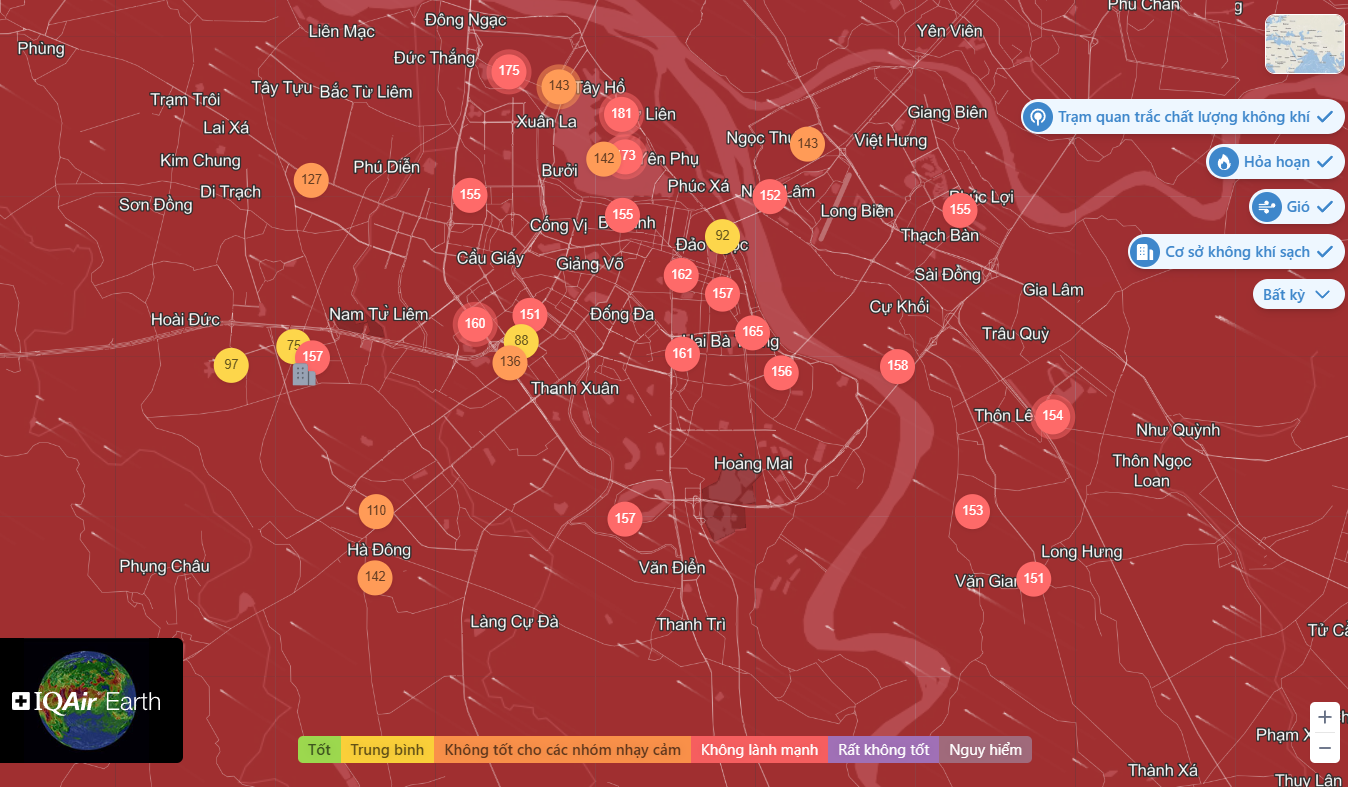
Fine dust index today April 18, 2025 in Hanoi
According to data from AQICN, the fine dust index today, April 18, 2025, in Hanoi was recorded at 157. This AQI level is in the "Unhealthy" category according to the AQI scale of the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA).
At this level, people may begin to feel health effects, especially sensitive groups such as children, the elderly, and those with respiratory or cardiovascular diseases.
Data from other sources, such as IQAir and AccuWeather, also confirm that air quality in Hanoi has frequently fluctuated between "Moderate" and "Unhealthy" in recent days, emphasizing the need for constant monitoring.
PM2.5 and PM10 fine dust levels
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is an important measure that provides information about pollution levels and helps people take health protection measures.
PM2.5
PM2.5 are fine dust particles with a diameter of less than 2.5 micrometers, capable of penetrating deep into the lungs and even into the bloodstream, causing serious health problems. On April 17, 2025, the AQI for PM2.5 in Hanoi was 156, which is in the "Unhealthy" category. According to the AQI scale, this corresponds to PM2.5 concentrations ranging from 55.5 to 150.4 µg/m³, with actual values likely being around 100-150 µg/m³, based on recorded AQI levels.
PM10
PM10 are particulate matter smaller than 10 micrometers in diameter, which often irritate the respiratory tract and affect people with underlying health conditions. The AQI for PM10 on the same day was 103, which is considered "Unhealthy for sensitive groups". This corresponds to PM10 concentrations between 155 and 254 µg/m³.
Below is a summary table of fine dust indexes in Hanoi on April 18, 2025
| Index | AQI | Level | Estimated concentration (µg/m³) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 156 | Unhealthy | 63.5 |
| PM10 | 103 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups | 207.9 |
AQI level 156 shows that air quality in Hanoi on April 18, 2025 can cause health problems such as:
Respiratory irritation: Cough, sore throat, or difficulty breathing, especially in sensitive people.
Increased risk of chronic disease: Long-term exposure to PM2.5 fine dust can increase the risk of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
More serious effects for sensitive groups: Children, older adults, and people with underlying medical conditions may experience more severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or chest pain.
According to IQAir, air pollution in Vietnam, including Hanoi, is estimated to be linked to more than 60,000 premature deaths each year, highlighting the importance of minimizing exposure to polluted air.
Causes of air pollution in Hanoi
Air pollution in Hanoi comes from many different sources, including:
Traffic: With nearly 8 million registered vehicles in Hanoi, vehicle emissions are the main source of PM2.5 fine dust and other pollutants such as NO2 and CO (Euronews).
Industry: Power plants, steel and cement factories around the city contribute about 35% of PM2.5, according to a 2020 World Bank report.
Construction: Construction activities generate PM10 dust, increasing the concentration of dust in the air.
Other factors: Burning of stubble in nearby areas and weather conditions such as high humidity or weak winds can aggravate pollution.


