Nghe An: Strengthening communication, monitoring and prevention of Marburg disease
(Baonghean.vn) - Currently, there is no vaccine or specific treatment for Marburg disease. This is a particularly dangerous disease, with a high transmission rate and mortality rate (50% can be up to 88%).
Recently, the Department of Health and the Department of Information and Communications of Nghe An have issued official dispatches to relevant units with the content of strengthening communication, monitoring and prevention work.pandemicMarburg. Accordingly:
Marburg disease is a diseaseinfectiousacute disease caused by Marburg virus. The natural reservoir is the fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptianus). The disease can be transmitted from animals (bats, primates) to humans.
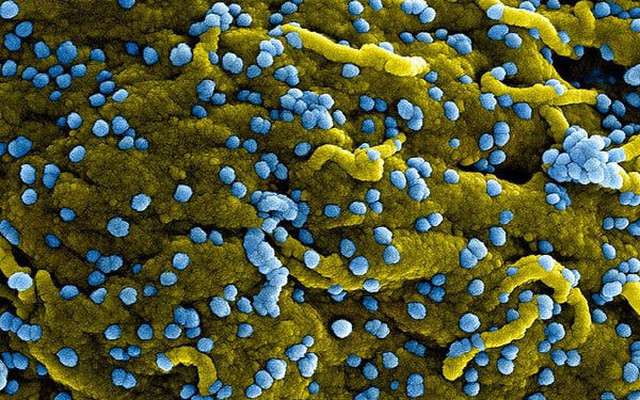 |
Marburg virus (blue), both replicating and attaching to the surface of infected cells (yellow). Photo: Internet |
The disease is transmitted from person to person through direct contact with blood, body fluids (urine, sweat, saliva, vomit, breast milk, semen...) or with the environment and objects contaminated with secretions of people infected/dead with Marburg virus.
Incubation period is 2-21 days; onset is with symptoms of high fever, headache, discomfort, then diarrhea, abdominal pain, cramps, nausea, vomiting, bleeding may appear.
There is currently no vaccine or specific treatment for Marburg. This is a particularly dangerous disease, highly contagious and has a high mortality rate (50%, up to 88%). The disease is classified as Group A in our country's Law on Prevention of Infectious Diseases.
To prevent and control the Marburg epidemic, the Department of Health and the Department of Information and Communications of Nghe An province request the People's Committees of districts, towns and Vinh city, and press agencies to proactively and promptly report on the epidemic situation and preventive measures so that people do not panic and worry and implement preventive measures well.
 |
Soldiers in biohazard suits bury two bodies during the 2005 Marburg outbreak in Uige, Angola. The deceased were not known to have contracted the virus. Photo: Internet |
Nghe An Department of Health assigned the Provincial Center for Disease Control to be the focal point for implementing, guiding, inspecting and supervising the implementation of Marburg disease prevention and control work in the province.
Strengthen close monitoring of entrants, in the community and at medical facilities to promptly detect suspected cases for epidemiological investigation (note those entering from epidemic countries in the African region within 21 days).
Local medical facilities coordinate with the provincial Center for Disease Control and the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology to collect samples for diagnostic testing; manage cases (if any) and handle them to prevent the disease from spreading to the community.
Medical facilities fully implement personal protective measures for medical staff and people in contact with suspected cases, to prevent infection among medical staff and spread in the community.
Organize training for medical staff at all levels on prevention, care and treatment measures, paying special attention to infection prevention and control; proactively develop response plans according to situations to be ready to respond in case of an epidemic occurring locally, not to be passive.
Prepare medicines, equipment, human resources, and funding to implement measures for admission, treatment, and disease prevention; strictly implement information and reporting between medical facilities and levels, especially when recording suspected or infected cases.
