Mastering Windows Environment Variables: Optimizing Command Line Efficiency
Discover how to edit environment variables and Path variables on Windows 10/11 to shorten commands, run applications faster, and personalize the system.
Editing Environment Variables is an advanced Windows technique that allows users to optimize their workflow, especially when interacting with Command Prompt or PowerShell. By customizing these variables, you can save time typing commands, make scripts cleaner, and manage how the operating system stores files flexibly.
What is an environment variable and why is it important?
Environment variables are dynamic values that contain information about the system environment for running programs. They can specify the location of important directories (such as the Temp folder), provide information about system configuration (such as Windows version, number of processor cores), and can be accessed by any application or script on the computer.
These variables are divided into two types: user variables (applicable only to the current account) and system variables (applicable to all users).
The Power of the Path Variable
Among the environment variables,Pathis one of the most important and useful variables. It defines a list of directories that the system will automatically search when you execute a command in Terminal. For example, you can typenotepadand the Notepad application will launch immediately because the path to its executable file is in the Path variable. Conversely, if you typeChrome, you may get an error because the default Chrome installation directory is not added to Path.
Customizing the Path variable allows you to run command line applications from anywhere without specifying the full path to the executable.
Important Note:Changing environment variables incorrectly can cause system problems. Make sure you understand the impact of the change and test it thoroughly before committing.
Detailed instructions on how to edit environment variables
The process of editing environment variables on Windows 10 and Windows 11 is basically the same, with only a few minor interface differences.
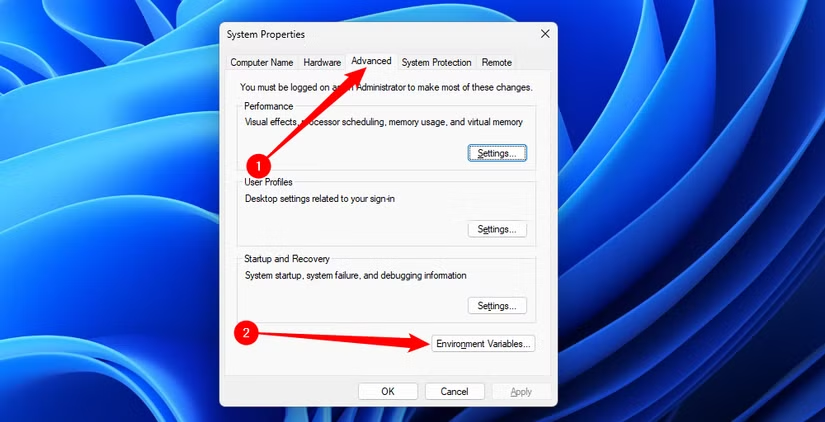
Step 1:Open the System Properties window. Click the Start button, type "environment variables" into the search bar, and select "Edit the system environment variables."
Step 2:In the System Properties window that just opened, click the "Environment Variables..." button.
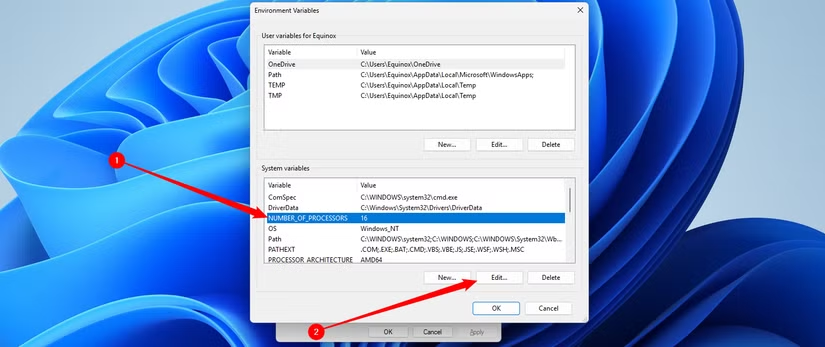
Add or edit a variable
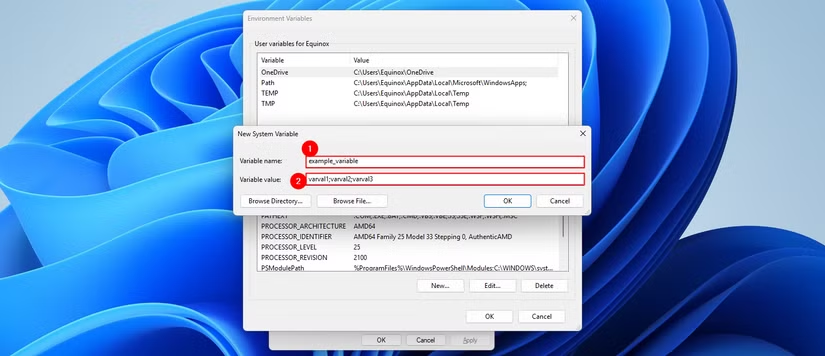
To create a new variable, click the "New..." button in the user variable or system variable section. You will need to provide a Variable name and a Variable value.
To edit an existing variable, select it in the list and click "Edit...". Change the value as desired and click "OK". Some variables can contain multiple values, separated by semicolons (;).
Customize Path variable
Editing the Path variable has a more user-friendly interface. When you select a Path and click "Edit...", a window listing the paths will appear.
- Add new path:Click "New", then paste or type the folder path you want to add.
- Edit:Select a path and click "Edit".
- Erase:Select a path and click "Delete".
Practical example: Integrating FFmpeg into the system
FFmpeg is a powerful command line tool for converting video, audio and image formats. To use FFmpeg conveniently, we can add it to the Path variable.
- Download and unzip FFmpeg:Download the latest version from the FFmpeg homepage and extract it to a permanent location on your computer, for example:
C:\ffmpeg. - Specify the path:The FFmpeg executable is located in the subdirectory
bin. The full path will beC:\ffmpeg\bin. - Add to Path:Open the Path variable editing window as instructed above. Click "New" and paste the path
C:\ffmpeg\binenter. - Confirm:Click "OK" on all windows to save changes.
Once done, you can open a new Command Prompt window and type the commandffmpegfrom any directory to check. This eliminates the need to manually point to the executable each time it is needed.
Mastering environment variables, especially Path variables, is an important step in turning Windows into a highly personalized and efficient work tool, increasing productivity for developers, system administrators, and power users.


