Zinc air batteries store five times more electricity than lithium-ion batteries
Chemical engineers at the University of Sydney and Singapore's Nanyang Technological University have successfully developed a new "zinc-air" rechargeable battery technology that can be applied to electronic devices to replace current lithium-ion batteries.
According to Professor Yuan Chen - author of this research - zinc-air batteries were previously often produced with expensive metal components such as Platinum and Iridium Oxide, so they were only applied in a very limited way on small electronic devices such as hearing aids or train signals.
This new research has presented a new solution, in which expensive components are replaced by lower cost but high performance components, produced through controlling the composition, size, and crystallization of metal oxides such as iron, cobalt, and nickel.
This new zinc-air battery could therefore "overcome the slow oxygen evolution and oxygen reduction reaction (OER/ORR) in many electrical energy conversion devices," the paper says.
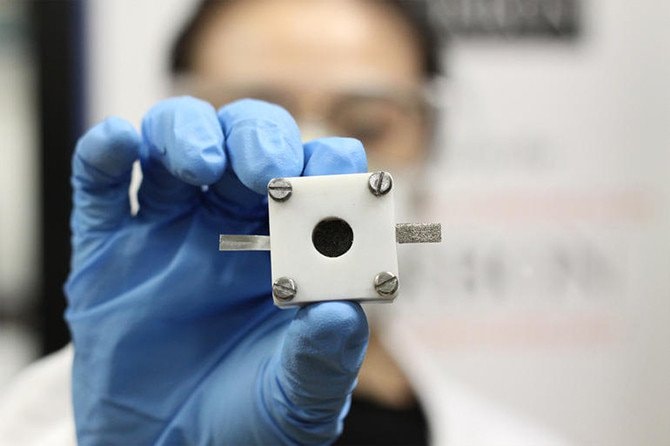 |
| Zinc air batteries work on the principle of zinc oxidation by air. |
Testing of this new battery also gave positive results, with only 10% battery wear after 60 charge/discharge cycles within 120 hours. From that, it can be seen that its application to mobile electronic devices is very feasible.
"Our method helps create low-cost but high-performance components for use in battery manufacturing. We are continuing to solve some other small technological problems to be able to create more sustainable metal-air batteries for humans," said Dr. Li Wei, co-author.
Zinc-air batteries are a type of metal-air battery that works on the principle of zinc oxidation by air. They are cheaper to produce than lithium-ion batteries (the most common type of battery used in electronic devices today), store 5 times more energy than lithium-ion batteries, and are much more environmentally friendly.
Meanwhile, lithium ion batteries are lighter and more efficient in generating energy, so they are widely used in smartphones, or even electric cars produced by Tesla. However, lithium ion batteries contain materials compressed under high pressure and are flammable, so it can cause unfortunate consequences when the battery has an internal circuit short.
An example of this problem is the battery failure on the Samsung Galaxy Note 7, which caused the device to explode and was eventually discontinued by Samsung itself. In a recent report, Samsung said that its lithium ion batteries were faulty, leading to short circuits and explosions.
Some other types of batteries can replace lithium ion such as magnesium batteries, which have the advantage of not being "depleted" when overcharged, or graphene batteries which are often used in high-level electrode structures.
According to Khoahoc.tv


