The oldest human ancestor in 540 million year old rock
The oldest human ancestor lived 540 million years ago and was shaped like a sack and had no anus.
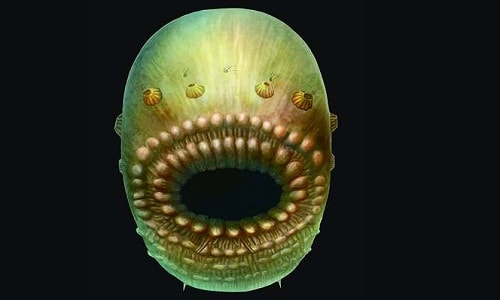 |
| Human ancestors had mouths that took up most of their bodies and no anus. Photo: Jian Han/Northwest University, China. |
Our oldest fossil ancestor is a deuterostome discovered in 540 million-year-old limestone in central China, International Business Times reports. This creature gave rise to a range of life forms that include today's starfish and sea squirts.
According to a study published in the journal Nature, the deuterostomes discovered are the earliest in this phylum. "Deuterostomes gave rise to a wide variety of animals, from humans to starfish and sea urchins. That richness raises the question: What did the common ancestor of animals look like?" said Simon Conway Morris of the University of Cambridge, UK, lead author of the study.
The 540 million year old fossil creature was very small, only about 1.3 mm long, 0.8 mm wide and 0.9 mm high, with a very large mouth compared to the rest of its body, measuring 0.3-0.5 mm across. It also had four conical holes on each side.
"This is a landmark deuterostome, and the precursor to fish gills. Water flows through the gills and out the side of the animal," said Conway Morris.
This is a primitive way for animals to get rid of waste. The researchers could not identify an anus in any of the deuterostome specimens they found.
Finding primitive deuterostomes is a big step in the fossil record between very small, simple organisms that had to gather oxygen by diffusion, and larger animals like fish that breathe through gills. “This is part of the answer to how complex things evolve,” Conway Morris said.
Forty-five specimens of deuterostomes were found in ancient limestone in Shaanxi Province, China. Researchers had to remove about three tons of limestone to retrieve the tiny fossils.
Deuterostomes have been discovered before, but none have dated back to 540 million years ago. The creatures were fossilized in a process called phosphate fossilization, in which phosphate molecules rapidly replace body parts before they break down. The researchers are still unsure how old the creature was.
According to VNE
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|

