What is malignant melanoma?
Although malignant melanoma is not a common disease in Vietnam, if left untreated for a long time, it will cause extremely serious complications for the patient.
Malignant melanoma is a malignant disease of melanin pigment-producing cells. These cells are mainly distributed in the basal cell layer of the skin epidermis, and are also found in the retina, rectum, etc. The disease is most common in Australia (25-30/100,000 people), and is rare in Vietnam.
 |
Early detection can increase the effectiveness of treatment with relatively simple surgery. On the contrary, when the disease is in the late stage, has metastasized to lymph nodes or distant metastases, the treatment effectiveness is low, the prognosis is very poor.
Exposure to ultraviolet rays from sunlight is recognized as the primary cause of malignant melanoma. The risk of malignant melanoma in second-generation offspring is increased fourfold.
Malignant melanoma can occur anywhere on the body or in areas of frequent friction: heels, genitals...
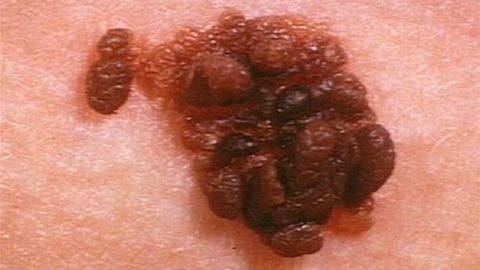
More than 90% are malignant melanomas of the skin, of which 70% appear on the background of a pre-existing mole. The tumor often grows protruding from the skin surface, jet black, sometimes red or white. Malignant melanoma can also be found in the retina, meninges, natural cavities, colon, and liver. Depending on the anatomical location of the tumor, it has symptoms borrowed from diseases specific to that anatomical location.
About 5% of cases of malignant melanoma do not produce pigment, the lesion is just a gradually growing lump of flesh, which can only be diagnosed by histopathology.
The typical symptom of UHTAT is a change in the nature of an old mole, an old hyperpigmented lesion, or even on a background of normal skin. These changes are classified in order of importance from most to least into three groups:
1.Highly suggestive symptom group: changes in size, shape, color.
2.Moderately suggestive symptom group: inflammatory reaction, flaking or bleeding, altered sensation, mole diameter greater than 7 mm.
3.Group of symptoms with low suggestive value: loss of symmetry, color abnormalities, lesions raised above the skin surface, changes in the margins of the lesions.
The disease is very common with lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis and about 6% of malignant melanomas have lymph node metastasis, but the primary tumor is unknown.
In summary, the most important measure to prevent the disease is to limit direct exposure to ultraviolet rays, self-examine the skin of the whole body periodically every month. For moles that change in size, shape, color or hyperpigmented lesions on the skin with the following characteristics: rapid progression, ulceration, bleeding, it is necessary to go to a specialist facility for timely examination and treatment.
According to Vietnamnet
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|

