Suggestions for taking the Geography exam
I. General part for all candidates
Question 1:
1. General presentation of the East Sea and the main natural disasters in our country's coastal areas:
The East Sea is a large sea, with an area of 3.477 million km2.
It is a relatively closed sea (the east and southeast are surrounded by island arcs).
The East Sea is located in the tropical monsoon zone. This characteristic of the East Sea is expressed through the following factors: temperature, seawater salinity, waves, tides, ocean currents and marine life.
* The East Sea, besides many favorable natural features and high economic value, also contains many dangers and natural disasters that every year have negative impacts on production activities and people's lives.
Storms: On average, there are 9-10 storms each year, of which 3-4 make landfall directly. Large storms are accompanied by rising waves, heavy rain, floods, and prolonged inundation in many areas.
Coastal erosion: Currently, many coastal areas have been and are at risk of landslides, especially in the Central Coast.
The phenomenon of flying sand and flowing sand encroaching on rice fields, especially in the central coastal region, causes agricultural land to shrink and makes people's lives difficult.
2. Characteristics of urbanization in our country
The urbanization process is slow and the level of urbanization is low.
The population and urban population ratio are increasing over the years: In 1990 the urban population ratio was 19.5% and increased to 26.9% in 2005.
Uneven urban distribution among regions: Most large cities are concentrated in areas with favorable locations and terrain.
* The urban population ratio in our country is lower than the world average, because:
The urbanization process is very slow: In 2005, the urban population rate was 26.9%.
Low level of urbanization;
Urban infrastructure is low and backward compared to other countries in the region and the world.
Large urban areas are still quite few, the whole country has 5 centrally-governed cities that are considered large urban areas of the country.
In addition, due to our country's long history of occupation and major wars, it has had a heavy impact.
Sentence II:
1. Favorable natural conditions for the development of our country's fisheries industry:
Our country has a long coastline and a large exclusive economic zone.
Seafood resources are quite abundant (total reserves of about 3.9 - 4.0 million tons).
There are many fishing grounds, with 4 major fishing grounds (Ca Mau - Kien Giang fishing grounds; Ninh Thuan - Binh Thuan - Ba Ria Vung Tau; Hai Phong - Quang Ninh; Hoang Sa archipelago - Truong Sa archipelago).
There are many advantages for brackish and freshwater aquaculture.
2. Exploiting mineral resources in our country's sea areas
* Currently, the following minerals are being exploited in our country's sea:
Salt making: Most developed in the North Central Coast.
Oil and gas exploration and exploitation on the continental shelf have been and are being promoted along with the expansion of joint venture projects with foreign countries.
In addition, in some places along the coast from Thanh Hoa to Ba Ria - Vung Tau, titanium ore is being exploited.
* Islands and archipelagos have strategic significance in economic development and protecting maritime security, because:
Affirming our country's sovereignty over the sea and continental shelf around the island (based on the 1982 International Law of the Sea).
The islands and archipelagos form a system of outposts to protect the mainland, a system of bases for our country to advance to the sea and ocean in the new era.
Effectively exploiting marine, island and continental shelf resources: aquatic resources, maritime transport, minerals and tourism resources. Thereby contributing to creating conditions to promote the country's socio-economic development.
Sentence III:
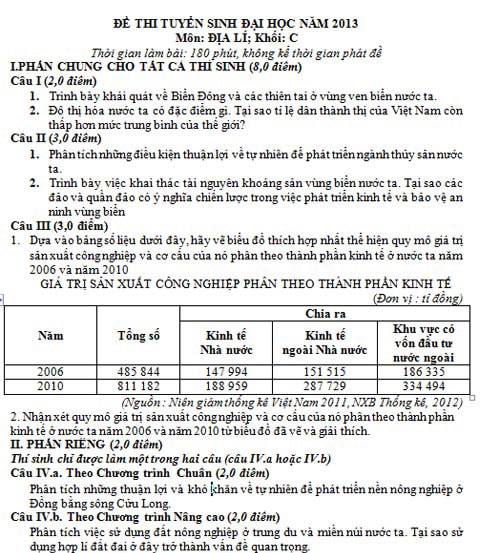
1. Draw a chart
* Process data table into percentage (%)
We have: Industrial production value by economic sector (unit: %)
Year | Total | Divide | ||
State economy | Non-state economy | Foreign invested economy | ||
2006 | 100 | 30.5 | 31.2 | 38.4 |
2010 | 100 | 23.3 | 35.5 | 41.2 |
* Calculate the radius of the circle:
We agree as follows:
The total in 2006 is the area of the circle in 2006: S1
The total in 2010 is the area of the circle in 2010: S2
The radius of the circle in 2006 is R2006, take it as 1.0 cm.
Calculate the radius of the circle in 2010 is R2010
Applying the formula for calculating the area of a circle S= πR2 we will calculate the radius of the circle in 2010.
* Draw a pie chart.
Note: The radius of the 2 circles is different, the chart has full legend and chart name.
2. Comments
* Industrial production value by economic sector of our country increased from 2006 to 2010 (evidence)
The industrial production value of our country by economic sector has changed in economic sectors, in which the strongest increase is in the non-state economic sector and the foreign-invested sector (increased 1.7 - 1.8 times).
* The economic structure has positive and appropriate changes:
In the structure of industrial production value classified by economic sector of our country, the state economic sector tends to decrease (evidence).
The structure of industrial production value by non-state economic sector and foreign-invested increased (evidence).
* This is consistent with the laws and policies of economic development of our country in the current and upcoming period: although the State economic sector has decreased in proportion, it still plays a leading role in the economy.
Question IV.a. Natural advantages and disadvantages for agricultural development in the Mekong Delta
Favorable:
* Fertile land, including 3 main groups:
Sweet alluvial soil: Covers an area of 1.2 million hectares, accounting for more than 30% of the delta's natural area, distributed in a strip along the Tien and Hau rivers. Favorable for growing rice and crops.
Acid sulfate soil: has the largest area with more than 1.6 million hectares (accounting for 41% of the delta area), including high acid sulfate soil, low and medium acid sulfate soil. Distributed in Dong Thap Muoi, Long Xuyen Quadrangle and the central lowland of Ca Mau peninsula.
Saline land with nearly 750,000 hectares accounts for 19% of the delta area, distributed in the coastal belt of the East Sea and the Gulf of Thailand.
Acid sulfate soil and saline soil are favorable for growing short-term industrial crops, aquaculture, etc.
* Climate: equatorial, high temperature regime, average sunshine hours are 2200 - 2700 hours, stable; high rainfall (1300 - 2000 mm), concentrated in the rainy months, favorable for agricultural production development.
* The dense network of rivers and canals facilitates transportation, trade, and the provision of irrigation water for agriculture (the canal system and the Mekong River).
* Has a long coastline, extremely rich marine resources with many fishing grounds, shrimp grounds... and more than half a million hectares of water surface for aquaculture.
Hard:
Water shortage in the dry season, the dry season lasts from December to April of the following year.
Most of the land area is contaminated with alum, salt, some types of soil lack nutrients, the soil is too compact, and has poor drainage...
There are also other natural disasters: floods causing inundation, high tides causing saltwater intrusion, tornadoes, hot and humid conditions causing epidemics, mold, etc.
Question IV.b. Use of agricultural land in the midlands and mountainous areas of our country.
Land use here in agriculture is mainly in the form of swidden fields and terraced fields.
Currently, thanks to promoting intensive farming and increasing the number of crops in places with irrigation capabilities (terraced fields), local food security is ensured.
Combined agroforestry production models are becoming popular.
Promoting the development of industrial crop cultivation and large-scale livestock farming with the support of the processing industry is being actively implemented.
The development of industrial and specialty crops will allow the development of highly efficient commodity agriculture and will have the effect of limiting shifting cultivation and nomadic settlement in the region.
The rational use of land here becomes a very important issue, because:
In the midlands and mountainous areas of our country, the area of arable land for agriculture is very small, very steep, easily eroded, and land preparation and irrigation are very difficult.
Cultivable land area is increasingly narrowing due to: erosion, forest burning for farming, environmental pollution, expansion of specialized production areas, construction of social works,... which have made many areas of land fallow again.
This is also the headwaters of most rivers in our country, so land and forests are destroyed, depleting water resources, leading to ecological imbalance.
Land in mountainous and midland areas is an important area, a means of production for mountainous agriculture and forestry, a residential area for ethnic minorities and a place to build national defense and security works for the whole country.
Source: Hocmai Center - NK






