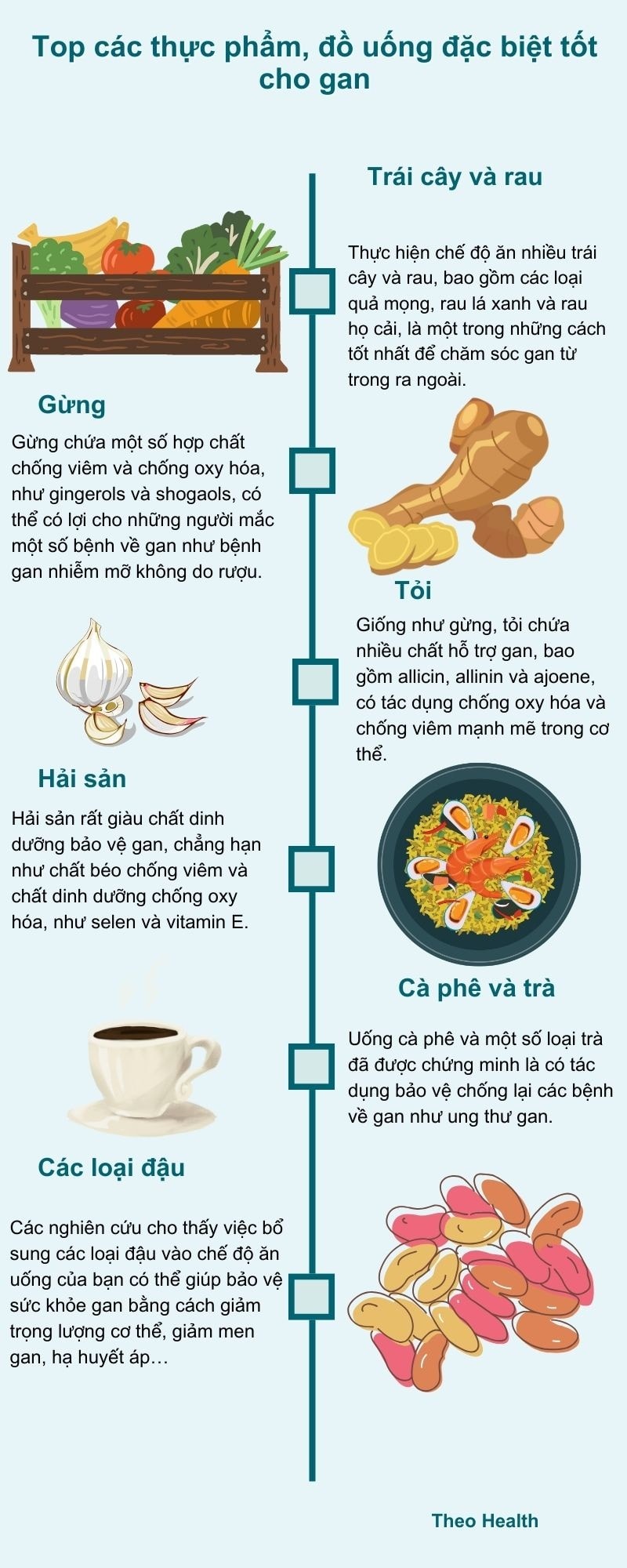
Foods that are good for the liver.
Eating a nutritious diet is one of the best ways to support liver health. Foods that are good for the liver include cranberries, cruciferous vegetables, nuts, and fatty fish.
The liver is the body's natural detoxification system and needs nutrient-rich foods to function properly.
The liver processes everything that passes through the body and determines which substances need to be eliminated and which need to be reabsorbed into the bloodstream. That's why regular liver care through healthy food choices is more important than undergoing detoxification or other short-term cleansing measures.
Foods to eat for a healthy liver
Liver health can also be improved by nourishing the entire body, including providing essential nutrients and avoiding foods that provide few or no nutrients.
Here are some of the best foods to support liver health and function:
cranberry
According toVerywell HealthCranberries are rich in anthocyanins, antioxidant compounds that give the fruit its color.
A study of 110 individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease showed that those who took cranberry capsules daily for 6 months improved their lipid profile, insulin resistance, and liver health compared to those who took a placebo.
Other dark-colored berries, such as blueberries, also contain antioxidants called polyphenols, which may help protect the liver from damage.
However, studies have only been conducted on animals. Therefore, more research is needed to determine whether polyphenols in berries have a positive effect on the liver in humans.

Coffee is a good drink for the liver. Photo: Impulse
Coffee
If you enjoy a morning cup of coffee, you'll be pleased to know that it may have more benefits than just helping you start your day. One review suggests that drinking coffee may help reduce the risk of permanent liver damage in people with chronic liver disease.
Green tea
If you prefer tea to coffee, green tea might be a beverage worth adding to your diet regularly.
A 2020 review of multiple studies suggests that green tea may help lower liver enzymes in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
However, the effects of green tea may vary depending on individual health conditions. The study authors note that consuming large amounts of green tea may increase liver enzymes in individuals who do not have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Another review concluded that green tea may reduce the risk of liver cancer.
Cruciferous vegetables

Cruciferous vegetables are also particularly good for liver health. Photo: NP
The liver benefits from the fiber and plant compounds found in cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, kale, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts. While more research is needed, some studies have found that cruciferous vegetables help support the body's natural detoxification process.
Nuts
Nuts are packed with protein, fiber, vitamin E, calcium, and healthy unsaturated fats that can be particularly beneficial for liver health. One study in Chinese adults found that diets high in nuts were associated with a lower risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, especially in men.
Fatty fish
Omega-3 fatty acids from sources such as fatty fish (salmon, sardines, herring, tuna, etc.) have been shown to help support the body's inflammatory response. One study found that consuming omega-3 fatty acids helped reduce liver fat in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.

Omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish are good for the liver. Photo: Tú Anh
Another study found that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation may be a viable and effective option for reducing blood lipids in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Grapefruit
Grapefruit contains two antioxidants, naringenin and naringin. These antioxidants may protect the liver by reducing inflammation and protecting liver cells. One study found that these antioxidants reduced liver scarring (cirrhosis).
Another study reported that naringin improved liver health in people with alcohol-induced liver damage by limiting fat accumulation and reducing oxidative stress.
Olive oil
Fat accumulation in the liver is part of the early stages of liver disease. Healthy fats in olive oil (monounsaturated fats) can help protect the liver in several ways, such as preventing inflammation, reducing oxidative stress, preventing cellular dysfunction, and reducing insulin resistance.
Studies in humans have shown that following a Mediterranean diet rich in olive oil is associated with reduced fat accumulation in the liver of older adults.
Garlic
In a 2020 study, 110 participants diagnosed with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease were given either 800mg of garlic powder or a placebo for 15 weeks. The results showed that those who took garlic powder experienced significant improvement in their fatty liver condition.
A study conducted in China showed that eating raw garlic two or more times a week was associated with a lower risk of liver cancer.
Foods to limit
For liver health, limiting unhealthy foods is just as important as incorporating nutrient-rich foods. Certain foods are associated with a higher risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. These foods are high in saturated fat, trans fat, and added sugar.
Limit these foods to support your liver health and function:
- Processed meats, such as sausages, bacon, etc.
- Red meat, such as beef and pork.
- Sugary drinks like soda…
Fast food and convenience items are often fried and contain high amounts of saturated fat and oil.
In addition to the foods mentioned above, excessive alcohol consumption also damages the liver. This is because alcohol alters the balance of bacteria in the digestive system, leading to nutrient deficiencies and reduced immunity.
Alcoholic liver disease can worsen, leading to irreversible damage, cancer, and even death. Therefore, limit your alcohol consumption to improve your long-term liver health.