Vietnamese cars cry and laugh because of new tax policy
There will be automobile manufacturing and assembly enterprises in Vietnam forced to leave the market, "giving way" to the wave of imported cars from ASEAN with 0% import tax from 2018.
Assembled car sales decrease, imported cars from ASEAN dominate
According to the report of the General Department of Customs, in the first 8 months of 2017, 7.8 thousand completely built-up cars were imported into Vietnam, worth 188 million USD, up 12.8% in volume and 12.7% in value compared to the previous month. In the first 8 months, Vietnam imported 65.5 thousand cars, worth 1.39 billion USD, down 4.9% in volume and down 14.1% in value compared to the same period last year.
 |
| Car lines with high localization rates such as Toyota Vietnam's Inova may have import component tax reduced if production continues to increase - Photo: Vu Han |
Notably, the number of imported cars from the ASEAN region continues to dominate, of which Thailand has 23.8 thousand cars, worth 432 million USD, up 12.8% in volume and 9.9% in value; Indonesia has 15.5 thousand cars, worth 277 million USD, 8.6 times higher in volume and 12.1 times higher in value. Thus, cars imported from Thailand and Indonesia alone account for 60% of the total imported cars in the market since the beginning of the year. Meanwhile, cars imported from Korea decreased by 53.4% in volume and 43.8% in value, reaching nearly 6 thousand cars, 127 million USD.
Meanwhile, according to a report by the Vietnam Automobile Manufacturers Association (VAMA), in August, the entire Vietnamese market consumed 22,099 vehicles of all kinds, down 6% over the same period and up 7% over the previous month. In total, from the beginning of the year to the end of August, the entire market consumed 177,029 vehicles. Meanwhile, the number of vehicles imported from Thailand and Indonesia was 39,300 units, equivalent to 22.1% of the number of vehicles sold. And the number of vehicles imported from ASEAN will increase sharply from 2018, when import tax falls to 0% for vehicles with a localization rate of 40% or more within the bloc. Statistics from VAMA show that in the past 8 months, sales of domestically assembled vehicles have decreased by 11%, while imported vehicles have increased by 10% over the same period last year.
Mr. Pham Anh Tuan, representative of Toyota (TMV) Vietnam, admitted that although 4/10 names are in the Top 10 best-selling car models in the market in August, TMV will have to compete fiercely with imported cars from ASEAN with 0% import tax and production costs about 20% lower than Vietnam thanks to large output and developed supporting industry. And this is also the concern of Vietnamese automobile manufacturing and assembly enterprises.
Which "door" for Vietnamese cars?
At the end of August, the Ministry of Finance proposed a sharp reduction in import tax rates on imported auto parts under the tax incentive program from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2022. Both options proposed by the Ministry of Finance are in the direction of sharply reducing component tax, possibly even to 0%. The condition is that the enterprises have an output growth rate of 16-18%/year (at least 20,000 vehicles/model for passenger cars under 9 seats and 4,000 vehicles/model for trucks); the localization rate is from 20% (for passenger cars under 9 seats) and 15% (for trucks), gradually increasing to 40%.
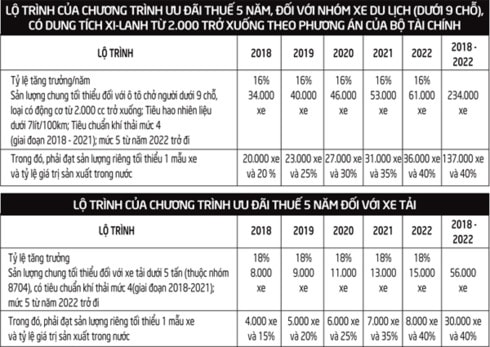 |
Previously, the Ministry of Industry and Trade also proposed applying a special consumption tax (SCT) rate appropriate to vehicles with a high percentage of domestically created value-added content and not imposing SCT on the value created domestically (components and spare parts). At the same time, adjusting corporate income tax on large-scale automobile manufacturing and assembly projects, regardless of investment location.
According to this proposal, some enterprises with large output and high localization rate have the opportunity to have import tax on components and special consumption tax significantly reduced.
Take Toyota's Innova model, for example, which currently has a localization rate of 37% and an output of 10,000 vehicles/year (at times up to 15,000 vehicles/year). If Innova reaches an output of 20,000 vehicles/year from 2018 and continues to increase its output by an average of 16%/year, the import tax on components for this model has the opportunity to decrease from 14-16% to 7%, or even to 0%. The special consumption tax on this model also has the opportunity to be reduced corresponding to the localization rate of 37% (only having to pay 63% of the special consumption tax rate that this model is subject to). Thus, adding up all the costs of components, production, assembly, management, sales, marketing..., the cost plus tax of an Innova car in Vietnam according to calculations by Giao Thong Newspaper reporters can only be around 550 million VND, a sharp decrease compared to the current price and has a chance to compete with imported cars from the ASEAN region.
Similarly, some product lines have "bright prospects" such as Kia Morning of Truong Hai (currently has a localization rate of 31%, output of 10,000 cars/year) or Hyundai Grand i10 of Hyundai Thanh Cong (localization rate of 10% - roadmap to increase to 40%, designed output of 25,000-30,000 cars/year)...
On the contrary, car lines with low output and localization rate such as Mercedes, Mitsubishi, Suzuki, even Ford... will find it very difficult to reduce costs, prices, selling prices and are at risk of being knocked out of the "home market" by not only imported cars from ASEAN, but also by the domestic car lines mentioned above.
For example, comparing the prices of Mercedes and BMW cars - two brands quite similar in quality, the factory price in Germany differs by at most 5-10% depending on the car model. Mercedes cars assembled in Vietnam are subject to a 25% CKD import tax, imported BMW cars are subject to a 70% import tax (a difference of 45%), but the selling price in Vietnam is still the same. That shows that Mercedes is having to shoulder many costs, one of the important reasons being the low localization rate and output.
Therefore, in order to compete fairly and fiercely, businesses have no choice but to invest in expanding production, increasing domestic production content and value, and making real contributions to the automobile industry and the economy./.
According to VOV
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|


