How to detect and give first aid for methanol poisoning
What is methanol and how dangerous is it to human health? How to treat alcohol poisoning to avoid dangerous situations?
» Priest Nguyen Dinh Thuc incited parishioners
According to Master, Doctor Luong Quoc Chinh, Emergency Department, Bach Mai Hospital said:
The only alcohol for drinking is called ethyl alcohol or ethanol which is produced by a special process and the product must meet food quality standards. There are also many other types of alcohol but they are very toxic such as methanol.
Methanol is produced industrially, as a final product of many manufacturing processes, from the transformation of many types of fruit, from the decomposition of waste... Methanol has many different applications in industry such as making paint, cleaning varnish, using as a solvent... However, methanol must absolutely not be used as food alcohol like ethanol.
 |
| Illustration photo. |
Most deaths from methanol poisoning are due to suicide or the use of methanol as a substitute for ethanol... In adults, methanol poisoning at a dose of 8g (1ml of 100% solution) can cause blindness, poisoning at a dose of 10g (30ml of 40% solution) can cause death. In children, methanol poisoning at a dose of 0.25ml/kg has caused blindness and 0.5ml/kg has caused death (100% solution).
Before causing toxicity, methanol is metabolized to formaldehyde and then oxidized to formic acid (formate). High blood concentrations of formic acid inhibit mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase in cells, causing cellular hypoxia, severe metabolic acidosis, optic nerve damage, and retinal damage. In addition, methanol causes central nervous system depression, vasodilation, hypotension, and decreased cardiac output.
Symptoms of Methanol poisoning and how to handle it
Symptoms of methanol poisoning usually appear within 30 minutes of ingestion but may be later, depending on the amount the patient drank, whether the patient also drank ethanol (symptoms appear later) and the patient's folate status. There are usually two stages, the latent stage (first few hours to 30 hours) and the stage of obvious poisoning that follows. Because the initial symptoms are often subtle and mild (mild nervous inhibition, sedation, numbness), they are often overlooked by the patient or not detected by young children.
- Neurological: when arriving at the hospital, usually awake and complaining of headache, dizziness, then forgetfulness, restlessness, euphoria, lethargy, confusion, coma, convulsions.
- Eyes: initially no symptoms, then blurred vision, photophobia, blind spots, eye pain, diplopia, central blind spots, reduced or lost vision, visual hallucinations (glare, dancing dots, tunnel vision,...). Pupils react poorly to light, funduscopy shows optic disc congestion, then retinal edema spreads along the blood vessels to the center of the fundus, blood vessels congest, optic disc edema, retinal hemorrhage. Fixed dilated pupils are a sign of severe poisoning and a poor prognosis. The signs seen on funduscopy do not correlate with the patient's visual signs but do correlate with the severity of poisoning. In severe poisoning, there may be hemorrhage or infarction of the nucleus pulposus, brain herniation.
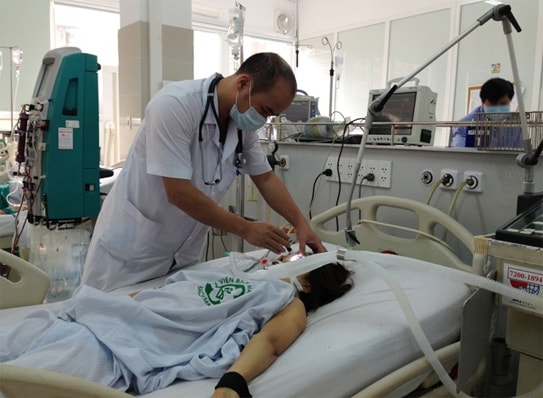 |
| Emergency examination of comatose patients at the Emergency Department of Bach Mai Hospital. |
- Vital signs: rapid heart rate, rapid and deep breathing (kussmaul breathing), blood pressure is usually normal until death. Before the current specific treatments, patients usually died from respiratory arrest.
When a patient is poisoned by alcohol, especially if there is a disturbance of consciousness, the basic first aid principle is to ensure a clear airway by keeping the patient's head elevated and in a safe tilted position. Every few hours, the patient must be woken up. If the patient is awake and able to eat and drink, give them porridge... to avoid hypoglycemia.
If the patient is not conscious, has a lot of congestion in the throat, is breathing quickly and deeply, or even has convulsions... keep the patient in a position where the head is elevated, lying on the side safely, then quickly call for help, call an ambulance to handle the situation, and take the patient to the hospital.
If the patient wakes up but has a severe headache, dizziness, blurred vision, photophobia, scotomas, eye pain, double vision, central scotomas, decreased or lost vision, hallucinations... then they need to be taken to the hospital for examination.
MSome other manifestations and sequelae of methanol poisoning:
- May have back pain, body pain, stiff neck (like meningeal hemorrhage), muscle stiffness, cold skin, sweating.
- Digestive: early manifestations, hemorrhagic gastritis, acute pancreatitis manifested by epigastric pain, vomiting, diarrhea. Moderate or severe poisoning can alter liver function.
- Neurological sequelae: Parkinson's disease, cognitive deficits, transverse myelitis and pseudo-ophthalmoplegia.
Doctor's recommendation
Drinking too much alcohol can cause many harmful effects on human health. Therefore, people should control their drinking and be moderate. If you experience headaches, dizziness, blurred vision, etc. after a few hours of drinking, you should go to the hospital immediately.
When receiving a patient with suspected methanol poisoning, medical staff must transfer the patient to a medical center capable of resuscitation and dialysis as soon as possible.
According to Songkhoe
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|

