Smoking causes a series of harmful problems for reproductive health.
(Baonghean.vn) - Smoking causes many dangerous diseases for smokers and passive smokers. Smoking also has a great impact on the reproductive health of both men and women.
Smoking reduces fertility in men
One factor that contributes to the reduced fertility of men who smoke is the inability of the body to produce normal sperm counts. Tobacco additives in semen and abnormal dilation of the veins and seminal vesicles reduce sperm count.
For those who quit smoking within 6 months, sperm density will improve. One study showed that compared with non-smokers, sperm density of smokers decreased by 13%.

Smokers have higher levels of white blood cells in their semen even when they do not have an infection. This makes it less likely that a smoker's sperm will reach the ovaries.
There is now some credible evidence that smokers have a higher percentage of abnormal sperm. This can lead to miscarriage, birth defects or complications during birth.
Some studies have found that a higher percentage of sperm in smokers do not move normally. For conception to occur, sperm need to move normally to reach the ovary.
Smokers tend to have lower semen counts than non-smokers. Reduced ejaculate capacity may be due to the effects of nicotine on the nervous system, impairing the nervous system involved in ejaculating.
The second cause may be due to the reduction in the amount of male sex hormones in smokers. The reduction in the amount of male sex hormones leads to a reduction in the amount of semen released each time.
Long-term smoking can lead to impotence or affect the ability to have an erection. Just like the mechanism that causes blood vessel blockage in the heart due to atherosclerosis, smoking is also one of the core causes of atherosclerosis in the blood vessels of the penis, reducing the ability to have an erection.
Smoking affects fertility in women
Women who smoke more than 15 cigarettes a day will take longer to conceive. But women who smoke not only have difficulty conceiving, but also have some difficulty nurturing a fetus. The more a woman smokes, the more her fertility is affected. There are many reasons why the fertility rate of women who smoke tends to be lower than that of women who do not smoke.
Smoking can damage or even destroy oocytes (eggs) and therefore reduce fertility. Smoking changes the levels of some hormones, including estrogen. Therefore, ovulation may not occur normally in smokers.
Some studies have found abnormalities in the function of the fallopian tubes in women who smoke. Hormonal changes lead to changes in the normal functioning of the egg through the fallopian tubes. In some cases, changes in hormone levels can increase the speed at which the embryo enters the uterus. Since timing is important to create a good environment and keep the embryo inside the uterus, if the embryo enters the uterus too early, it can lead to failure because it has not yet firmly attached and can easily lead to spontaneous abortion.
Smoking in women also increases the risk of birth defects. In one study, the risk of birth defects in women who smoke is 2.2 to 4 times higher than in non-smokers.
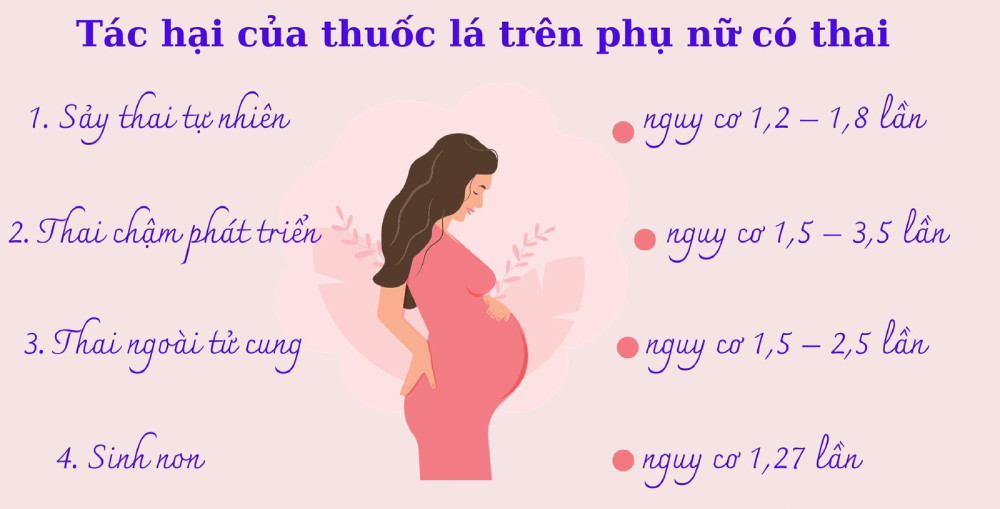
Studies have shown that smokers have a 1.5 to 3.2 times higher risk of spontaneous abortion than non-smokers. Women who smoke may have a reduced ability to sustain a pregnancy.
Smoking tends to lead to early menopause. The primary reason for early menopause is that smoking reduces estrogen levels in women. Although all older women experience a gradual decline in estrogen levels after age 40, women who smoke tend to start menopause 2 to 3 years earlier than non-smokers. Nicotine is thought to play a role in this process.






