Spinal stenosis: Does eating a lot of calcium have any effect?
Spinal spurs are elongation of the bones on the vertebrae, cartilage discs or ligaments around the joints. The risk of this disease increases with age and men are affected more than women.
Causes of spinal stenosis and treatment
Chronic spondylitis: The inflammation affects the cartilage of the vertebrae, over time this cartilage gradually wears away, causing its smooth surface to become rough and jagged, and finally the two bone surfaces come into contact and rub against each other. At this point, the body will have a self-correcting process to overcome the above phenomenon, but the result of the correction process is the formation of bone spurs.
Calcium deposits in the ligaments and tendons that contact the vertebrae:
This is common in degenerative spine disease in the elderly; it is the deposition of calcium in the form of calcipyrophosphate.
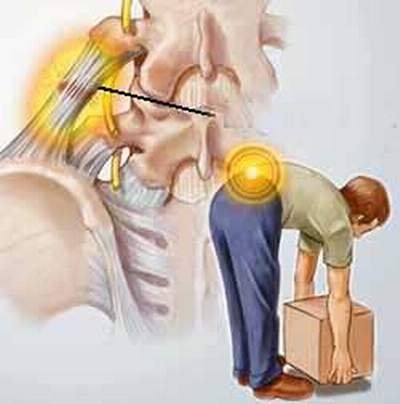
Treatment of spinal stenosis is often conservative. Commonly used drugs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain relievers and muscle relaxants. Sometimes people use some support devices such as neck braces... to reduce the burden on the diseased vertebrae.
Supportive treatments include acupuncture, physical therapy (to help reduce pain and increase mobility in some affected joints and muscles), and regular exercise. Avoid heavy sports that require the spine to bear a large weight such as weightlifting, high jumping, etc. You should practice water sports such as swimming and aerobics to help reduce body weight.
Yoga is also a method to help reduce body weight on the diseased vertebrae, while relaxing the affected muscles.
Patients must ensure moderate body weight and avoid excessive weight gain.
Surgery is indicated by doctors when there is compression of the spinal cord, narrowing of the spinal canal or nerve roots in the spine. However, removing the spur does not mean the disease will be cured permanently because the bone spur can grow back in the same location.
Milk is a food source rich in calcium.
Nutrition plays an important role
Many people believe that when suffering from spinal spurs, they should not eat foods rich in calcium. This concept is wrong because 90% of calcium when eaten is excreted in the feces, only 10% is absorbed. In addition, the amount of calcium in the blood is very tightly controlled, not to increase too much or decrease too much. This shows that eating a lot of calcium does not affect or cause more spurs to grow. Calcium is a major element that makes up bones, the body needs about 1,200mg of calcium every day. Foods rich in potassium such as milk, dairy products, green vegetables, shrimp, crab, small fish eaten whole with bones are the richest and most easily absorbed sources of calcium.
Lifestyle also plays an important role in preventing spinal spurs. Therefore, you should exercise regularly to increase calcium absorption and strengthen your bones. You should go outdoors to increase vitamin D production because skin exposure to sunlight will help synthesize vitamin D. This vitamin helps absorb and metabolize calcium in the body.
Symptoms of spinal osteoarthritis Spinal spurs are usually only a few millimeters long. Most of the spinal spurs appear on the front and sides, rarely growing in the back, so there is less compression on the spinal cord and nerve roots. Common symptoms that cause patients to go to the doctor are back pain, shoulder or neck pain, radiating down the arm, numbness in the hand..., sometimes limiting movement in the neck, shoulder, and lower back. Most spinal spurs cause pain due to contact with nerves or vertebrae when moving. |
According to Health & Life - NT
