7 important notes when taking children for vaccination
Getting your children vaccinated on time is the best way to help prevent diseases. Here are 7 important things parents should remember when taking their children for vaccinations.
Before vaccination
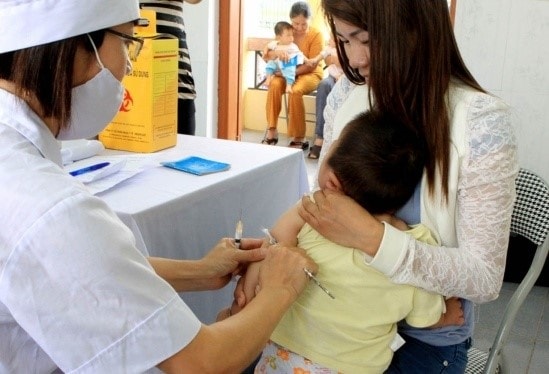 |
Children need to stay in the hospital for at least 30 minutes after the injection. |
Parents should avoid overfeeding or overfeeding their children, but should also not let their children go hungry because this can cause hypoglycemia after the injection.
Keep your child clean to reduce the risk of infection. In addition, dress your child in simple clothing to make it easier for the doctor to perform the vaccination.
Mothers need to bring complete records and documents of the child, especially previous vaccination records.
Before vaccination, parents should not forget to discuss with the doctor the child's health status, whether he/she is malnourished, has an acute illness (such as fever, pneumonia, bronchitis...), medical history, allergies to drugs, chemicals, food...
If your child shows signs of allergy, fever, etc. in previous injections, you should inform the doctor so that timely treatment can be provided in case of emergency.
After injection
After the child is vaccinated, the mother should not take the child home immediately but should stay and monitor for 15-30 minutes to prevent the child from going into anaphylactic shock.
If the child does not have any reaction, the mother can take the child home but still needs to monitor further. Monitor whether the child has a fever, skin manifestations, gestures, fussiness, breastfeeding normally, and bowel movements. Especially for children who have their first vaccination at 2 months of age, the first vaccination and the 5-in-1 vaccine.
In children with sensitive skin, the injection site may be red, swollen, and have a hard lump, but mothers do not need to worry too much, this phenomenon will disappear after 6 - 8 hours. At this time, mothers need to apply a cool compress to the child's injection site (not a hot compress) to reduce pain, give the child plenty of water, breastfeed more, and wear loose clothing.
After the next 24 hours, you can apply hot compresses to help the swelling disappear quickly, helping the skin to easily exchange with the outside environment and recover quickly.
In addition, some mothers are now passing on to each other the experience of rubbing lemon or applying a thin slice of potato to the injection site to reduce pain and swelling for children. However, this method is not recommended by medical experts because children's skin is extremely sensitive, doing so can increase the risk of infection at the injection site.
In case the child has a mild fever, 37-38 degrees Celsius, the mother can use cooling measures, reduce the temperature, and use rectal antipyretics. If the fever is above 38 degrees, use antipyretics, which will work faster.
Cases where children should not be vaccinated
Each type of vaccine is contraindicated for different groups of children. For example, with the tuberculosis vaccine, premature babies weighing less than 2.5 kg must temporarily postpone the vaccination. The vaccine is given in the first month up to 2 months of age.
Therefore, before vaccinating your child, you need to find out whether your child is eligible for vaccination or not, and discuss with your doctor about your child's current condition.
In some other cases, children should not be vaccinated, such as: children with acute illnesses, often showing symptoms of high fever, fatigue, cough, runny nose, diarrhea; children with diseases related to allergies, immunity,...
Dosage for children in each vaccination
Two live vaccines should not be given within four weeks of each other. It is also possible to give more than one vaccine at a time. Live vaccines include those for tuberculosis, measles, chickenpox, etc.
Multiple injections at one time can cause reactions, allergies and are difficult to monitor because it is not known which type of vaccine the child's body reacts to. Therefore, it is best to give one type of vaccine at a time.
Two or more vaccines can be given in cases where the vaccination site is far from home, or if the child has had an organ transplant, etc.
Some reactions after vaccination
Mild fever: Fever is the most common reaction in children after vaccination. This is the child's body's response to the medicine and usually goes away on its own after 1-2 days of vaccination. However, there are some cases where children may have a high fever above 39 degrees Celsius, in which case parents should take their children to see a doctor immediately for timely treatment.
Redness, swelling, and pain at the injection site: This problem can last for several days, but this is a completely normal reaction and will go away on its own, not a cause for concern. You can use a cold compress at the injection site to reduce pain for your child.
Allergy: Children may develop hives or itching all over their body… Usually, these allergic symptoms will go away on their own after a few days, but if the child feels very uncomfortable, some anti-allergy medication must be used.
Other reactions: In some cases, children will experience rare reactions such as stroke, lymphadenitis, encephalitis... These are severe reactions that can threaten the child's life if parents do not take their child to the hospital promptly.
Notes when taking children for vaccination on cold days
On cold or drizzly days, parents taking their children for vaccinations should pay attention to keeping their children's bodies warm. Avoid cold air from entering, making children susceptible to respiratory diseases. At this time, parents need to ensure that their children's feet, hands and body are warm enough, and not let them get wet from the rain,...
When to take your child to the hospital
After vaccination, if the child shows abnormal symptoms such as fever above 39 degrees Celsius, high fever lasting more than 2 days, convulsions, cold limbs, cyanosis, difficulty breathing, fussiness, not responding to common fever-reducing drugs, refusing to breastfeed, swelling, redness around the injection site..., parents need to immediately take the child to the hospital.
According to Zing.vn


