New points in 10 laws taking effect from 2016
10 amended laws take effect from January 1, 2016 including the Law on Social Insurance, Citizen Identification, Civil Status, Amended Special Consumption Tax and Law on Military Service...
Social Insurance Law
One of the most important changes in the Social Insurance Law is the increase in insurance contributions. Specifically, when this law takes effect until the end of 2017, the contribution rate will be based on salary plus allowances stated in the labor contract; from January 1, 2018 onwards, the contribution rate will be based on salary plus allowances and additional amounts stated in the labor contract. Allowances are defined as fixed amounts with little fluctuation, including money to compensate for working conditions, the complexity of the job, living conditions, and the level of labor attraction that the salary agreed in the contract has not taken into account or has not fully taken into account.
In addition, the new law adds maternity leave for male workers. Specifically, the husband is entitled to 5 working days off in case his wife gives birth naturally, 7 days off in case his wife has a caesarean section, or gives birth before 32 weeks. If his wife gives birth to twins, the husband is entitled to 10 days off; from triplets onwards, each additional child is entitled to 3 more working days off. If his wife gives birth to twins or more and has to have a caesarean section, the husband is entitled to 14 days off...
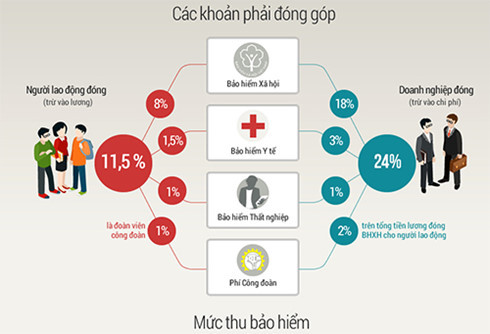 |
| Graphic of new contributions under the Social Insurance Law effective from January 2016. |
Citizen Identification Law
Since 2016, the Law on Citizen Identification has been in effect, all Vietnamese citizens aged 14 and over will be issued a 12-digit identification card instead of an identity card. This is an identification document, showing basic information about the background and identity of Vietnamese citizens, used in transactions within Vietnam.
Citizen identification cards are used instead of passports in cases where Vietnam and foreign countries sign treaties or agreements allowing citizens of the signatory countries to use citizen identification cards instead of passports in each other's territories.
Civil status law
This Law has provisions for strong reforms in the order and procedures for household registration, creating maximum convenience for people (such as simplifying and cutting down on many unnecessary documents when registering household registration; improving the method of submitting documents for people to choose - submitting directly, sending by post or via the online household registration system when conditions permit; reducing the processing time for most household registration matters).
The Law on Civil Status also stipulates that individuals have the right to choose their own civil status registration agency without having to depend on their place of residence as before. Individuals can register their civil status at the registration agency of their permanent residence, temporary residence or current residence...
Military Service Law
The Law on Military Service stipulates the age of conscription in peacetime up to 27 (currently up to 25) for citizens who have been temporarily deferred from conscription to study university or college training programs.
In addition, to ensure that citizens proactively prepare to perform their military service obligations and create favorable conditions for localities to develop and implement annual plans to call citizens to join the army, the Law stipulates a specific time to call citizens to join the army in February or March every year.
Amended Law on Special Consumption Tax
According to the Law amending and supplementing a number of articles of the Law on Special Consumption Tax, for cigarettes, cigars and other products from tobacco plants, the special consumption tax rate (SCT) will increase from 65% to 70% from January 1, 2016 and 75% from January 1, 2019; for alcohol under 20 degrees, the SCT rate will be 30% from January 1, 2016 and 35% from January 1, 2018...
For imported cars with less than 24 seats, the price used as the basis for calculating tax is the selling price of the importer (wholesale price) but must not be lower than 105% of the cost price of the imported car. If lower than this level, the tax price will be determined by the tax authority. "Cost price" is explained as the price for calculating import tax plus import tax and special consumption tax.
Law on Government Organization
The Law on Government Organization specifically stipulates that the number of deputy ministers and deputy heads of ministerial-level agencies shall not exceed 5; the number of the Ministries of National Defense, Public Security, and Foreign Affairs shall not exceed 6. In case of merger of ministries and ministerial-level agencies or the request for transfer or rotation of officials by competent agencies, the Prime Minister shall submit it to the National Assembly Standing Committee for consideration and decision.
Regarding the duties and powers of the Prime Minister, the Law on Government Organization (amended) has added two powers: During the period between two sessions of the National Assembly, the Prime Minister decides to delegate the authority of a minister or head of a ministerial-level agency upon the proposal of the Minister of Home Affairs in case of vacancy of a minister or head of a ministerial-level agency; During the period between two sessions of the Provincial People's Council, the Prime Minister decides to delegate the authority of the Chairman of the Provincial People's Committee upon the proposal of the Minister of Home Affairs in case of vacancy of the Chairman of the Provincial People's Committee.
Law on the Organization of the National Assembly
The Law supplements many provisions to ensure that National Assembly deputies play a central role in the organization and operation of the National Assembly, and supplements provisions to specifically define the legal position of full-time National Assembly deputies.
 |
| The Law on Organization of the National Assembly has new provisions on the position of Secretary General of the National Assembly, with the role of a National Assembly deputy concurrently holding the role of Chief of the National Assembly Office. |
The Law also provides new provisions on the position of Secretary General. Accordingly, the Secretary General of the National Assembly is elected, dismissed, or removed by the National Assembly to advise and serve the activities of the National Assembly, the National Assembly Standing Committee, and National Assembly deputies. The Secretary General is a National Assembly deputy and concurrently holds the role of Head of the National Assembly Office, responsible to the National Assembly and the National Assembly Standing Committee for the activities of the National Assembly Office.
Law on organization of local government
The Law on Organization of Local Government replacing the Law on Organization of People's Councils and People's Committees in 2003 has new points such as increasing the number of People's Council delegates of Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City from 95 to 105 to suit the population size, characteristics and nature of these large cities.
In addition, all administrative units organize People's Councils and People's Committees (local government level), ending the pilot program of not organizing People's Councils at district, ward and commune levels.
State Audit Law
This Law adds the following audited entities: Public use management agencies; enterprises in which the State holds more than 50% of the charter capital. For enterprises in which the State holds 50% or less of the charter capital, when necessary, the State Auditor General shall decide to select appropriate audit objectives, criteria, contents and methods.
Law on Vietnam Fatherland Front
The Law on the Vietnam Fatherland Front stipulates that the Vietnam Fatherland Front is allowed to participate in preventing and combating corruption and waste with the following contents: propagating and mobilizing people to implement the law on preventing and combating corruption, practicing thrift and combating waste; requesting competent agencies, organizations and individuals to apply measures to prevent corruption and waste; verifying corruption and waste cases; handling people who commit acts of corruption and waste; recommending competent state agencies to protect and reward people who have contributed to detecting and denouncing acts of corruption and waste.
In addition, the Law on the Vietnam Fatherland Front has supplemented and increased forms of supervision such as: Researching and reviewing documents of competent authorities related to the legitimate and legal rights and interests of the people; organizing supervision delegations; through the activities of the People's Inspection Board established at the commune level, and the Community Investment Supervision Board./.
According to VOV
