a capacity of 50 MW. This was the first nuclear power plant (NM Đ HN) to be considered truly commercial and operated until March 2003.
The world nuclear power industry
After that historic 5-year initial period, over the past 50 years, to March 11, 2014, there were 31 countries with nuclear power plants with 435 reactors completed and generating 372 GW of electricity. Nuclear power plants have provided about 11.5% of the world's total electricity output and more than 3 times the total electricity output of France and Germany from all sources combined, being a solid baseload source and not causing harmful CO2 greenhouse gas emissions. About 72 reactors with 68 GW are under construction in 15 countries, equivalent to 20% of the existing capacity, and more than 160 reactors are planned to be built firmly, equivalent to half of the existing capacity. In addition, there are about 240 research reactors and more than 180 other nuclear reactors powering about 150 ships and submarines in 56 different countries.
More details on the status of nuclear power plants worldwide can be found in the Data Table (According to IAEA, as of 11/3/2014) and Figures 2 and 3 below.
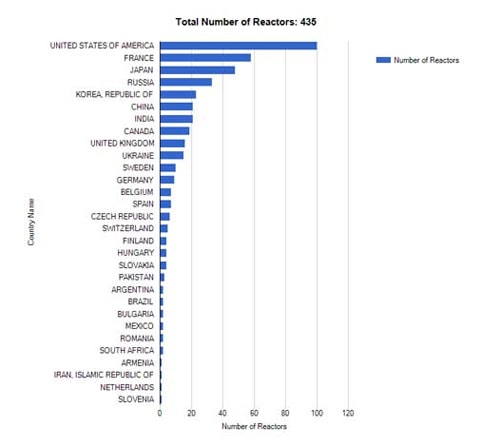 |
| Figure 2- Distribution of operating reactors in the world (Relative number % for each country. Data as of 11/3/2014 according to IAEA). |
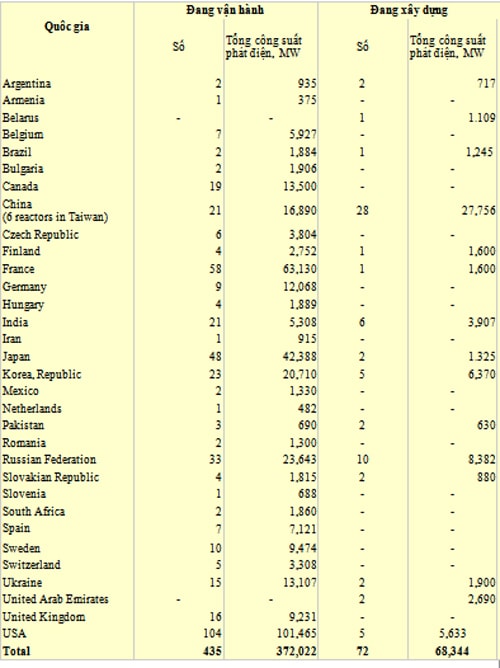 |
| Table of figures: Number of nuclear power plants worldwide in operation and under construction. |
Among the 31 nuclear countries listed in the Table above, the United States, Russia and France are considered the most prominent nuclear powers.
The US is at the top of the list with 104 operating nuclear reactors with a total generating capacity of 101,465 MW and five under construction with a total planned capacity of 5,633 MW.
France is in second place with 58 nuclear reactors in operation with a total generating capacity of 63,130 MW and one reactor under construction, the largest of its kind currently with a generating capacity of 1,600 MW.
Russia is in third place with 38 operating nuclear reactors with a total generating capacity of 23,643 MW and 10 reactors under construction with a total planned capacity of 8,382 MW.
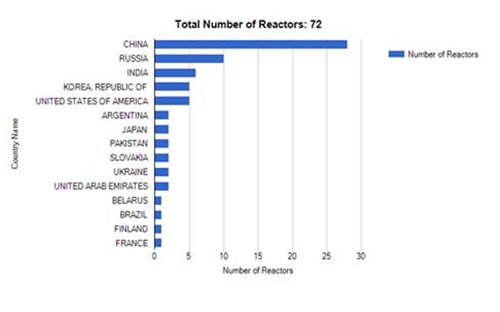 |
| Figure 3- Distribution of reactors (Relative % between countries) under construction in the world (Data up to 11/3/2014 according to IAEA). |
The three nuclear power countries mentioned above are also the biggest partners that Vietnam has been aiming for in terms of investment cooperation, technology transfer and human resource training to serve its young nuclear power technology industry.
According to Vietnamnet
