How to properly screen for colorectal cancer
People over 40 years old, even if they have no symptoms, should still have a fecal occult blood test every year and a colonoscopy every 10 years.
Colorectal cancer has the third highest mortality rate after lung cancer and stomach cancer in men, and after breast cancer and cervical cancer in women. The disease has a complex progression, and if not detected and treated promptly, cancer can spread to other parts of the body, especially the liver and lungs.
The group at high risk of the disease is nPeople aged 40 and over, especially after 50 years old, people with a personal or family history of colorectal cancer, polyps in the colon, people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease and people who are sedentary or obese...
 |
| Illustration photo. |
Colorectal cancer can be prevented by detecting polyps before they develop into cancer and removing them by endoscopy. Even if they develop into cancer, they can still be cured if detected early and treated promptly.
Early stage colorectal cancer often has no symptoms or vague symptoms that can be easily confused with other diseases. To detect it early, you must proactively go for screening even when you have no symptoms.
Three methods are commonly used to screen for colorectal cancer:
Fecal occult blood test
This is an inexpensive, simple test with a sensitivity of 70-80% in detecting cancerous tumors.This is recommended annually to detect early signs of disease. It is a simple test that looks for hidden blood in the stool, which is invisible to the naked eye. Each person is given a finger-sized test tube along with instructions on how to collect a stool sample at home. The stool sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
This test is used to determine whether or not there is hidden blood in the stool, but it cannot immediately confirm whether there is cancer or not. Because there are many causes of blood in the stool such as peptic ulcers, hemorrhoids, colon polyps and colorectal cancer.
For positive test results, the patient will be notified to see a doctor for further diagnostic steps to determine the cause of bleeding. If the bleeding is due to polyps and colorectal cancer, the patient will be instructed to receive timely treatment to prevent the development of the disease.
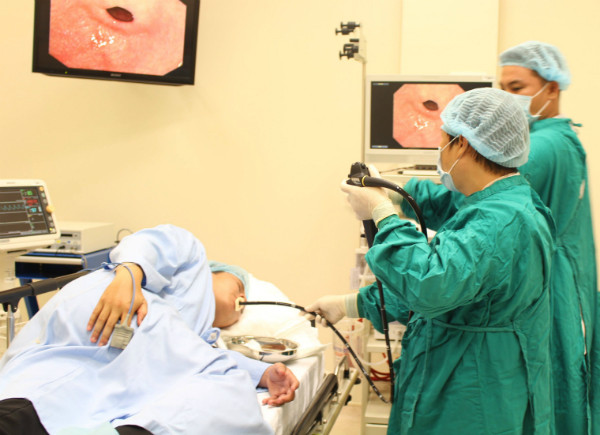
Colonoscopy
This is the most accurate method, but the implementation is quite complicated. The patient must be purged, fasting because the endoscopy can cause pain, so pre-anesthesia is often required. If polyps are detected during colonoscopy, the doctor will remove the polyps during the examination.
Virtual colonoscopy
The patient must undergo a bowel cleansing and a multi-slice CT scan, after which the computer reconstructs the colon lumen. Virtual colonoscopy can detect most polyps in the colon lumen. After virtual colonoscopy detects polyps, a real colonoscopy must be performed to remove the polyps.
Based on the research results, the doctor makes a recommendation on choosing a screening method, starting age, and repeat interval for people at risk of colorectal cancer.
|
Colonoscopy helps detect and treat cancerous polyps early. Photo:MT |
Screening recommendations by age and risk group
- Medium risk group:
Asymptomatic people over 40-50 years old or family history of cancer not in first-degree relatives (parents, siblings): annual fecal occult blood test, colonoscopy every 10 years, virtual colonoscopy every 5 years.
- High risk group:
Have one first-degree relative with colon cancer before age 45 or two first-degree relatives with cancer: colonoscopy every 3 years, starting 10 years before the age of the youngest relative with cancer or from age 40 onwards.
Have a first-degree relative with cancer after age 45: colonoscopy every 3 years, starting 10 years before the age of the youngest relative with cancer or from age 50.
Personal history of colorectal polyps: colonoscopy one year after polypectomy if polyps are high risk.
Personal history of colorectal cancer: colonoscopy one year after surgery.
Personal history of ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer: colonoscopy one year after surgery.
- Very high risk group:
Family history of colon polyposis: sigmoidoscopy, testing, and genetic counseling annually, beginning at age 12-14.
Family history of nonpolyposis colon cancer: colonoscopy, testing, and genetic counseling beginning 10 years before the age of the youngest relative with cancer, performed periodically every 2 years.
People with idiopathic ulcerative colitis should have colonoscopy every 2 years, beginning 15 years after diagnosis.
It should be noted that for colonoscopy results to be valid for up to 10 years as recommended, the colonoscopy must be performed very carefully, the colon must be cleaned of stool, and observed very carefully so as not to miss small polyps.