Herniated disc: Consequences of bad habits
Spinal disc herniation (SDD) is often the result of disc degeneration.
As we age, the discs become drier, less flexible and more vulnerable to injury. Few people know that the cause of the disease is mainly due to bad habits in life.
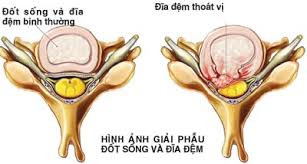 |
Spinal disc herniation refers to the pathology of the spinal disc being displaced from the normal position of the vertebral body, leading to compression of the nerve roots or spinal canal. Herniated disc is common in the cervical spine and lumbar spine, causing compression of the nerve roots or spinal canal at the compressed location.
Disc herniation is often the result of disc degeneration. Few people know that the real cause of disc herniation is mostly due to repetitive microtrauma, which the patient does not pay attention to. For example, carrying heavy loads can lead to disc herniation. Some cases are caused by spinal trauma when falling from a height, traffic accidents, work accidents... causing disc herniation.
Risk factors to consider
Some factors that increase your risk of developing a herniated disc include:
Body weight: Being overweight increases the burden on the lumbar discs, leading to an increased risk of lumbar disc herniation.
Occupation: Occupations that require a lot of physical activity, such as regularly carrying heavy loads, pushing or pulling heavy objects, tilting or scoliosis to the side... all increase the risk of herniated discs.
Genetic factors: Some people with herniated discs have a genetic predisposition to the condition.
When to see a doctor?
People with spondylolisthesis may have no symptoms - the herniated disc may be discovered incidentally on an X-ray. Some cases of spondylolisthesis cause spinal pain. Herniated discs are most common in the lumbar and cervical spine.
Typical symptoms
Leg or arm pain: Lumbar disc herniation can cause pain in the lower back that radiates down the buttocks, back of the thigh, back of the leg, and possibly the foot. Cervical disc herniation can cause pain in the neck, shoulders, and arms. Pain in the arms and legs can be triggered or worsened by coughing, sneezing, or moving the spine.
Numbness: Patients with spinal disc herniation are often bothered by numbness in the body area corresponding to the nerve area controlled by the disc.
Muscle weakness: Herniated disc compresses the nerve, reducing the motor response of the muscle group controlled by that nerve, causing muscle weakness. Symptoms of muscle weakness can be subtle and only detected when a doctor examines, but can also be very obvious, affecting the patient's daily activities or causing disability.
You should consult a doctor if you have symptoms of neck pain radiating to the shoulder or arm or back pain radiating to the hip or leg or combined with symptoms of numbness or muscle weakness.
Complications of herniated disc
The spinal cord does not occupy the entire length of the spinal canal but ends in the upper part of the lumbar spine. The lower part of the lumbar spine contains the nerves in the spinal canal such as the cauda equina. Some cases of disc herniation can cause acute spinal cord compression or cauda equina syndrome and require emergency surgery to relieve the compression, avoiding permanent paralysis.
Go to a medical facility immediately if you experience:
More severe symptoms: pain, numbness, and weakness in the limbs become more severe, making it impossible for you to perform daily activities.
Bowel or urinary disorders: urinary retention or urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence.
Loss of sensation in the anogenital area, inner thighs and calves.
Change your lifestyle
Use of pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers should be used judiciously to avoid misuse. Consult your doctor before choosing stronger pain relievers.
Use heat therapy: During acute attacks, cold compresses can be used to relieve pain and reduce the inflammatory response of the disease. When the attack is over, the patient can apply warm compresses to relax the muscles and feel more comfortable.
Avoid lying down too much: Lying down too much makes the spinal joints stiff and the muscles weak. You should lie down and rest for about 30 minutes, then stand up and walk around or do some housework. You should avoid positions that cause pain to the spine.
How to prevent disease?
Exercise: Exercises that strengthen the muscles next to the spine will help stabilize the spine and prevent disc disease.
Maintain good posture: Maintaining good posture while studying, working and doing activities will help avoid injuries to the spine. Sit up straight and do not maintain the same posture for a long time. To lift heavy objects, bend your knees instead of bending your back.
Maintain a healthy weight: Maintain a healthy weight for your height to avoid putting pressure on your spine.
According to Health & Life
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|






