Answering frequently asked questions about antibiotic resistance
(Baonghean.vn) - Vietnam is a country with a high rate of antibiotic resistance in the world, emphasized Mr. Nguyen Viet Tien, Deputy Minister of Health at the 2016 Vietnam Antibiotic Resistance Communication Rally held on November 30, in Hanoi.
The cause of antibiotic resistance is identified as limited awareness of the community and medical staff about antibiotics and antibiotic resistance, and the use of antibiotics even when not prescribed. To help people gain knowledge about using medicine to limit antibiotic resistance, we introduce some frequently asked questions.
 |
What are antibiotics?
These are natural substances cultured from microorganisms, or chemically synthesized or semi-synthetic. They have the ability to destroy or slow down the growth and expansion of disease-causing microorganisms. These substances can be antibiotics, sulfa drugs, antivirals, fungicides, disinfectants, and antiseptics.
What is antibiotic resistance?
Antibiotic resistance occurs when pathogens or bacteria are not killed by antibiotics, they still exist, producing offspring that are not sensitive to one or more types of antibiotics.
Why can drug tolerance occur?
There are many causes, such as the indiscriminate and incorrect use of antibiotics, failure to respect the dosage and duration of treatment, and failure to take the full dose of medication as prescribed by the doctor. In addition, the abuse of antibiotics in veterinary medicine, agriculture and fisheries also contributes significantly to the formation of antibiotic resistance in humans. Finally, the problem of using disinfectants (nettoyant antibactérien) for cleaning too often and not according to instructions can also help produce strains of bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics. Doctors, dentists, pharmacists, veterinarians and patients all have responsibility for the problem of antibiotic resistance.
How does drug resistance occur?
Bacteria acquire drug resistance from many ways. From other bacteria that already have this property, or from natural mutations. Is this a natural phenomenon to protect the survival of an organism? Resistance is attached to the genes of bacteria, or can also be located in the chromosome subunits, called plasmids. These are extremely small and mobile DNA circles. When bacteria die, these plasmids will be released into the environment, and from there infect other bacteria. As for viruses, when reproducing (called replication), they need to penetrate bacteria to extract plasmids and transmit them to other bacteria.
When to use antibiotics and when not to use antibiotics?
Antibiotics are only effective against certain bacterial infections, and overuse is the cause of antibiotic resistance. According to Dr. Louise Selby, when antibiotics should really be used and when they are not necessary:
Sore throat
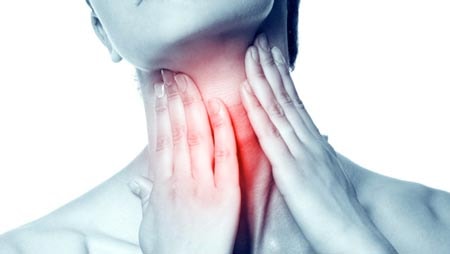 |
This is one of the most common reasons most people come in and ask for antibiotics.
No need for antibiotics:
In most cases, sore throats are caused by viruses, not bacteria. Antibiotics work by killing or inactivating bacteria. They have no effect on viruses.
Better yet, ease the discomfort with painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen. Combine that with rest to help your immune system fight the virus.
Use of antibiotics:
A high fever above 38.5 degrees combined with white spots on the tonsils can be a sign of a bacterial infection. Some common symptoms of bacterial pharyngitis are runny nose, sneezing, swollen and painful lymph nodes in the neck... If the symptoms last more than 24-48 hours, antibiotics such as penicillin can be used.
Sinusitis
No need for antibiotics:
Most sinus infections are viral, so antibiotics won't help. Steaming your nose over a bowl of steaming water with a towel over your head can help moisten and loosen secretions, making it easier to clear your nose. Pain relievers can also temporarily relieve congestion.
Use of antibiotics:
Antibiotics may be used if symptoms do not improve after a week or if sinusitis occurs several times a year. About one-third of people with sinusitis will develop a secondary bacterial infection in the sinus membranes that requires antibiotic treatment.
Eyesore
 |
Eye inflammation, pain, and infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
No need for antibiotics:
Mild eye infections can be treated with antibacterial medications such as Brolene Eye Drops and GoldenEye, which contain propamidine isetionate. Instead of killing bacteria, these medications slow their growth, allowing the body to fight the infection.
Use of antibiotics:
When the eyes show severe pain and signs of bacterial conjunctivitis, antibiotic eye drops are necessary.
Chest infection
No need for antibiotics:
Bronchitis is usually caused by a virus. Symptoms can be relieved with aspirin, paracetamol and ibuprofen.
If you have a cough that lasts for about 2 weeks, you may not need antibiotics. If it lasts longer than 3 weeks, you may have a secondary bacterial infection from a chest infection, so watch for other symptoms such as high fever and wheezing.
Use of antibiotics:
When you have symptoms such as fever higher than 38.5 degrees, difficulty breathing, headache, cough up phlegm... it can be symptoms of pneumonia. Unlike bronchitis, pneumonia can be caused by bacteria and antibiotics are often necessary. If you cough up blood or have a persistent cough for more than 3 weeks, you must see a doctor.
Ear infection
No need for antibiotics:
Middle ear infections are usually caused by a virus. Paracetamol or ibuprofen can help relieve pain or fever.
Use of antibiotics:
In adults or children, if symptoms are severe, including high fever above 38.5 degrees and vomiting, do not go away within 2-3 days or if there is pus draining from the ear, antibiotics are needed.
Urinary tract infection
 |
No need for antibiotics:
Mild symptoms include a slight burning sensation on urination, frequent urination which can be relieved by drinking plenty of water and cranberry juice 250-500 ml daily.
If urinary tract infections recur, it is sometimes simply due to not drinking enough water or using too much soap when cleaning the genital area.
Use of antibiotics:
If you have lower back pain, it could be a sign that the infection has spread to your kidneys and antibiotics are needed. Antibiotics also play a key role in treating cystitis.
To help reduce the rate of antibiotic resistance, Deputy Minister of Health Nguyen Viet Tien has called on each citizen to only buy and use antibiotics when examined and prescribed by a doctor and to use antibiotics according to the doctor's instructions. Medical staff must strictly follow professional instructions and use antibiotics in treatment appropriately and safely...
Pear Flower
(Synthetic)
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|
