Smoking is the cause of many lung diseases.
Smoking is known to be the most common cause of lung cancer. In addition, smoking is linked to 90% of all lung disease cases.
Lung cancer
In most countries,cigaretteis responsible for more than 90% of lung cancer deaths. In fact, lung cancer was a rare disease before the use ofcigarettebecome more common. Over the past 60 years, lung cancer rates have increased dramatically along with the increase in smoking.
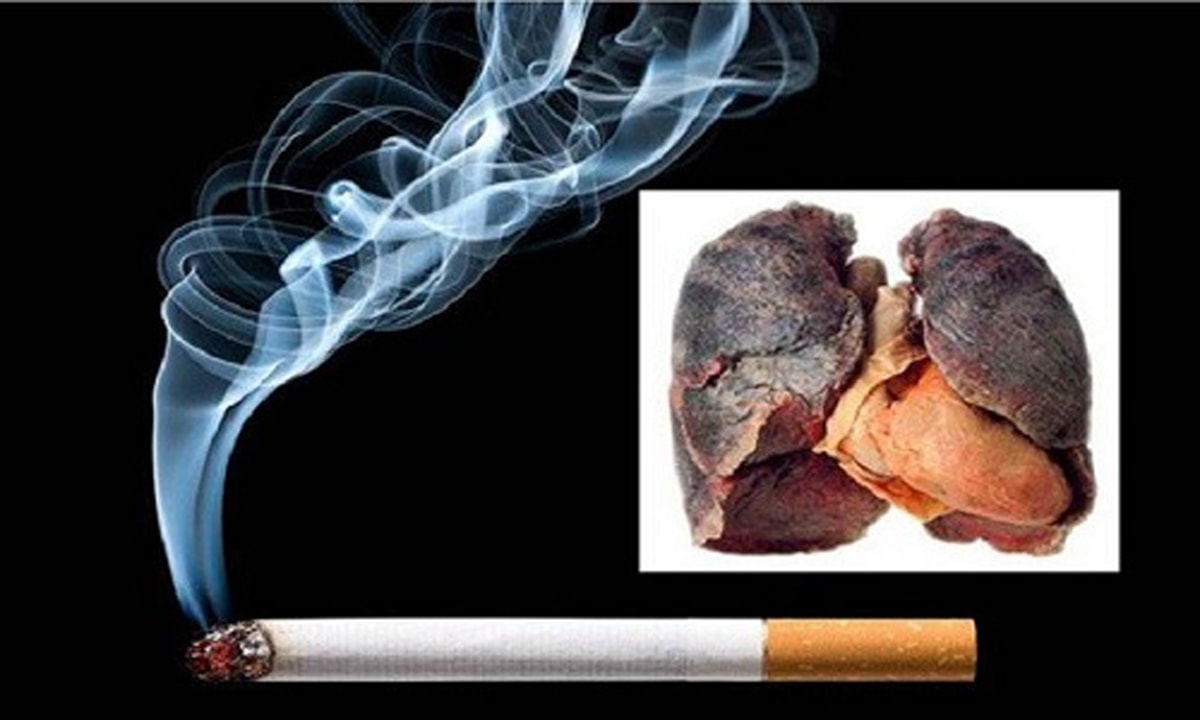
On average, smokers increase their risk of lung cancer by 5 to 10 times. Many studies have identified three important trends: Cancer risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked/number of cigarettes per day; cancer risk increases with smoking duration, measured in years; and cancer risk increases with people who start smoking at a young age.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a disease classification that refers to lung involvement associated with airway obstruction. The two main forms of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Smoking is the primary cause of both diseases.
The association between tobacco use and COPD is similar in strength to the association between smoking and lung cancer. Because smokers often have impaired bronchial mucosal function than nonsmokers, they are more vulnerable to environmental, infectious, and toxic fumes.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is estimated to be 10 times more common in smokers than in nonsmokers, and tobacco use may be involved in most deaths from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Hen
In smokers, asthma will be more severe. Asthmatic people who smoke have to endure a lot of phlegm, reduced cilia activity, are susceptible to infection, are susceptible to allergies and affect air circulation in the small airways.
One study found that the death rate from asthma among current or former smokers was double that of non-smokers.
Respiratory tract infection
Smoking weakens the body's immune system. Smokers are more likely to develop respiratory infections such as pneumonia and influenza than non-smokers.
Smokers not only suffer more from illness, they suffer from more severe illness. Studies show that smokers suffer more from cough, phlegm and wheezing than non-smokers.
