How to choose resolution when buying a TV: Full HD, 2K, 4K or 8K?
When choosing a TV, you may come across terms like Full HD, 2K, 4K, 8K, but what do they really mean? In this article, we will decode the difference between Full HD, 2K, 4K and 8K to help you make the most appropriate choice.
What is TV resolution?
TV resolution, simply put, is the number of pixels that make up the image on the screen. Each pixel is a small dot that helps display color and detail, and the more pixels, the sharper the image.
TVs come in different resolution levels. Older models or 32-inch screens typically have around 1 million pixels (720p). Popular TVs under 49 inches typically have over 2 million pixels (1080p – Full HD).

Meanwhile, 4K Ultra HD models have 8 million pixels, common in TVs 50 inches and larger. And with today's top-end TVs, 8K has up to 33 million pixels, providing incredible detail.
Resolution is often touted as an important factor when choosing a TV, because the terms "4K" or "8K" sound extremely advanced and impressive. But in reality, resolution is not the only factor that determines image quality.
A TV with better HDR (high dynamic range), a more impressive contrast ratio, or the ability to display more vivid colors will look better than one that simply has more pixels, so consider these factors when choosing a TV rather than just relying on the resolution number.
Full HD TV
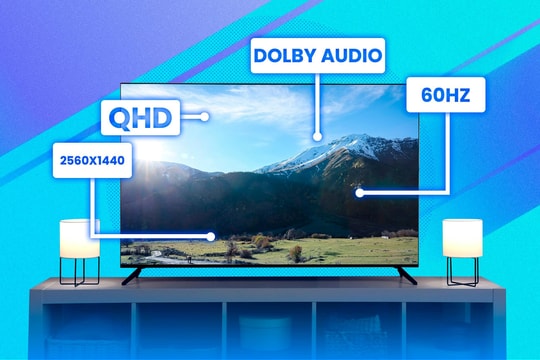
Full HD TV (short for Full High Definition) is a TV line with a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels, commonly known as 1080p. This is one of the popular standards of TV screens, providing sharper, more detailed images and more realistic colors than TV lines with lower resolutions, such as HD (1280 x 720 pixels).

Full HD TVs are usually available on TV models 32 inches or larger and are suitable for many entertainment needs such as watching movies, playing games, watching TV or connecting to other multimedia devices.
Although there are more advanced display technologies like 4K (Ultra HD) or 8K, Full HD TVs are still a popular choice thanks to their reasonable price and good picture quality for the price.
2K TV
2K TV is a TV line with a resolution of 2048 x 1080 pixels, higher than Full HD (1920 x 1080 pixels) but lower than 4K. Although the term "2K" is less common in the home TV market, it is commonly used in the film industry and digital cinema (DCI 2K).

In fact, many TVs advertised as "2K" are actually just Full HD TVs with 1080p resolution, as the difference between 1920 x 1080 and 2048 x 1080 is negligible. Compared to 4K, 2K TVs have fewer pixels, which means the image may appear less sharp when displayed on a large screen.
Nowadays, 2K TVs are no longer popular as most modern TVs have moved to 4K for a sharper and more vivid visual experience.
4K TV
4K TV is a TV line with a resolution of 3840 x 2160 pixels, which is about 8 million pixels, 4 times more than Full HD TV (1080p). This means that the displayed image is sharper, more detailed and smoother, especially when viewed on a large screen.
With a 4K TV, you can enjoy more realistic picture quality and more vivid colors thanks to HDR (High Dynamic Range) technology that comes with many modern TV models. Furthermore, most streaming platforms such as Netflix, YouTube, Disney+ and Apple TV+ support 4K content, helping you get the most out of this TV.
.jpg)
However, for the best experience, you should choose a TV with a high refresh rate (120Hz), image upgrading technology (Upscaling) to clearly display even content that does not meet 4K standards, and most importantly, a screen with a high-quality panel such as OLED, QLED or Mini-LED to make the most of 4K resolution.
8K TV
8K TV is a TV line with a resolution of 7680 x 4320 pixels, equivalent to more than 33 million pixels, 4 times higher than 4K TV and 16 times higher than Full HD TV (1080p). This brings super sharp images, extremely delicate details and impressive realism, especially on large screens of 65 inches or more.
However, one of the major challenges of 8K TVs today is that the source of native 8K content is still very limited. To solve this problem, most high-end 8K TVs integrate image upgrading technology (AI Upscaling), which improves the quality of 4K video, even 1080p, to almost reach the sharpness of 8K.

8K TVs often come with the most advanced technologies such as Mini-LED, QLED, OLED, along with HDR, high refresh rates (120Hz or more) and surround sound to deliver the ultimate entertainment experience.
However, the price of 8K TVs is still quite expensive, and to make the most of its quality, you need a high-quality content source as well as a viewing space large enough to feel the difference compared to 4K.
In the future, resolution may no longer be the most important factor when evaluating the display quality of a TV. Currently, TVs often follow a common standard, such as 4K for both 50-inch and 100-inch screens, but differences in pixel density can affect image quality.
However, with the development of MicroLED technology, the relationship between screen size and resolution will gradually disappear. This technology allows for the creation of flexible-sized screens without being bound by fixed resolutions.
This means that a 50-inch TV in the bedroom and a 100-inch one in the living room could have completely different resolutions, rather than both being 4K as they are today.
Thanks to dramatic advances in video processing and upscaling technology, the difference in resolution will become less noticeable to the naked eye. Advanced AI algorithms and image processors can improve sharpness, reproduce details, adjust color and contrast, making images displayed on any screen size look equally sharp and vivid.
This opens a new era for TV, where the visual experience is no longer limited by traditional specifications, but instead optimized by smart display technology.


.jpg)

