Car Engines and the Basics You Need to Know
What is a car engine, what is its structure, how does it work? To answer these questions, let's learn about the engine in today's cars - a part that is considered the heart of the car.
 |
What is the engine?
An engine is a device that converts a form of energy such as gasoline or oil into kinetic energy. Basically, we can divide heat engines into two main types: internal combustion engines and external combustion engines.
Each type is divided into many sub-types with different advantages and disadvantages. Internal combustion engines include gasoline engines, diesel engines, gas turbine engines, rotary engines, 2-stroke engines, etc. External combustion engines include two representatives: steam engines and Stirling engines.
Heat engines are of two main types: internal combustion engines and external combustion engines. |
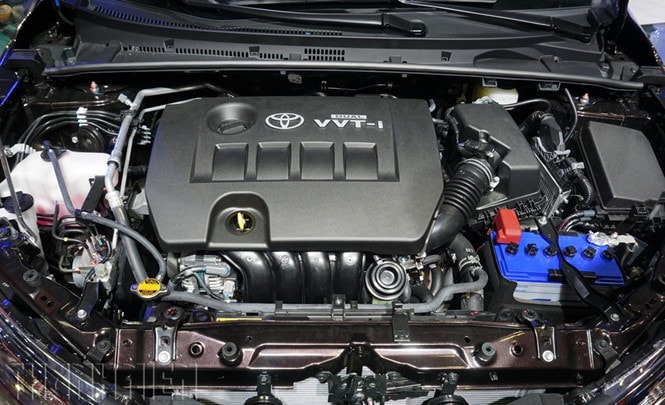
Thanks to higher efficiency and more compact size than external combustion engines, internal combustion engines are commonly used today for many vehicles, and cars and motorbikes are the most typical representatives.
Vehicle engine structure
Classifying cars by engine or classifying cars by power source is divided according to operating structure, type of fuel used in each power source with the current popular structure:
• Gasoline engine
• Diesel/Oil Engine
• Electric motor
• Hybrid engine
In this article, we will learn about internal combustion engines that use gasoline or diesel fuel because they are commonly used in vehicles on the market today. Electric motors and hybrid motors will be introduced in the following articles.
Internal combustion engine |
The main parts of an engine are the cylinders, with pistons moving up and down inside the cylinders. Most car engines have more than one cylinder, usually 4, 6 or 8 cylinders, with sports cars having 12 or 16 cylinders. In multi-cylinder engines, the cylinders are arranged in one of the following ways: in a row (in-line cylinders), in a V-shape (V-shaped cylinders), or two cylinders facing each other horizontally (opposite cylinders).
Spark plug
The spark plug in a car engine is responsible for creating an electric spark to ignite the air and fuel mixture in the cylinder. The spark must be created at the right time at the end of the compression stroke to create maximum efficiency.
Spark plug in car engine |
Valve
The exhaust and intake valves open and close at the right time to supply fuel and allow exhaust gases to escape. During the compression and combustion strokes, these valves are closed. These valves are operated by a camshaft system as shown below.
Engine Valve Parts. |
Camshaft
On the camshaft there are cam lobes, when rotating these cam lobes will push the valve down to help the valve open. There are two types of camshafts: single camshaft and double camshaft, single camshaft will control the opening and closing of both intake and exhaust valves. Meanwhile, double camshaft has two camshafts that separately control the intake and exhaust valves.
Camshaft part of the engine. |
Crankshaft
The crankshaft is used to convert the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotary motion like the shaft in a worm gear - worm.
Engine crankshaft |
How does the engine work?
Its operating principle is based on the mechanism that when using a small amount of high-energy fuel such as gasoline (or diesel) in a small closed space and burning, a large amount of energy will be generated through the pressure of expanding air. This energy can make a potato fly 150m away.
Internal combustion engines use that principle with a closed cycle, explosions occur hundreds of times per minute inside the engine cylinder. The mixture of air and fuel (called air-fuel mixture) is burned in the cylinder of the internal combustion engine. When burned, the temperature increases, causing the gas to expand, creating pressure on a piston (piston) to push this piston to move.
|
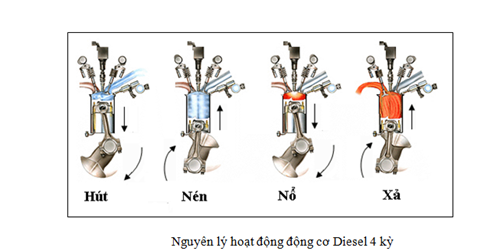
Almost all cars today use an engine with a 4-stroke cycle to convert gasoline into moving energy, also known as a 4-stroke engine. The cycles include: intake, compression, combustion and exhaust.
- During the first stroke (intake - intake valve open, exhaust valve closed), the air and fuel mixture is "charged" into the cylinder while the piston moves from top dead center (TDC) to bottom dead center (BDC).
- During the second stroke (compression - both valves are closed), the piston compresses the mixture of air and fuel in the cylinder as it moves from BDC to TDC. At the end of the second stroke (the piston is at TDC), the mixture of air and fuel is ignited in a gasoline engine by an ignition device called a spark plug, and in a diesel engine by self-ignition.
- In the third stroke (power stroke - the valves continue to be closed), the mixture of air and fuel is burned. Because the temperature increases, the pressure of the air mixture increases and makes the piston move from TDC to BDC. The reciprocating motion of the piston is transferred by the connecting rod (also called the connecting rod) to the crankshaft and is converted into rotary motion.
- In the fourth stroke (exhaust - intake valve closed, exhaust valve open) the piston moves from BDC to TDC, pushing gas from the cylinder through the exhaust pipe (commonly called the muffler) into the environment.
The movement of the piston in the first, second and fourth strokes is due to the energy stored by the flywheel attached to the crankshaft in the third stroke (the working stroke). A four-stroke engine therefore has an ignition angle of 720 degrees calculated from the crankshaft rotation angle, which means that when the crankshaft rotates 2 times, there is only one ignition. With more cylinders, the ignition angle will be smaller, more combustion energy is put into the two rotations of the crankshaft, making the engine run smoother.
The replacement of exhaust gases with fresh air mixture is controlled by the camshaft. This shaft is attached to the crankshaft, rotates with a 1:2 reduction gear, opens and closes the valves on the cylinder head of the engine. The timing of the crankshaft closing and opening the valves is adjusted so that the intake and exhaust valves are opened at the same time for a short time when switching from the exhaust stroke to the intake stroke. The exhaust gas exits at high speed, drawing new air into the combustion chamber to better charge the cylinder and increase the combustion pressure.







.jpg)






