Why are cars assembled in Vietnam expensive and of low quality?
After nearly a quarter of a century of protection, the Vietnamese automobile industry remains stagnant, with a low localization rate, small production scale, and product quality not commensurate with cost.
Vietnam's auto industry is facing an important transition period. On January 1, 2018, imported cars within the ASEAN region will enjoy 0% tax. "Judgment Day" is approaching, and businesses are still struggling with the question of whether to invest in domestic assembly or switch to importing.
20 years of production can't make a brake pad
As of 2017, the Vietnamese auto industry is about 20 years old. As a result, after 20 years of protection, cars assembled in Vietnam are priced twice or even three times higher than in the US market, despite enjoying many incentives on import tax on components. The quality of the cars is extremely low, with a localization rate of only 15-40%, while the corresponding figure in Thailand is 80%.
The auto industry is targeted to contribute 10% of GDP, but so far it has only reached about 3%. Car production output has only reached about 1/3 of the registered figure.
Specifically, in 2005, the target was 120,000 units but only 59,200 units were produced. In 2010, the target was 239,000 units but actually 112,300 units were produced. In 2020, the target was 398,000 units but only about 198,600 units were produced.
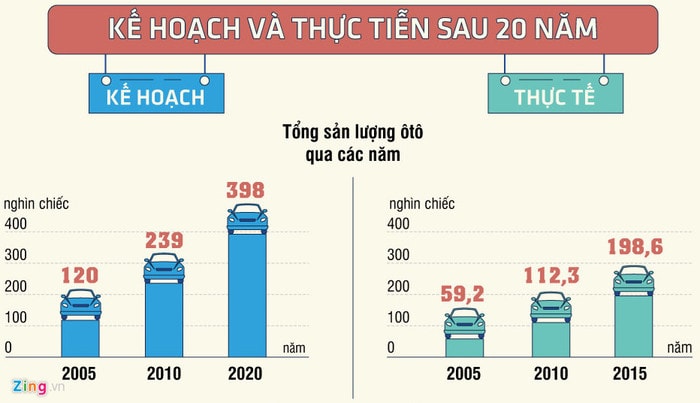 |
| Domestic assembly target and actual numbers. |
According to the Institute for Industrial Policy and Strategy Research, the cost of car production in Vietnam is currently about 20% higher than in other countries in the ASEAN region. Car production technology has not improved much, mostly just stopping at the level of importing components and assembling. The supporting industry is almost nothing, only producing a few simple components such as batteries and tires.
Master Nguyen Minh Dong, a former Volkswagen car engine design expert who has lived and worked in the German auto industry for 40 years, shared: "I do not trust products made in Vietnam. Cars are a unique product, and the technical barriers as well as the qualifications of car experts in Vietnam are extremely low."
Reasons for failure
The domestic auto industry is protected by the Government, but inconsistent protection policies make companies lazy to localize, failing to stimulate the supporting industry.
During the period 1991 - 2008, import tax on complete cars was about 90%, corresponding to import tax on components was only 23%. During the period 2008 - 2015, the above two figures were 70% and 19% respectively.
Currently, import tax on complete cars ranges from 47% to 52%. Import tax on auto parts averages around 18%.
According to the proposal of the Ministry of Finance, in early 2018, import tax on auto parts will be reduced to 0% to increase competitiveness for domestic cars, facing pressure from imported cars from the ASEAN region.
In addition, domestic car assembly enterprises also receive corporate income tax incentives and a 5% value-added tax reduction for spare parts and machinery used to assemble cars.
The preferential treatment given to domestically assembled cars is also a loophole that companies take advantage of. Instead of focusing on localizing components to reduce costs, companies disassemble each car part and import it into Vietnam as a set of components to enjoy low taxes.
Due to the low localization rate, the cost of cars assembled in Vietnam is about 20% higher than cars produced in the ASEAN region. And therefore the selling price of the product is also higher.
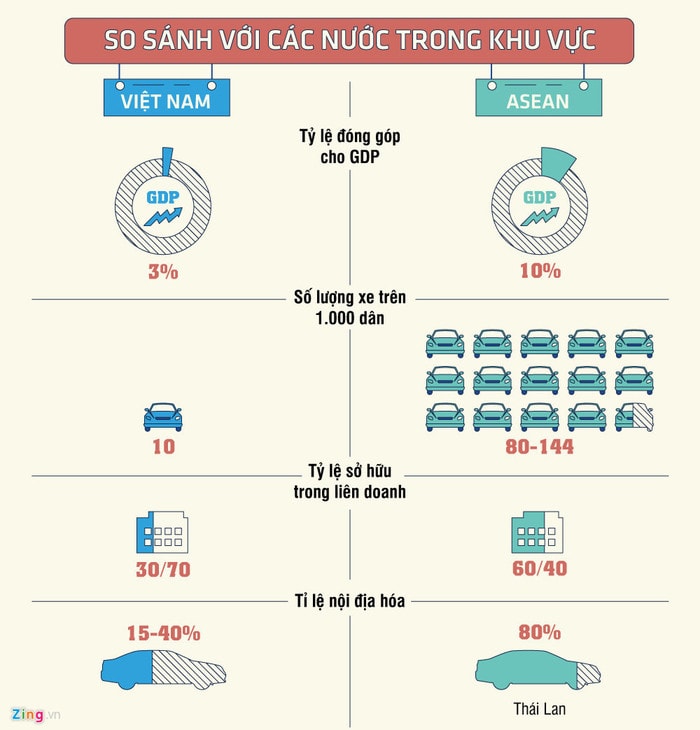 |
| Comparing Vietnam's automobile industry with ASEAN countries. |
The technology used in Vietnamese cars is extremely outdated, the production lines are old, dependent on human power and productivity is low. This is also one of the reasons why the price of a car is higher than the average.
In the world, handmade cars are usually super cars, luxury cars, the selling price has been included in the labor cost. But in factories in Vietnam, workers do it by hand to create popular car models, so this cost is included in the price.
In addition, the lack of machinery and the use of old technology make cars assembled in Vietnam fail to meet safety standards. Many cases of airbags not deploying are due to improper installation or untested quality of components; weak welds and thin steel cause the car to be crushed in accidents.
 |
| The rudimentary assembly line mainly relies on human power of Toyota Vietnam Company. |
However, to be fair, every manufacturer is a business unit. The first thing in business is profit. So they will find the most optimal solutions to recover the cash flow they spend.
According to a representative of a major car company in Vietnam, the reason why car prices in Vietnam are high and the localization rate is low is because the market size is too small. Although the population is nearly 100 million, most Vietnamese people are poor or near-poor, with an average income of only about 2,000 USD/person/year.
In the world, the average income to be able to use a car must be from 6,000 USD/person/year. Due to the small market size, manufacturers are not interested in setting up large factories to produce components in Vietnam.
Supporting companies also do not see the future and profits so they do not invest. As a result, Vietnam does not have a supporting industry, everything has to be imported, making the cost higher.
Second, the tax policy on cars is too high, which increases the selling price of the products. Although the value of finished cars assembled in Vietnam is about 20% higher than in the region, the price after tax will be 150% - 200% higher.
As 2018 is approaching, although no manufacturer has announced that they will stop assembling domestically, market developments in the first months of 2017 show that the structure of the Vietnamese car market is shifting from assembly to import.
For example, Toyota's popular car models such as Fortuner were switched from assembly to imported from Indonesia. Honda Civic was imported from Thailand, Hyundai Grand i10 was imported from India...
If the policy for Vietnam's auto assembly industry does not change, it is inevitable that manufacturers will abandon assembly and switch to importing complete vehicles. With a 0% import tax on complete vehicles, while the import tax on components is 18%, the balance will definitely tilt towards imported vehicles.
According to VNN
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|

