7 Internal Organs You Can Still Live Healthy Even If You Lose Them
Several studies have shown that men who have their testicles removed are more likely to live longer than normal.
The human body is amazing and powerful. When you donate blood, you lose about 3.5 trillion red blood cells, but the body can quickly replace them. People can even live relatively normal lives with only half a brain. Other internal organs can also be completely removed without too much of a disruption to life.
1. Spleen
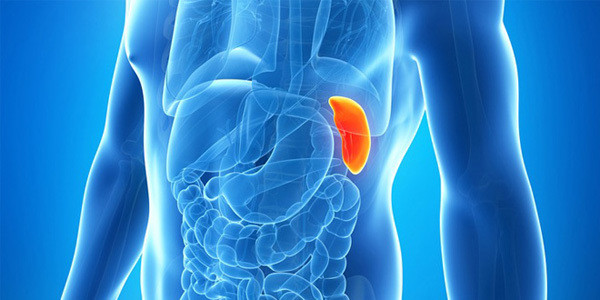
This organ is located on the left side of the abdomen, towards the back below the ribs. Because it is located near the ribs and has a very thin membrane, once it is torn, the spleen can cause bleeding leading to death. In this case, doctors are forced to remove it to ensure the patient's life.
When you look inside the spleen, it has two noticeable colors. A dark red one and a small white sac, they are involved in different functions. The red part stores and recycles red blood cells. Meanwhile, the white sac will contain white blood cells and platelets.
You can live comfortably without a spleen. This is because the liver plays a role in the regeneration of red blood cells. Other lymphoid tissues in the body take over the spleen's immune functions.
2. Reproductive organs
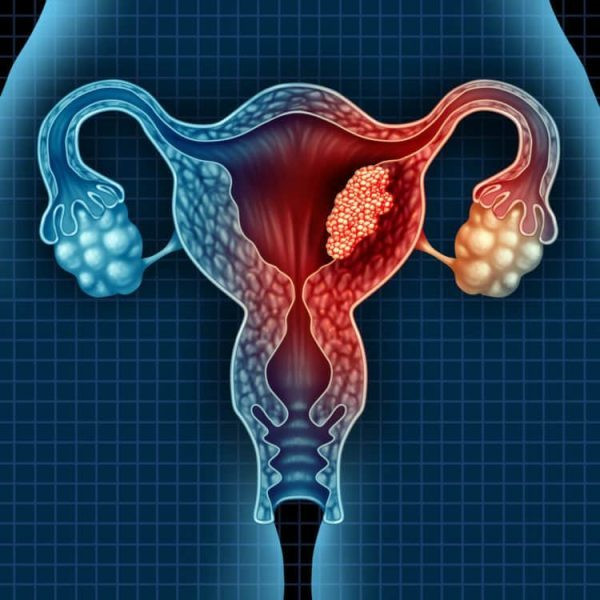
The main reproductive organs of humans are the testicles and the ovaries. Men have two testicles and women have two ovaries. They are usually removed due to cancer or trauma (violence, sports, traffic accidents).
In women, the uterus can also be removed. This procedure makes them unable to have children and also stops menstruation in premenopausal women. However, studies have shown that the life expectancy of women who have their ovaries removed is not affected.
Some studies have shown that women who have their ovaries removed do not have a reduced life expectancy. On the contrary, some men who have both testicles removed may have an increased life expectancy.
3. Colon
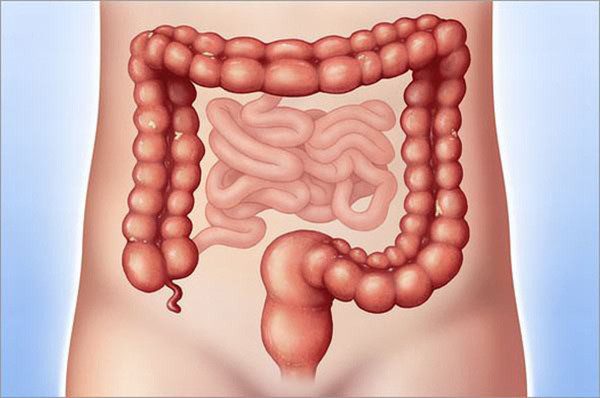
The colon, also known as the large intestine, is about 1.8 m long and is a long tube that absorbs water and nutrients left over from food after passing through the small intestine, and contracts to excrete feces through the anus. Cancer or other diseases can cause a person to have part or all of the large intestine removed.
Most people recover well from this surgery, although they may notice a change in bowel habits. A soft food diet is recommended initially to help speed up the healing process.
4. Stomach
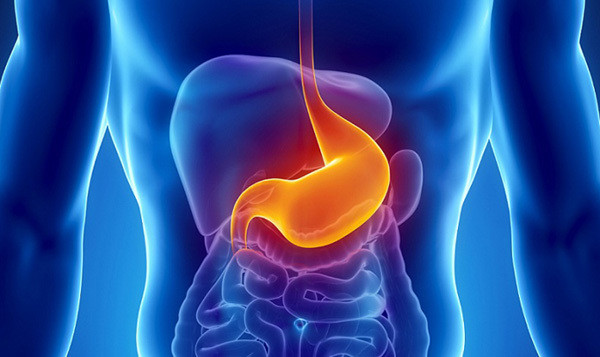
The stomach performs four main functions: mechanical digestion by contracting to crush food, chemical digestion by releasing acids to help break down food, and then absorption and excretion.
The stomach is sometimes surgically removed due to cancer or injury. In 2012, a British woman had her stomach removed after drinking a cocktail containing liquid nitrogen.
After surgery, the doctor will connect the patient's esophagus directly to the small intestine. If the surgery is successful and the patient recovers well, they can return to normal life, eating normally with vitamin supplements for the rest of their life.
5. Appendix
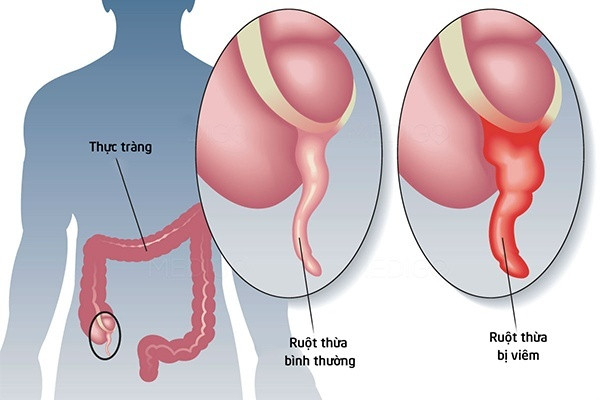
The appendix is a small worm-like structure at the junction of the large and small intestines. Originally thought to be “leftovers,” it is now believed to be involved in being a “safe house” for the beneficial bacteria in the gut, allowing them to repopulate when needed.
However, because the appendix is located at the junction, it is prone to stagnation and infection. This is the cause of appendicitis. Sometimes the patient notices the pain disappears and thinks he is healthy.
However, it can signal that the appendix has ruptured, and fluid seeps into the abdominal cavity, causing infection and peritonitis. In this case, the patient needs immediate surgery to clean the abdominal cavity, otherwise it will be life-threatening. Appendectomy has almost no effect on quality of life.
6. Kidney
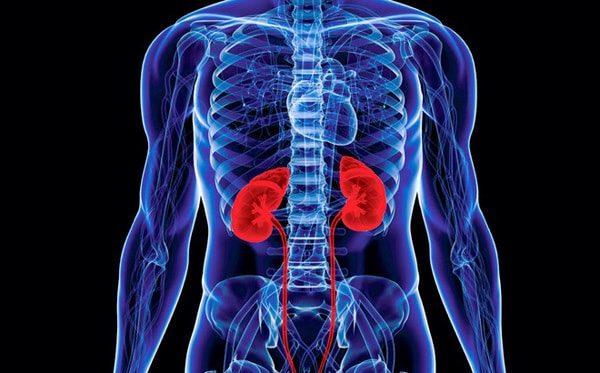
Most people have two kidneys, but you can survive with just one. The function of the kidneys is to filter blood, maintaining the body's water and electrolyte balance and acid-base balance. They do this by acting like a sieve, using a variety of processes to keep useful things out, such as proteins, cells, and nutrients that the body needs.
7. Gallbladder
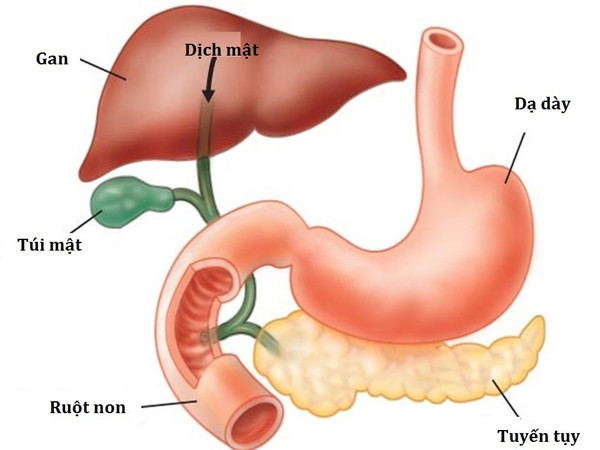
The gallbladder is located under the liver, in the upper right part of the abdomen, just below the ribs. It stores a liquid called bile. When the intestines detect fat, a special hormone is released that causes the gallbladder to contract, pushing the bile into the intestines.
However, sometimes bile accumulates cholesterol and forms gallstones. The stones block the ducts that carry bile. When this happens, the gallbladder needs to be removed. It is estimated that around 70,000 people in the UK have their gallbladders removed each year.



