What you need to know about the Omicron variant that is causing concern around the world
The B.1.1.529 variant (Omicron variant) is spreading very quickly in South Africa, in less than 2 weeks directly wiping out the wave of epidemics caused by the Delta strain from February 2021 to present.
“We don’t know much about this variant yet. What we do know is that it has a large number of mutations, and that when you have a lot of mutations, it can have a big impact on how the virus behaves,” Dr. Maria Van Kerkhove, WHO’s technical director, said in a livestream on the organization’s social media channels.
Just 15 days after the first detection of the B.1.1.529 variant (Omicron variant) through genetic sequencing, we have seen it spreading in Africa, pushing the number of cases to record levels and making scientists around the world concerned about its danger level.
WHO also had to convene an emergency meeting on Friday (November 26) to discuss this variant directly. In the following article, we will find out why.variantB.1.1.529 is so worrying, and what can we do to prevent its emergence and spread in Vietnam?
Mutations in the B.1.1.529 variant and their impact
Scientists in South Africa have discovered more than 30 different mutations in the spike protein, the part that attaches it to the body's cells, ofvirus. The list of recorded mutations (which may not be complete) includes:
Conserved Spike mutations: A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493K, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F;
 |
| Image source: Brain Light/Alamy |
Conserved non-spike mutations: NSP3 – K38R, V1069I, Δ1265/L1266I, A1892T; NSP4 – T492I; NSP5 – P132H; NSP6 – Δ105-107, A189V; NSP12 – P323L; NSP14 – I42V; E – T9I; M – D3G, Q19E, A63T; N – P13L, Δ31-33, R203K, G204R.
Many of the spike mutations are not common, such as N856K, Q954H, N969K or L918F, which are all new mutations recorded in less than 100 patient samples worldwide, or mutations such as Q493K and Y505H, which have been collected from wastewater samples in New York, but are still extremely rare in human samples (less than 200 samples worldwide).
The potential effects of the above mutations on the expression of the variant can be listed as follows:
- Multiple mutations in the RBD (receptor binding domain) and NTD (N-Terminal Domain) regions confer resistance to neutralizing antibodies (and/or monoclonal antibody therapy);
- The H655Y+N679K+P681H mutation cluster adjacent to the furin cleavage site may facilitate more efficient cell entry, increasing infectivity;
- The nsp6 deletion mutation (Δ105-107), similar to the deletion mutations on the Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Lambda variants, may be associated with evasion of the innate immune system (interferon antagonism), and may also increase infectivity;
- The R203K+G204R mutations in the nucleocapsid, found in the Alpha, Gamma, and Lambda strains, may increase infectivity;
- The NSP4-T492I mutation is similar to the ORF1b:T2163I mutation in the recent AY.43 strain in Chile, which allows the virus to have super-infectious ability.
Many virologists around the world agree that, if the world were not facing the Covid-19 pandemic, this variant alone could be defined as a new strain rather than just a mere variant.
Epidemiological impact
Although it is still too early to calculate the exact transmission potential, we still see this variant spreading very quickly in South Africa. In less than 2 weeks, this variant has accounted for 75% of all sequenced samples, directly wiping out the wave of epidemics caused by the Delta strain since February 2021 until now. On November 23 alone, South Africa recorded nearly 19,000 infections, 20 times more than the previous 3 days.
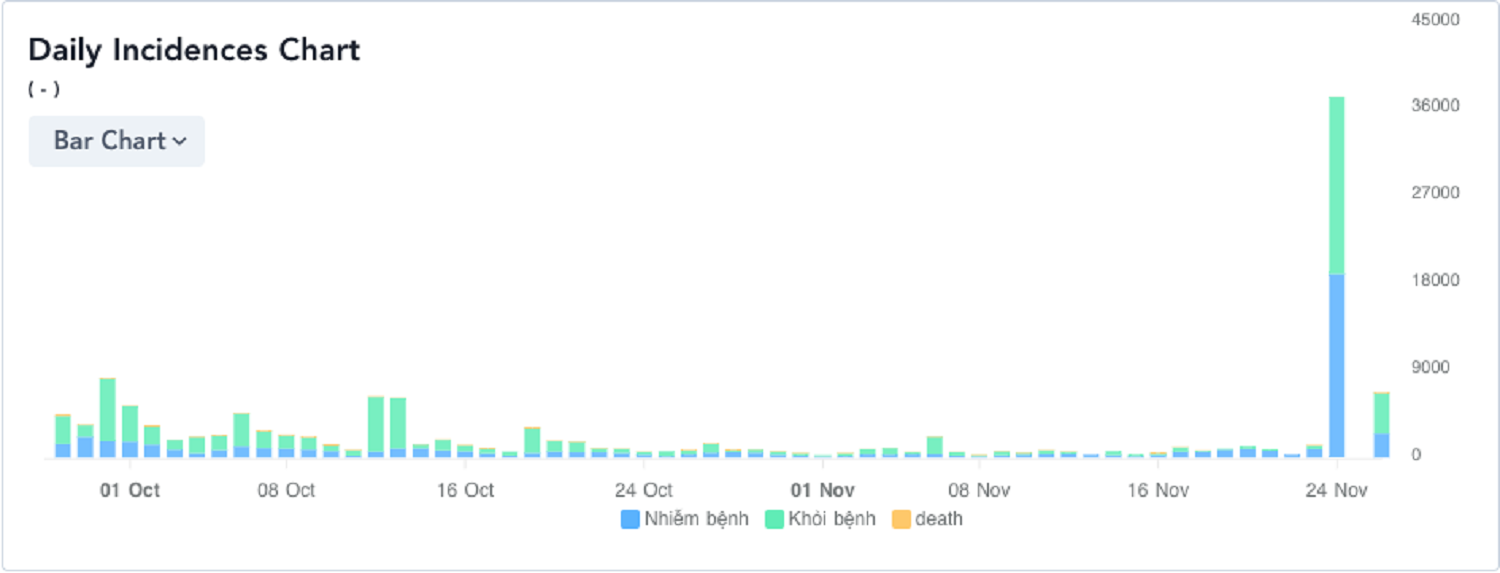 |
| Number of infections and recoveries per day in South Africa. Source: CoronaTracker |
One positive point is that the Omicron variant can be detected by RT-PCR without sequencing because B.1.1.529 has a mutation in the S gene at position 69-70, similar to the Alpha variant. This allows all countries to monitor and prepare as soon as this variant starts to appear. This is also the only good point so far.
Thanks to this characteristic, scientists at CERI (South African Epidemic Preparedness and Innovation Institute) have estimated that at least 90% of the cases recorded in Gauteng province are of this variant, which is more than 1000 cases/day. This number is increasing and increasing dramatically in all regions of South Africa.
In Tshwane (Guateng province, South Africa), the situation is getting worse rapidly as the positive rate of the new variant in the total number of samples has skyrocketed from 1% to more than 30% in just 2 weeks.
Measures taken
Despite recommendations from the WHO, European countries and the UK have imposed travel restrictions on several African countries, including South Africa. In her statement, European Commissioner Ursula von der Leyen said, “The European Union, in close coordination with Member States, will propose to activate an emergency mechanism to prevent air travel from the Southern Africa region due to the new variant of concern B.1.1.529.”
Meanwhile, the UK has placed six countries including South Africa, Namibia, Lethoso, Eswatini and Zimbabwe on the red list, meaning that from 12 midnight on Friday, all flights from these countries will be suspended until 4 am on Sunday (November 28). Singapore has also denied entry to short-term visitors and those with long-term study/work visas who have traveled to the above countries within 14 days.
However, travel restrictions, even the most extreme measures, are not a long-term solution. Recently, countries on different continents have started to record their first cases, including one in Belgium, one in Israel and four in Hong Kong.
So what should we do?
Faced with the risk of this variant entering Vietnamese territory, we must take careful preparations, including:
- Temporary measures: Restrict entry to countries with circulating variants/geographically adjacent countries, including: Botswana, Eswatini, Lethoso, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zimbabwe, Hong Kong, Belgium, Israel. Continue to monitor and add to the above list if necessary. These measures should be maintained until we have a full understanding of the variant and its impact on vaccine efficacy, or the health system is ready for a new outbreak;
- Develop a system to screen for circulating variants by sequencing genes or performing random TaqPath on collected specimens, including domestic or imported specimens;
- Develop a national vaccination strategy to safely vaccinate in the shortest time, moving towards the third dose for at-risk groups, including people over 65 years old, medical staff, and those with underlying diseases, especially those who have received two doses of vaccines in addition to the two licensed mRNA vaccines.
- Strengthen the grassroots health system, increase sampling capacity as well as real-time RT-PCR testing capacity to be able to return results within 24 hours of sample collection;
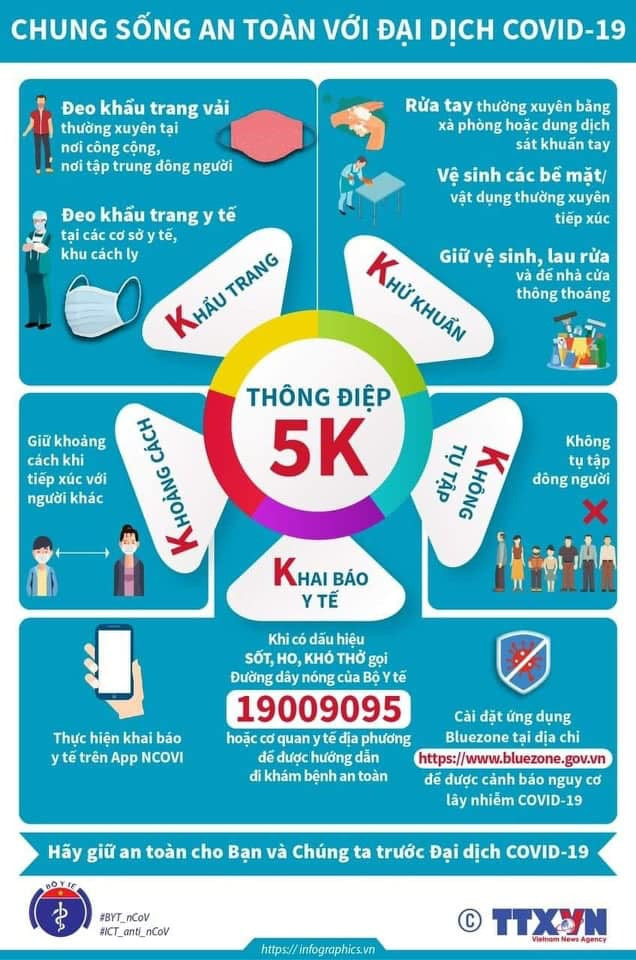 |
| 5K Message. |
- Seriously implement the 5K message
- Develop vaccines that can increase protection against this variant. In theory, the combination of mutations in the spike protein should significantly reduce the effectiveness of current vaccines, and Delta has shown that to be the case. So, while not completely inactivated, the ability to protect us against this variant will be significantly reduced.
While we still do not fully understand the mechanism and impact of this variant on the course of the epidemic, we must remain vigilant against any risk of this variant entering the country, once again placing a terrible burden on a fragile health system that is still in the process of recovering.
Facing an outbreak caused by the Delta strain has brought us too many losses in human resources, material resources, and spirit, and we absolutely cannot let that happen again, completely erasing the vaccination efforts of the past time.

