How long after eating should you sleep to avoid digestive problems?
Many people often make the mistake of going to bed right after eating. What harm does this do to your health?
Common harmful habits after eating
Most people feel sleepy around noon, which often happens in the early afternoon, which is after many people have eaten lunch. However, going to bed right after eating makes the digestive system work harder, affecting blood pressure, cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
A study presented at the 2011 European Congress of Cardiology found that waiting at least an hour after dinner before going to bed reduces your risk of stroke by about two-thirds. And for every 20 minutes you wait, your risk of stroke drops by another 10 percent, says researcher Cristina-Maria Kastorini, MSc, a nutritionist at the University of Ioannina Medical School in Greece.
The study involved 500 healthy people, 250 people who had suffered a stroke and 250 people with acute coronary syndrome. All 1,000 people filled out detailed questionnaires asking about their sleep habits as well as when and what they ate.
Compared with people who went to bed within an hour of dinner, those who waited 60 to 70 minutes had a 66% lower risk of stroke. Those who waited 70 minutes to two hours had a 76% lower risk of stroke. After two hours, the risk reduction began to taper off.
While the study does not prove cause and effect, it does suggest a link between waiting an hour or more between dinner and bedtime and a reduced risk of stroke. However, it does offer some insight into changing the harmful habit of eating too close to bedtime.
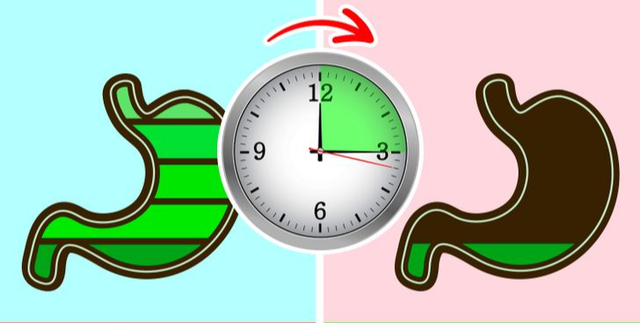 |
Try to leave 3 hours between meals and bedtime. For example, if you have dinner at 6 p.m., try to wait until 9 p.m. to go to bed. |
American College of Cardiology president David Holmes, professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine in Rochester, Minn., has another theory: "When we eat, our blood sugar changes, our cholesterol levels change, our blood flow changes. All of these temporary changes can affect our risk of stroke."
While the study didn't delve into why waiting longer after eating to go to bed might reduce stroke risk, researcher Cristina-Maria Kastorini said that previous research has shown that eating too close to bedtime is associated with an increased risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease, which is linked to sleep apnea (a risk factor for stroke).
Acid reflux, causing symptomsheartburn, acid reflux
Falling asleep right after eating causes undigested food to remain in the stomach, pushing on the valve separating the stomach from the esophagus, causing this "valve" to open, causing digestive juices and food from the stomach to reflux into the esophagus. This symptom makes you uncomfortable, prevents you from sleeping well, and even causes bad breath.
According to Dr. Tran Canh, Central Cancer Hospital, gastric reflux can be treated based on lifestyle adjustments and controlling gastric acid secretion through the use of antacids and, when necessary, surgical treatment with anti-reflux surgery, in which lifestyle adjustments play a leading role.
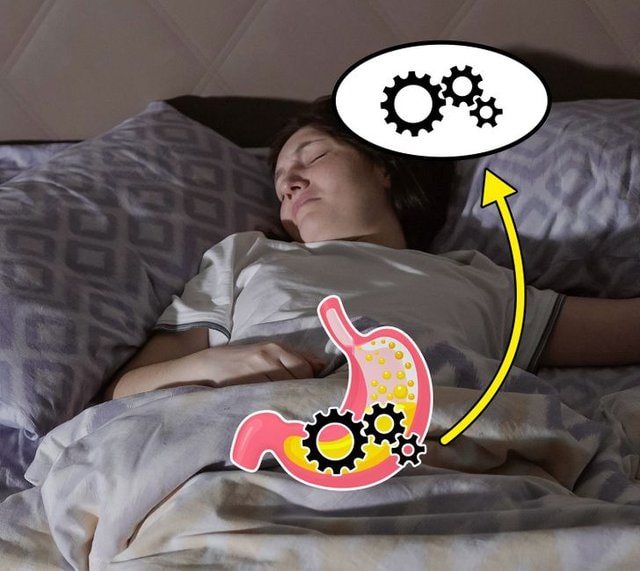 |
Sleeping immediately after eating increases the risk of gastrointestinal diseases. |
Harmful to the stomach
Sleeping after eating will cause the blood flow to the stomach to stagnate, not enough blood, making it impossible to digest food, allowing bacteria to attack and cause stomach and intestinal diseases. The most obvious symptoms are stomach pain, stomach ulcers, bloating, indigestion...
Risk of esophageal ulcers
Going to bed right after eating weakens the lower esophageal sphincter, opening and closing abnormally, allowing acid to reflux into the esophagus, causing heartburn and affecting the esophageal mucosa, causing inflammation and ulcers.
Chronic acid reflux can lead to a condition called Barrett's esophagus. This is a condition in which the cells in the lower part of the esophagus are damaged and replaced by abnormal cells. These cells are not cancerous, but they can develop into precancerous cells.
What should I do after eating?
Whether it is breakfast, lunch or dinner, you should take a light walk after every meal. Usually, nutritionists recommend a light walk of 10 minutes after a meal. If you have eaten or overeaten, just walk around for a while, you do not need to put on your walking shoes and go to the park. You can take a light walk indoors or outdoors to relieve discomfort. This will push the food further and will also speed up the digestion process.
Be careful, never go for a brisk walk or jog after eating, as this can cause nausea and stomach pain. In particular, never lie down immediately after a full meal. Lying down after a meal can cause reflux or acid reflux. This can irritate the lining of your food pipe and may even make you feel nauseous.


