How to cure sciatica, can it be cured?
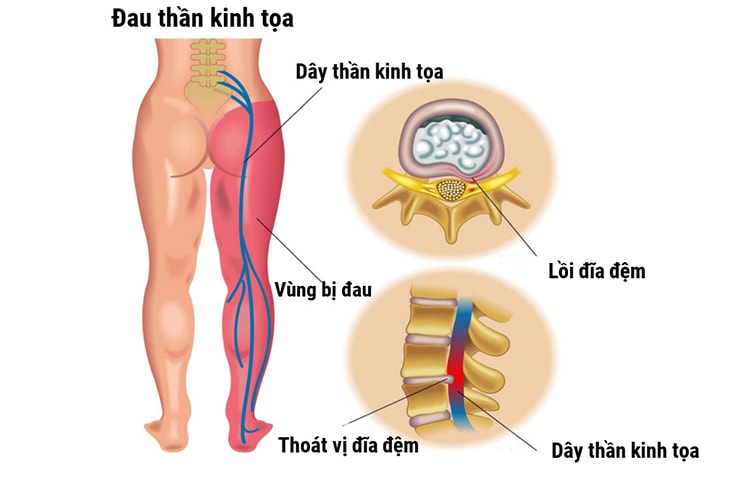
Sciatica is pain that radiates along the course of the sciatic nerve from its starting point to its ending point.
The cause of sciatica is mostly due to herniated disc L4/L5 or L5/S1 causing compression of the corresponding nerve roots. In addition, sciatica also has other rare causes such as inflammation, neuroma, invasive cancer compressing the sciatic nerve.
Recognizing sciatica
The symptom of the disease is pain along the sciatic nerve. Usually, it is pain in the right or left lumbar spine. Depending on the location of the lesion, the clinical manifestations are also different:
- L5 nerve root pain: pain in the hip area spreads to the middle of the buttocks, the back and side of the thigh, the outside of the calf, the top of the foot, ending at the big toe and the 3 middle toes.
- S1 nerve root pain: pain in the lower back radiating to the middle of the buttocks, back of the thigh, back of the lower leg (calf), heel, sole of the foot and ending in the little toe (5th toe of the foot).
If the patient has sciatica for a long time, it can lead to muscle atrophy on the painful leg.
Diagnosis of sciatica
Diagnosis of sciatica is based on typical clinical manifestations and definitive diagnosis of the cause is based on paraclinical tests, mainly lumbar spine MRI or lumbar spine CT in places without MRI conditions.
Note that some symptoms help guide the diagnosis of causes other than disc herniation due to inflammation or other spinal diseases such as: fever, weight loss, severe pain at night, affecting health, high lumbar spine pain L1-L3 or S1-S3 pain, the patient has some other symptoms besides sciatica signs,...
Commonly ordered tests include: hematology, biochemistry, inflammatory index, etc. and some abnormalities in hematology and/or biochemistry tests... to help guide the diagnosis of other causes.
- Lumbar spine X-ray: Helps differentiate when there are abnormalities such as spondylolisthesis, spondylodiscitis, signs of bone destruction or abnormal bone density.
- CT scan of the spine: helps diagnose the cause of sciatica due to herniated disc or other causes.
- MRI of the spine: this is a method that helps diagnose the exact location, level, and type of disc herniation. In addition, MRI also helps diagnose other causes such as inflammation, neuroma, cancer metastasis, etc.
Diagnosis helps differentiate sciatica from other diseases such as: Femoral neuralgia, femoral neuralgia, obturator neuralgia; Hip joint diseases such as: aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, hip arthritis, hip osteoarthritis; Lumbopelvic musculoskeletal diseases: inflammation, abscess, tumor; Sacroiliitis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoporosis, vertebral compression fractures, etc.

How to treat sciatica?
Once the cause of sciatica has been determined, appropriate treatment will be given depending on the cause.
- Treatment of acute sciatica
Most cases of acute sciatica respond well to self-care measures, including: Pain relievers such as ibuprofen. However, not all pain relievers are suitable for everyone; patients should consult a doctor. Exercises such as walking or light stretching. Heat or cold compresses help relieve pain.
- Treatment of chronic sciatica
Treatment of chronic sciatica often includes a combination of self-care measures and medical treatments: Physical therapy, rehabilitation, especially cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) – which helps control chronic pain by training people to respond differently to their pain, and pain medication.
Surgery may be an option if symptoms do not respond to other treatments and continue to worsen.
Depending on the cause of your sciatica, your surgeon will consider the risks and benefits of surgery and may recommend an appropriate surgical option.
In addition, patients also need physical therapy. There are many ways to reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve through exercise to help patients reduce pain symptoms, reduce or avoid medication... Massage; Physical therapy with spinal stretching exercises, swimming, hanging on a horizontal bar... or wearing a back support belt.
In short,Sciatica not only causes pain, affects the patient's life but can also lead to complications leading to movement, so early prevention is needed. Apply the following measures: Exercise every day. Maintain a suitable sitting posture, do not sit in one place for too long. Limit heavy lifting. Limit frequent lifting or twisting of the waist.
Sciatica can be completely cured if detected early and treated properly. For mild cases of sciatica, patients can adjust through measures such as:
- Change living and exercise habits: To reduce pressure and improve sciatica, patients need to pay attention to rest and exercise properly. Avoid staying up late, limit heavy work and activities that affect the nerves, pay attention to sitting and lying positions, and combine work and rest properly.
- Adjusting the diet: Through nutritional supplements will support the treatment process, reduce pressure on bones, joints, nerves as well as prevent disease progression. Sciatica patients should supplement foods rich in calcium, omega 3, B vitamins...
- Supportive exercises: Patients can refer to and perform gentle movements and postures to reduce nerve compression such as the cobra pose, baby pose, bridge pose... In addition, sports and exercises that do not require too much effort are also encouraged.
