2 inventions that will change the future of humanity
Cameras that can see through the body and using genetic modification to neutralize deadly biological weapons are considered two breakthrough inventions that will influence the future of technology.
1. Magic camera better than X-ray
Endoscopy medical techniques have come a long way, but in the future, it could bring even more breakthroughs as doctors are able to see through to what's going on beneath our skin.
Researchers have invented a new type of camera that can see through the body's internal structures. By doing so, they can detect light sources behind body tissues.
The first prototype was developed by researchers at the University of Edinburgh, UK. When combined with an endoscope, the device can "see" into the cavities inside the human body.
An endoscope is a long, thin instrument, often equipped with a camera, sensors, and light. It is a must-have tool for all types of medical procedures. However, without an X-ray, it is difficult to determine exactly where in the body the endoscope is working.
The new camera can overcome this by detecting light sources inside the body. With thousands of photon detectors built into the camera, the device can detect light particles being passed through human tissues.
 |
| New camera can see through the body. |
When photons come into contact with body structures, light often scatters or bounces off the tissue, and the camera's sensitivity allows it to capture the smallest traces of light.
By combining the camera's directed light signals with scattered photons, the device can determine where the endoscope is emitting light inside the body.
This technique can help doctors know the exact location of the organs inside the body that they are observing by endoscopy. This plays an important role in diagnosis and treatment.
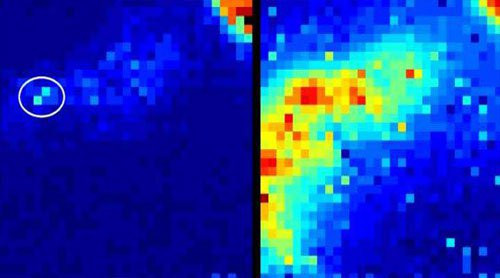 |
| This technique can help doctors know the exact location of organs inside the body. |
In the image above, you can see an example of light being detected by a camera from a confocal microscope used in sheep lungs. The image on the left is what the new camera would look like – it reveals exactly where the instrument is in the lung.
On the right, the image shows the scene as seen in a conventional camera, with the sensor capturing noises as scattered light. But we cannot determine the location of the photons as the light particles bounce around the structure of the lungs.
"This is technology that allows us to see through the human body," said lead researcher Kev Dhaliwal. "The ability to see where a device is located is important for many applications in healthcare. It's especially useful when we're doing minimally invasive procedures to treat diseases."
The project, called Proteus, is exploring a range of new imaging technologies to help visualize previously unsolved “biological secrets.” The research focuses on respiratory and lung diseases.
The improved vision provided by the new camera will help doctors visualize the position and length of the endoscope they are using, the researchers say. They also hope to improve the resolution of the images in the future.
We certainly won't see this magical camera in clinical practice any time soon, but it's a promising step forward in imaging and diagnostic technology.
2. Neutralize deadly biological weapons
Francisella tularensis (F. tularensis) bacteria have been used as biological weapons since World War II. Recently, scientists have used genetic modification to neutralize their toxicity.
F. tularensis causes a nasty disease called tularemia, whose prominent symptoms include joint and muscle pain and weakness. During World War II, the Soviet Red Army used it to hinder German troops before the Battle of Stalingrad.
To date, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) considers F. tularensis to be one of the most dangerous bioterrorism agents, along with anthrax, botulism, plague, smallpox, and viral hemorrhagic fevers. However, researchers have found a way to neutralize this dangerous bacteria.
By mapping the bacteria's molecular circuitry, researchers are making them harmless. The approach focuses on a group of genes known as the "Francisella pathogenicity island."
 |
| Bacteria that cause tularemia. |
Through a series of structural, biochemical and cellular studies, the researchers identified how these disease-causing genes are “turned on” and “turned off.” From there, they created genetic mutations that prevented the bacteria from being able to cause disease.
The biggest benefit of treating tularemia is that it doesn’t rely on antibiotics. With the growing threat of antibiotic resistance, the need to find alternatives to antibiotics is clear. And any research that helps us reduce our use of antibiotics is invaluable.
However, this is not the first time that people have found an alternative to antibiotics to treat tularemia, including a therapy to kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria through CRISPR.
Of course we still have to use antibiotics when necessary, but what is more important is that we need to increase research on new therapies to reduce unnecessary use of drugs.
According to Khoahoc.tv
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|


