How do submarines work?
As a state-of-the-art weapon, the construction and operation of submarines requires strict technical standards and discipline.
 |
German Navy U-boat. Photo: History |
Although born quite early, it was not until World War I that German U-boat submarines proved the value of this weapon in real combat, when they sank many Allied ships.
By World War II, after Britain developed radar and sonar technology for submarines, the US Navy also improved these systems along with German-made snorkels.significantly increased the diving time of submarines, making them indispensable weapons for any military power.
However, to become "killers" under the ocean, submarines must be built according to strict procedures, with the most stringent standards, according to Marinebio.
Floating diving mechanism
A submarine surfaces or dives depending on ballast tanks located between its inner and outer hulls.
To dive, a submarine must have a buoyancy force less than gravity. At this time, valves on the ballast tank are opened to allow seawater to rush in and push air out to help the submarine dive. The depth of the submarine is controlled by adjusting the ratio of seawater and air in the ballast tanks. When the weight of the submarine is equal to the displacement of water inside the ballast tank, the submarine will be in a state of equilibrium, not floating or sinking deeper.
To help the ship float to the surface, simply use compressed air to push seawater out of the ballast tanks, making the lifting force of the water greater than gravity.
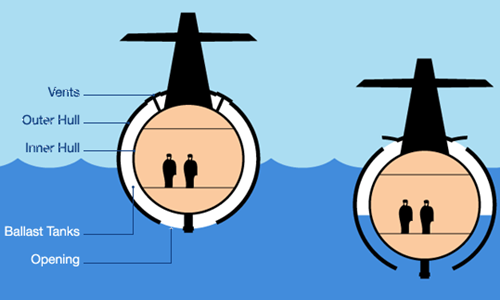 |
Ballast tanks are filled with gas to help the ship float (left). Ballast tanks are opened to let in water to help the ship sink. Graphic: submarinesafaris |
Design and control
Submarines are always cylindrical in shape with a small head and two hulls, an inner hull and an outer hull. The inner hull, also known as the pressure hull, protects the crew from the high pressure of deep diving and helps the ship avoid the freezing temperatures of the seawater. The outer hull is the shell that encloses the ship.
Technological advances have changed the way submarines are observed and operated. A major breakthrough in the Virginia-class submarines is the use of Photonics masts, which eliminate the need for conventional periscopes. Instead of mirrors and lenses to see the water, several high-resolution color cameras are integrated to transmit images to large screens in the bridge via fiber optics.
 |
Model of the Soviet Project 641B diesel-electric submarine compartment. Photo: spox.ru |
Submarines use various types of engines including diesel engines, electric engines (or diesel-electric combinations), and nuclear-powered engines.
Electric motors help submarines travel underwater for longer periods of time.and does not emit toxic gases likesteam or petrol engines. Electric motors are relatively small, but their battery systems are large, heavy, and cumbersome. These batteries, when exposed to seawater, emit toxic gases due to chemical reactions and contain toxic acids themselves.
Submarines use diesel engines to create steam to turn turbines to produce electricity, which helps to heat the ship and provide lighting. However, diesel engines burn air and emit toxic gases, so people often combine them with electric motors on submarines.
Nuclear submarines use nuclear-powered engines so they do not need an air supply and can remain submerged indefinitely, only surfacing when needed to resupply.
Rescue capabilities
In addition to operating rules, submarines also need to ensure other factors when diving, including submarine survival support (air, temperature, clean water), power supply and orientation.
When a ship encounters an accident, the crew will send out a distress signal or drop a buoy to announce the location of the ship in distress. Depending on the severity, the nuclear reactors may be shut down and the ship will only use batteries.
When an accident occurs, the crew faces major risks such as water entering the ship, lack of oxygen, dangerously high levels of toxic gases, and a drop in temperature when the ship's heating system batteries fail. At this time, surface rescue efforts need to be carried out urgently, usually within 48 hours of the accident.
According to VNE
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|


