How dangerous is diphtheria?
Up to now, Quang Nam has had 3 deaths due to diphtheria. So what is diphtheria? Who is susceptible to the disease? How to prevent it?
Transmission mechanism of diphtheria
According to Associate Professor, Dr. Tran Dac Phu - Director of the Department of Preventive Medicine, Ministry of Health, diphtheria is an acute infectious and toxic disease caused by diphtheria bacteria; the disease is common in young children, but can also occur in adults if they are not immune. The disease is easily transmitted through the respiratory tract or through direct contact with secretions from the nasal mucosa of patients or healthy people carrying the virus when coughing or sneezing, especially in crowded residential areas or places with poor hygiene conditions.
Symptoms can range from mild to severe, often with white pseudomembranes in the tonsils, pharynx, larynx, nose, and can appear on the skin, other mucous membranes such as the conjunctiva or genitals. Severe cases can cause complications and death.
"Previously, the disease was quite common in most localities across the country; since the diphtheria vaccine was included in the expanded immunization program, the disease has been controlled and only a few sporadic cases have been recorded due to lack of vaccination, often occurring in remote areas with low vaccination rates. Currently, diphtheria has not been eliminated in our country, so people can still get the disease if they do not have immunity due to lack of vaccination and exposure to the pathogen," said Mr. Phu.
Mr. Phu said that in recent years, there have been almost no cases of diphtheria in children nationwide, however, in the past two years, there have been sporadic small outbreaks (1 case/outbreak) in some localities such as Nghe An and Gia Lai. The cases are adults who have not been vaccinated.
“Diphtheria often attacks young children, while adults can carry the bacteria but show no symptoms and can be a source of infection for children. Families delaying vaccination for young children often causes diphtheria to return. Therefore, children need to be fully vaccinated,” Mr. Phu advised.
What are the complications of diphtheria?
According to Mr. Phu, diphtheria is dangerous because it can cause complications in the heart, bronchi, and lungs, leading to death if not treated early.
Master Nguyen Hong Ha - Vice President of the Vietnam Association of Infectious Diseases said that in the past, when there was no vaccine to prevent the disease, the patient mortality rate was 15 - 20%.
There are two forms of malignant diphtheria that cause myocarditis, heart failure, kidney failure, and splenic necrosis. The most common complication in diphtheria patients is myocarditis, which can appear early in the first days of the disease but can be 3-5 weeks later even after the disease has recovered.
Peripheral neuritis complications can cause paralysis of the cranial nerves, causing paralysis of the palatine membrane, paralysis of the eye muscles, flaccid paralysis of the limbs, diaphragm, and intercostal muscles causing respiratory failure. In recent years, in the North, no cases of diphtheria have been recorded.
To treat diphtheria, the principle of treatment is to neutralize diphtheria toxin as soon as possible, doctors will infuse malignant diphtheria antiserum. In the past, treatment was mainly with horse antiserum, but recently this type of serum is not produced because diphtheria is rare.
Is vaccination the best way to prevent disease?
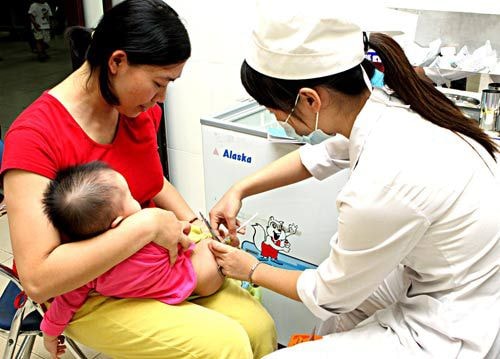 |
| Vaccination - the best way to prevent diphtheria in susceptible children |
According to experts from the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology, the most effective way to prevent diphtheria is to maintain high vaccination rates in the community. In most countries, diphtheria toxoid vaccine is given together with pertussis and tetanus toxoid vaccine (BH - HG - UV vaccine). Recently, some countries have used a combination vaccine including diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B and sometimes Hib vaccine.
Every 10 years, a booster dose of the adult vaccine, tetanus-diphtheria toxoid (Td), is needed to maintain immunity.
According to Suckhoedoisong.vn






