Special uses of calcium for the human body
Most of us know calcium because it is a mineral that helps build and develop strong bones. In fact, calcium has many other special uses for the human body.
In addition to its role in bone health, calcium has many other important functions in the body. It is essential for nerve and muscle function, cell metabolism, and blood clotting. It also plays an important role in keeping the heart healthy.
So, what roles does calcium play in the human body? What are the adverse effects of calcium deficiency and how to supplement calcium safely and effectively?
 |
In addition to its benefits for the skeletal system, calcium also has many other special uses for the body. |
1. The role of calcium in the human body
Calcium is a mineral that plays a very important role in the human body. Calcium accounts for 1.5 - 2% of the human body weight, 99% of calcium exists in bones, teeth, nails and 1% in the blood.
Calcium combined with phosphorus is the basic structural component of bones and teeth, making bones and teeth strong. In addition, calcium is also needed for neuromuscular activity, heart activity, cell metabolism and blood clotting.
For children, calcium will help them grow taller, strengthen their immune system and destroy disease-causing bacteria when they enter the body.
For adults, calcium helps strengthen bones, helps prevent osteoporosis, reduces pain and difficulty in movement, and heals bone fractures quickly. Calcium is also necessary for heart function and stable mental, mental and memory health.
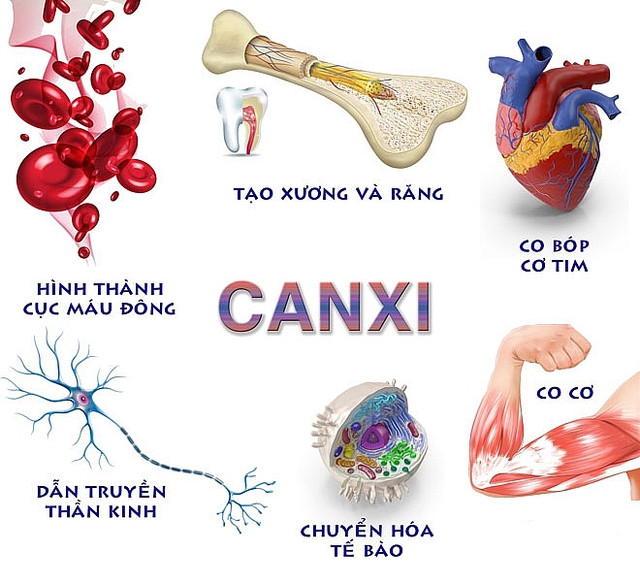 |
The role of calcium in the human body. |
2. What diseases can calcium deficiency cause?
Lack of calcium in the diet, poor calcium absorption and/or excessive calcium loss lead to bone mineralization disorders. Chronic calcium deficiency (due to poor calcium absorption in the small intestine, insufficient calcium in the diet, etc.) is one of the important causes leading to reduced bone density, causing osteoporosis in adults and rickets in children.
The effects of calcium deficiency will lead to the following risks: Osteopenia (lower than normal bone mineral density); Osteoporosis (very low bone density); Increased risk of bone fractures
Calcium directly participates in the formation of bones and teeth in children. Therefore, if not provided with enough calcium, children will grow slowly, be malnourished, have small and weak bones, which can easily lead to rickets, poor tooth quality, tooth decay and uneven teeth growth.
Calcium is also very important for children's nervous systems. Children with calcium deficiency often cry at night, startle easily and get irritable easily.
In adults, in addition to the risk of osteoporosis, prolonged calcium deficiency will cause the heart muscle to contract weakly, making it easy to get tired and sweaty while working. In the elderly, calcium deficiency can easily cause nervous breakdown, mental instability, headaches, memory loss, etc.
When blood calcium decreases, the body must mobilize calcium from the bones into the blood to participate in metabolic processes, causing symptoms of bone pain, especially long bones in growing children. In addition, it can cause insomnia and irritability. Long-term calcium deficiency can also lead to serious diseases such as high blood pressure and colon cancer.
Some symptoms of calcium deficiency include:
Frequent cramps More yellow teeth Frequent dizziness, numbness or bone pain Colon problems Weak and brittle nails Bone loss Osteoporosis Risk of seizures or muscle spasms, insomnia…
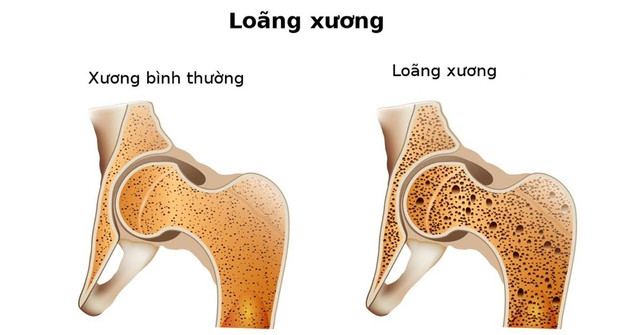 |
Calcium deficiency causes osteoporosis. |
3. How much calcium does our body need each day?
Calcium needs vary according to age and physiological condition. Those with high calcium needs are children under 5 years old and children in puberty.
Pregnant women, women with young children and the elderly also have higher calcium needs than normal people. When pregnant, the mother needs a high amount of calcium because she has to provide calcium for the fetus. During breastfeeding, the mother also needs a lot of calcium to provide calcium for the baby through breast milk.
For the elderly, because the process of bone destruction is stronger than the process of bone formation and the amount of calcium lost through urine increases, especially during menopause, the need for calcium in the diet is also higher. Therefore, it is necessary to provide enough calcium to prevent osteoporosis.
Calcium requirements by age:
Calcium requirement for children from 6-11 months is 400mg/day Children 1-2 years old is 500mg/day Children 3-5 years old is 600mg/day Children 6-7 years old is 650mg/day Children 8-9 years old is 700mg/day Children 10-19 years old and people ≥ 70 years old is 1000mg/day Adults 20-49 years old and men 50-69 years old is 800mg/day Women 50-69 years old is 900mg/day Pregnant women is 1200mg/day Breastfeeding women is 1300mg/day
4. How to supplement calcium safely and effectively
The way to supplement calcium is through the food we eat every day or using calcium supplements. However, the safest and most effective way is to supplement calcium through diet, do not arbitrarily take calcium supplements.
Only take calcium supplements if you have a severe calcium deficiency. The following people often have a diet lacking in calcium-rich foods and may need to take calcium supplements as prescribed by a doctor:
- Vegetarians, especially vegans.
- People who show signs of lactose intolerance and drink little milk.
- People who eat a lot of meat or salt, causing the body to excrete a lot of calcium, have osteoporosis.
- People with the disease must use corticosteroids for a long time.
- People with digestive tract diseases that do not absorb calcium such as enteritis or celiac disease.
5. Is excess calcium harmful?
For calcium supplements through food, cases of excess calcium in the blood or excess calcium storage in tissues due to excessive calcium consumption are very rare because excess calcium intake will be excreted from the body.
However, in cases of long-term use of high doses of calcium, the body will reduce its absorption, or when too much calcium is added to soft tissue and blood vessels, it will adversely affect vascular diseases.
Excess calcium from taking calcium supplements can lead to some side effects such as: kidney stones, hypercalcemia and kidney failure, reduced absorption of other essential minerals such as iron, zinc, magnesium and phosphorus. Therefore, it is important to note that calcium supplements should only be taken as prescribed by your doctor.
 |
The safest way to supplement calcium is to use calcium-rich foods through diet. |
6. Measures to prevent calcium deficiency
To provide enough calcium for the body, from birth, children need to be fully breastfed. During the period when children start eating solid foods (from 5 to 6 months), in addition to breastfeeding, it is necessary to pay attention to preparing calcium-rich foods in the child's menu. When reaching puberty and adulthood, calcium-rich foods still need to be prioritized in the daily diet.
Follow a varied diet, use foods rich in calcium such as: shrimp, crab, fish, fish with bones, snails, sesame, soybeans, wood ear mushrooms, spinach, eggs, especially egg yolks, milk and dairy products...
The diet should provide enough protein. If the diet has too much protein compared to the recommended needs, the body will increase the risk of calcium deficiency. Too much protein in the diet will increase the excretion of calcium through the urinary tract and increase the risk of kidney stones. Limit the intake of coffee, alcohol and salt because these substances often inhibit the ability to absorb calcium.
Use calcium supplements in case of high calcium deficiency as directed by your doctor.
Vitamin D helps regulate calcium levels in the blood and bones, helping the body absorb calcium better. Therefore, in addition to supplementing calcium-rich foods, we need to pay attention to choosing foods rich in vitamin D such as seafood, eggs, milk... in our meals to provide vitamin D for the body.
In addition, you should spend at least 10 - 20 minutes sunbathing in the morning (9am - 9:30am every day) to help your body absorb more Vitamin D through your skin. Your diet should include enough fat so that Vitamin D can be better absorbed through the digestive tract.


