Techniques for using slow-release pellet fertilizer for rice
(Baonghean) - In agricultural production, single fertilization and the use of broadcast fertilization and unbalanced fertilization have led to low fertilizer efficiency. Of which, nitrogen is the element that is lost the most.
The efficiency of using broadcast nitrogen fertilizer in conventional rice production is only 30% - 35%; it increases input costs and also pollutes the environment and causes the greenhouse effect; the amount of fertilizer is lost through leaching, evaporation, deep penetration, and microorganisms decomposing into weeds. To improve the efficiency of fertilizer use, especially nitrogen fertilizer on rice, we would like to introduce to you the technique of using slow-release pellet fertilizer (PVNC) for rice:
a. Preparation:
Apply 200 - 300 kg of composted manure per Northern pole (360 m2). Plow and harrow the soil as with normal rice fields. Keep the water level in the field at 3 - 5 cm from planting until fertilizing. (For fields with poor fertility, add 8 - 10 kg of Van Dien phosphate fertilizer or Lam Thao super fertilizer per pole).
b. Rice planting:
- Plant in a straight line.
- For every 8 rows of rice, leave a 30cm wide space (working line).
Plant 1-2 shoots/clump, distance between clumps 18cm (pure rice) - 20cm (hybrid).
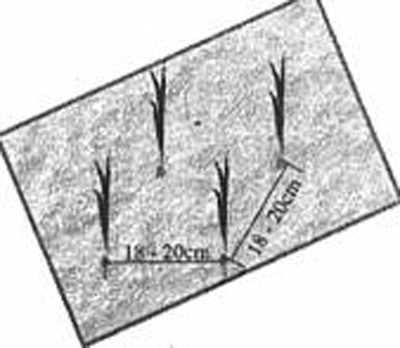
Slow-release fertilizer application techniques
a. Fertilization time: Fertilize immediately after planting, the shorter the fertilization time the better (spring crop 1-5 days after planting, summer crop 1-3 days after planting).
b. Fertilization method:

Place manure between 4 rice clumps, 1 row between 1 row.
Sow 1 pellet of manure 6 - 8cm deep between 4 rice clumps, 1 row apart.
c. Fertilizer amount: Depending on planting density, you can fertilize from 12.5 - 13 kg/Northern sao.
d. Note: Within 20 - 25 days after pushing the manure, do not step on the position where the manure was pushed to avoid displacing the manure pellets.
a. General principles:
- The fields are plowed and harrowed thoroughly, the soil must be soft, weed-free and harrowed flat to facilitate the fertilization process and create conditions for the rice plants to grow and develop well.
- The pellets must be placed deep in the mud layer, preferably at a depth of 6 - 8cm.
- Other technical measures are still implemented as usual.
b. Soil preparation and fertilization time:
- Plow the soil (or use a tiller) the first time so that the straw and plant residues are deep in the soil. If conditions permit, before plowing the soil, spray a microbial solution (EMINA, AZOTOBACTER,...) to decompose the straw and plant residues faster and add nitrogen-fixing microorganisms to the soil.
- For soil with thin arable layer: Apply PVNC fertilizer before the last harrowing (or machine harrowing). After applying fertilizer, harrow (or machine harrow) the soil for the last time and level it. After finishing the soil preparation, proceed to sowing or transplanting.
- For soil with thick cultivation layer, swampy soil: Immediately after the last harrowing, when the mud is still thin, apply PVNC fertilizer. When applying, throw it strongly so that the fertilizer sinks deep into the soil. After applying, level the soil. After leveling, proceed to sowing or transplanting.
Dau Thi Trieu (Anh Son Agricultural Extension Station)

.png)






