Rehabilitation of hemiplegia due to stroke
(Baonghean) - Hemiplegia is paralysis of one arm and one leg on the same side. Cerebrovascular accident (stroke) is a rapidly progressing clinical condition of localized brain dysfunction, usually caused by a blockage or rupture of a blood vessel supplying an area of the brain, causing damage to that area of the brain, resulting in dysfunction of the part of the body controlled by that area of the brain.
Stroke is a common disease, usually occurring in people over 45 years old, of which 2/3 occur in people over 65 years old, men are more often affected than women. Stroke can cause rapid death, has a high mortality rate, is the leading cause of neurological diseases and is the second leading cause of death after cardiovascular diseases. Stroke also leaves many sequelae at different levels and leads to the most disability.
 |
| Guide patients to walk during rehabilitation due to cerebrovascular accident. |
Risk factors for stroke:Age, gender, family history, hypertension, heart disease, lipid disorders, obesity, diabetes, smoking, alcohol consumption, oral contraceptives, hyperuricemia. Symptoms of sensory disturbances, hemimotor disorders; visual disturbances; language disturbances; perceptual disturbances...
To diagnose hemiplegia due to a stroke, a clinical examination is first needed to detect disorders of movement, sensation, perception, cognition, language, and senses (vision, visual field, etc.). Indications for paraclinical tests: CT scan or MRI of the brain; electrocardiogram; X-ray of the heart and lungs; echocardiography; biochemical, hematological, and coagulation tests; carotid ultrasound; cerebral angiography.
Definitive diagnosis:Sudden onset and rapid progression, with focal neurological signs lasting more than 24 hours. Brain CT or MRI. Differential diagnosis: Transient ischemic attack (dysfunction lasting less than 24 hours; Traumatic brain injury; Brain tumor; Encephalitis, meningitis; Multiple sclerosis.
Diagnosis of the cause:Cerebral vascular accident due to cerebral hemorrhage: Usually occurs in the elderly (related to high blood pressure), or young people (related to cerebral vascular malformations); Cerebral vascular accident due to local cerebral ischemia: There are 3 types (Thrombosis: Blood clots form in atherosclerotic plaques that gradually enlarge, causing blockage of the vessel lumen and blockage); Vascular occlusion due to emboli moving from elsewhere: Most commonly, blood clots in the atria in patients with atrial fibrillation, which can be atherosclerotic plaques from the aortic arch or emboli due to infective endocarditis; Local cerebral ischemia can also occur when atherosclerosis causes narrowing but not complete blockage.
 |
| Team of doctors, nurses, technicians of Nghe An Rehabilitation Hospital. |
Principles of rehabilitation and treatment:Ensure ventilation: Lie on side; remove foreign objects from mouth; suction mucus when necessary. Patients with Glasgow coma < 8 points, with sputum retention, must have endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation. Closely monitor vital signs to have timely treatment measures. Control blood pressure: for patients with cerebral hemorrhage, when blood pressure is equal to or above 200/120 mmhg, blood pressure should be lowered. For patients with local cerebral ischemia, only moderate blood pressure should be lowered, blood pressure should be maintained. at 150/90
Comprehensive care:Ensure nutrition, prevent ulcers, regulate water, electrolytes, blood sugar, prevent infection; The patient's best recovery ability is from 1 to 6 months after paralysis. During the training process, it is necessary to promote the positivity and initiative of the patient and family, and guide the patient and family so that they can perform the exercises themselves.
Rehabilitation methods and techniques:Early stage (flaccid paralysis), positional techniques: Correct posture in bed (lying on back, lying on healthy side, lying on paralyzed side), correct posture when sitting in bed, on chair or wheelchair...
Physical therapy:Passive movement exercises for paralyzed joints; Shoulder joints; Elbow joints; Wrist joints; Fingers; Hip joints; Knee joints; Ankle joints; Toes; Speech therapy; Occupational therapy; Psychotherapy. Later stage (Spastic paralysis): Physical therapy; Range of motion exercises; Exercises in positions: lying, sitting, standing, walking; Gait training; Balance training (positions); Exercises with assistive devices. Occupational therapy: Practice performing self-care activities, Practice using paralyzed hands (CIMT: constraint-induced movement therapy), mirror therapy. Speech therapy: Practice speaking, communicating (with aphasic patients), practice swallowing... Physical therapy: Heat, electrotherapy, FES (functional electrical stimulation)... Provide orthopedic tools (slings, splints...) and assistive devices (walkers, crutches, canes...). Psychotherapy. Integration phase (post-hospital): Counseling for patients and families: prevention of sequelae and recurrence of complications. Renovating housing and surrounding environment to suit patients.
 |
| Early rehabilitation for patients after stroke with orthopedic table. |
Necessary tools for this stage:mobility assistance, living assistance, work assistance. Participation in community integration activities: support groups, disabled people's associations, access to public services, community activities. Psychological support for patients and families after stroke: Accepting that functions cannot be restored, the patient becomes disabled. Employment and income: the ability to continue the old profession, or the patient must learn a new profession or have income-generating activities.
Other treatments:Medications: Anti-cerebral edema (if any): Mannitol 0.5 - 5g/time, intravenous infusion for 2,030 minutes. Blood pressure control: in the emergency phase, Labetalol can be used intravenously at a rate of 0.5 - 2mg/minute; Nicardipine intravenously at 515mg/hour. Anticoagulants and platelet inhibitors for patients with focal cerebral ischemia: Aspirin and platelet inhibitors should be given early, although they do not improve prognosis in the acute phase, they are effective in preventing recurrent stroke.
Thrombolytic drugs should only be used when:The patient arrived early, within 3 hours of onset; definite diagnosis of ischemic stroke and no cerebral hemorrhage (CT scan or MRI results); No traumatic brain injury or stroke within 3 months; No gastrointestinal bleeding within 3 weeks; No surgery within 2 weeks; No arterial puncture within 1 week; maximum blood pressure < 180mmhg, minimum blood pressure < 110mmhg; no coagulation disorder, platelet count > 100,000/ml.
Among thrombolytic drugs, only t-PA (tissue Plasminogen Activator) is indicated at a dose of 0.9 mg/kg, injected intravenously, 10% of the total dose, then intravenously infused the remaining 90% of the dose within 1 hour. The maximum dose should not exceed 90 mg. Neuroprotective drugs (eg Cerebrolysin, Galatamine, Nootropyl, Citicolin, Tanakan...). However, no drug has been clearly proven to have a neuroprotective effect in the acute phase. Treatment of muscle spasms: Oral drugs (Baclofen, Seduxen, Dantrolene...) and injectable drugs (injection of Botolinum toxin group A or group B, nerve blockade with Phenol 5% or Alcohol). Antidepressant drugs (if any).
Other treatments:Hyperbaric oxygen, hydrotherapy…
Stroke prevention:Prevention based on causes and risk factors, specifically: Changing lifestyle; eliminating risk factors such as not smoking, not drinking alcohol; Eating moderately; Increasing physical activity and sports; living happily and avoiding stress; early detection and timely treatment of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and blood pressure.
About acupuncture - hydroacupuncture - acupressure massage:
Acupuncture:Acupuncture points on the whole body: Baihui, Dachui, Hegu, Yanglingquan, Xuanzhong, Zusanli, Quchi, Taichong, Xuehai, Taixi, Sanyinjiao, Neiguan, Shenmen, Waiguan, Jiaji. Local acupuncture points: If there is a 7th cranial nerve palsy, add the following acupuncture points: Chengqing, Renzhong, Dishang, Taiyang, Yuyao, Tongziliao, Tyzhukong, Qingming, Toanzhu, Yangbai, Quanliao, Jiaxa. If there is tongue retraction, difficulty speaking, lisping, or loss of voice, add the following acupuncture points: Amen, Dashi, Shanglianquan, Waijinxin, Waiyuyi.
If accompanied by urinary and bowel disorders:Acupuncture points: Zhongji, Qugu, Shaohai, Changqiang, Huiyin. Acupuncture points on the paralyzed side: Jiaji, Zhabian, Baliao, Huanqiu, Baxie, Yangchi, Yangxi, Jianjing, Jianzhen, Jianning, Quchi, Liangqiu, Duzi, Biyan... Each time, perform acupuncture from 5 to 10 points according to the above regimen, alternating between choosing appropriate whole-body and local points to achieve the best treatment and rehabilitation effects for the patient.
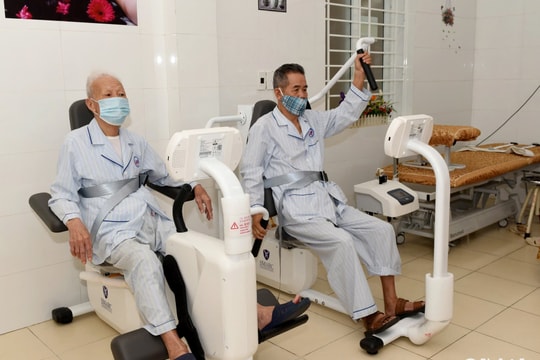
 |
| Bicycle ergometer in the rehabilitation of hemiplegia due to cerebrovascular accident. |
Acupuncture:Usually acupuncture on the following points: Stomach 36, Yanglingquan, Quchi, Sanyinjiao, Jianjing, Jianngung, Zhabian, Jiaji (paralyzed side). Medicines used in acupuncture: Commonly used drugs: Vitamin B group, Nucleo, Methycobal, Citicolin, etc. Moxa and herbal compresses, herbal baths: Moxibustion, herbal compresses, Faraffne candles, herbal baths using the Hydrotherapy system. Massage, acupressure: Massage the paralyzed side, press and massage the above points.
Follow-up and follow-up:After being discharged from the hospital, patients continue to be monitored and rehabilitated at home in the Community-Based Rehabilitation program. Patients need to be re-examined at least once every 6 months at the nearest rehabilitation facility; or when there are abnormal signs, patients need to go to the Rehabilitation facility for further examination and rehabilitation.
The next articles will cover:Rehabilitation for patients with: Spinal disc herniation, Sciatica, Arthritis, Joint stiffness, Spinal degeneration, Facial nerve palsy, Cerebral palsy, Childhood polio, Muscle weakness, Patients after bone fractures, Patients after Obstetrics, Surgery, Trauma, Orthopedics, etc. Please follow and read the next issues to find the most effective methods of Treatment, Rehabilitation, exercise and especially the most effective methods of disease prevention and disability prevention! |
| Nghe An Rehabilitation Hospital, with the spirit: "All for patient satisfaction" "Where patients place their trust". Model: The first Green - Clean - Beautiful "Hospital - Hotel" in Nghe An. Address: No. 220, Binh Minh Street, Cua Lo Town, Nghe An. Contact phone: Clinic: 0383.949.709; 24/7: 0383.952.020; Hotline: 0966.251.414; Hotline: 0912.002.210; Director's phone: 0912.487.568. |
PV
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|