Things not to do with a car using a turbocharged engine
There are some things you should not do with a turbocharged car to protect the engine, increase its life and performance.
Using poor quality fuel
Naturally aspirated engines do not require strict fuel specifications. However, poor quality fuels containing impurities can damage turbocharged engines. Impure fuels make the engine unstable and directly affect the turbocharger. When driving a turbocharged vehicle, drivers should make sure to find reputable gas stations to refuel.
Sudden shutdown
The turbocharger is operated based on the exhaust gas of the engine. The exhaust gas has a high temperature and the high rotation speed of the turbocharger makes the heat after driving in the turbocharger area very high. This leads to a lot of engine oil burning and quality loss. In addition, when the engine is suddenly turned off, the engine exhaust gas can still linger in the turbocharger and affect this part over time.
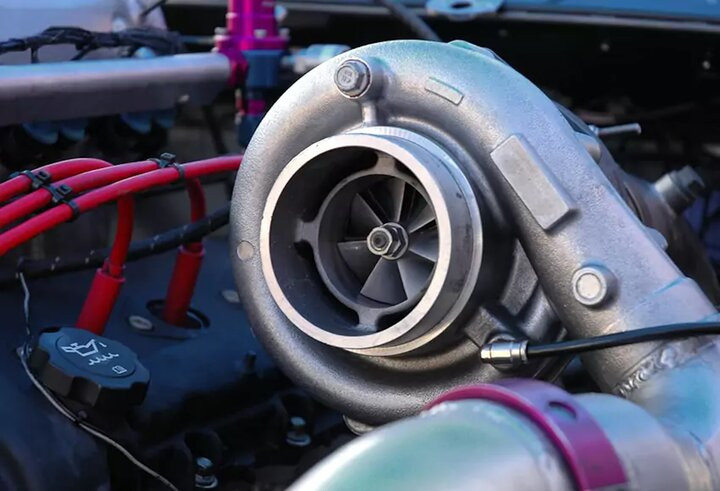
To ensure the turbocharger works efficiently and does not retain exhaust gases, drivers should get into the habit of driving slowly, at low rpm for the last few kilometers of the journey or letting the engine idle before turning it off completely.
Driving overloads the engine
Driving in high gear at low speeds is one of the things that can damage a turbocharger. This puts the engine at a low speed, creating the illusion of more fuel economy. However, for a turbocharged engine, low rpm does not equate to fuel economy.
The turbocharger uses exhaust gases to increase the amount of air entering the engine. If the turbocharger does not reach a certain rpm threshold, the engine will have low power. This means that the vehicle will not reach the optimal power level that the engine can produce.
For diesel engines, fuel is supplied through the accelerator pedal, when driving in high gear at low speed, the user needs to step on the accelerator more to keep the engine running. This causes the engine to operate with excess fuel, lack of air in the combustion chamber and causes the fuel to not burn completely. Drivers should use the appropriate gear for the driving speed.
Operate the vehicle at high rpm immediately upon starting
Engines are often sensitive when they are idle. This is no exception for naturally aspirated or turbocharged engines, so users should not accelerate suddenly when starting. Engine oil lubricates machine parts and helps the engine last longer. Only when it reaches a certain temperature threshold will the oil be able to penetrate every corner of the mechanical parts inside.
Therefore, when the engine is at rest, it is necessary to start a short period of no load, to create enough lubricating oil temperature to cover the mechanical parts. Normally, modern cars do not need to warm up the engine, but old cars really need this process.
Accelerate as you are about to exit the corner.
The feeling of accelerating right out of a corner is a big thrill for the driver. However, drivers should understand turbo lag and know exactly when the engine will kick in. Turbocharged cars often have lag because the power increases as soon as the turbocharger kicks in. This can cause the car to understeer or oversteer, which can cause skidding and loss of control.
For turbocharged vehicles, drivers should not step on the gas pedal when exiting a curve.
Not maintaining a regular maintenance schedule
Turbocharged engines require regular maintenance to ensure that components such as engine oil, oil filter, air filter and turbocharger bolts are checked and replaced on time.
Lack of preservatives
Components such as engine oil, filter pump and coolant need to be properly checked and maintained to ensure that the turbocharged engine runs smoothly and without problems.





