Decoding car safety systems
More and more features are being installed in each car to reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. However, not all car users are familiar with the safety systems.
 |
Car safety systems are divided into two types: Active and Passive. Active safety systems include features equipped on the car to minimize the possibility of accidents, such as anti-lock braking system ABS, electronic brake force distribution EBD or electronic balance ESC.
Passive safety systems such as airbags and seat belts are only activated when an accident occurs to protect the driver and passengers from injury.
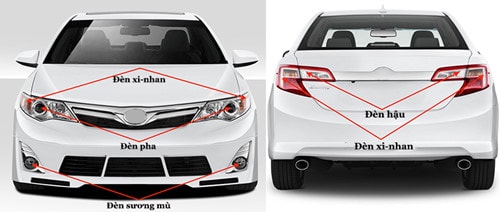
1. Active safety featuresLighting systemis a lighting system used on vehicles for lighting, signaling and notification purposes.
High beam (far) - low beam (cos): The lights are placed at the front of the vehicle, with the task of illuminating the road ahead in dark conditions, helping the driver observe traffic conditions and obstacles to handle. The headlights have the function of illuminating at a long distance, the low beams illuminate at a close distance in front of the vehicle.
Turn signal lights: Helps the driver signal the next direction of the vehicle to other vehicles and traffic participants by turning on/off the lights in the direction they want to go. In addition, this type of light also has the task of warning of danger when it is turned on/off continuously through the triangular button on the dashboard.
Basic lighting system on cars |
Fog lights: Helps increase the ability to recognize vehicles in front and behind in foggy weather conditions or dusty roads that reduce the driver's visibility. Fog lights are usually placed low at the front of the vehicle.
Rear lights: Placed at the rear of the vehicle, red is required to increase visibility for vehicles behind and warn when the driver brakes, helping to minimize rear-end collisions.
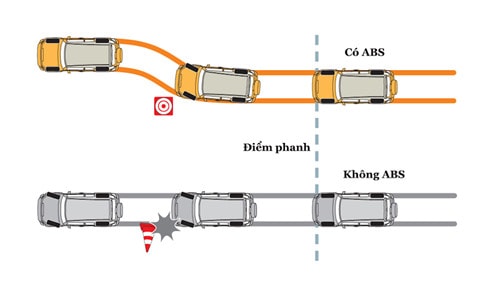
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
This is an important safety feature that is quite commonly equipped on current car models. This system will support the braking process to be safer and more accurate, especially in the case of sudden braking. Simply explained, this is a system that continuously squeezes and releases the brake when the driver suddenly brakes, helping the wheels not to lock while still ensuring traction, preventing the steering wheel from becoming stiff and causing loss of control.
ABS only activates in emergency braking situations, and the brake pedal pulsates to alert the driver. Today, the system has become a standard feature on both drum and disc brake vehicles.
Simulation of obstacle avoidance situations with and without ABS |
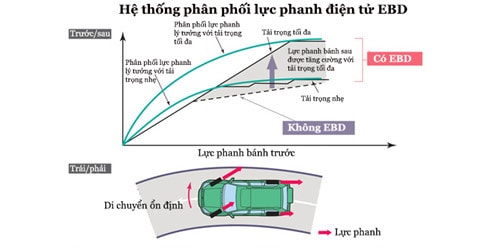
Electronic Brakeforce Distribution (EBD)
Most cars used for normal commuting purposes have the engine located in the front, so the load on the front wheels is greater than the rear wheels. At the same time, during braking, due to inertia, the load increases on the front wheels and decreases on the rear wheels. In addition, when the car turns a corner, the load will increase on the two outer wheels and decrease on the inner wheels.All these cases require proper redistribution of braking force to ensure braking efficiency.
By calculating speed, load and traction of the wheels, the EBD system will adjust and balance the braking force to help the braking process become more optimal.
Braking force with and without EBD |
Emergency brake assist system BA (Brake Assist)
When detecting the driver's sudden braking action, the BA system will automatically assist to speed up the process. For example, if the car is traveling on the road and suddenly encounters an obstacle, the driver will reflexively brake, but due to the surprise, the braking force is not strong enough to stop the car. At that time, the BA emergency brake assist system will automatically compensate with enough braking force and in time to help the car stop, avoiding a collision.
This system often goes together with ABS and EBD systems, supporting each other to ensure optimal emergency braking efficiency even on slippery surfaces.
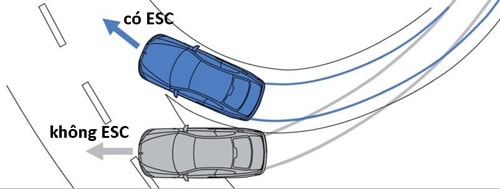
Electronic balance system ESC (ESP, VSC, VSA...)
In case the driver turns the steering wheel too quickly to avoid obstacles or turns at high speed on slippery roads, causing the vehicle to lose control and slide to both sides, ESC will act on the braking system to help readjust the steering direction, and automatically reduce engine power to give the driver time to regain control of the vehicle.
ESC not only works when driving on wet or icy roads, but also when accelerating or cornering. The key is that ESC detects potential wheel slip before it becomes a real threat.
Simulate cornering situations with and without ESC. |
2. Passive safety equipment
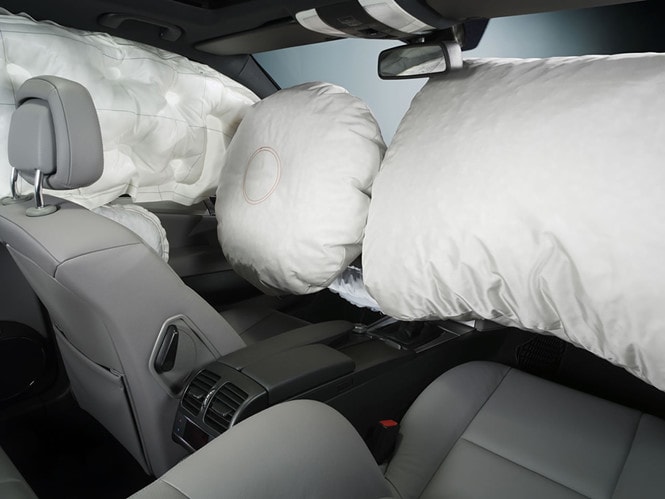
Airbag: It is a system of bags that automatically fill with air and inflate in a very short period of time when a collision/accident occurs to minimize the level of injury to the occupants of the vehicle due to collision with interior details. Front airbags have the effect of reducing injuries to the head, neck, chest and face of the driver and passenger sitting next to the vehicle when the vehicle is collided from the front. Side airbags only operate when there is a collision on the side of the vehicle, protecting the head and shoulders from injury.
However, just equipping the car with airbags does not mean that the people sitting inside the car can avoid casualties in any accident.
Airbag and seat belt systems help reduce injuries when an accident occurs. |
Seat belts: This is just a basic equipment compared to a series of technologies on cars today, but its importance to the lives of people in the car is put first. When the car brakes suddenly, people in the car will be thrown forward due to inertia, the higher the speed of the car, the more the force is multiplied, leading to collision and injury.
A standard seat belt consists of a lap belt and a shoulder belt, with the ends fastened to the vehicle frame and a buckle to help fasten the belt. When worn correctly, these belts are effective in keeping passengers from being thrown out of their seats and thrown forward when the vehicle stops suddenly.
In addition to the basic safety system as above, car manufacturers have now added many advanced safety features such as blind spot warning, forward collision warning, lane departure warning, pedestrian detection... to help minimize risks when participating in traffic. However, these features only appear on some high-end car models or as options, not yet popular on popular car models in the country and also difficult to fully utilize in the special road conditions of Vietnam.