During the rainy season, be careful with skin diseases caused by insects.
Insect contact dermatitis is a common disease that occurs during the rainy season and has sometimes become an epidemic, causing confusion and anxiety for patients.
The cause and transmission of this disease is due to insects, scientific name Paederus.
The causative agent of the disease
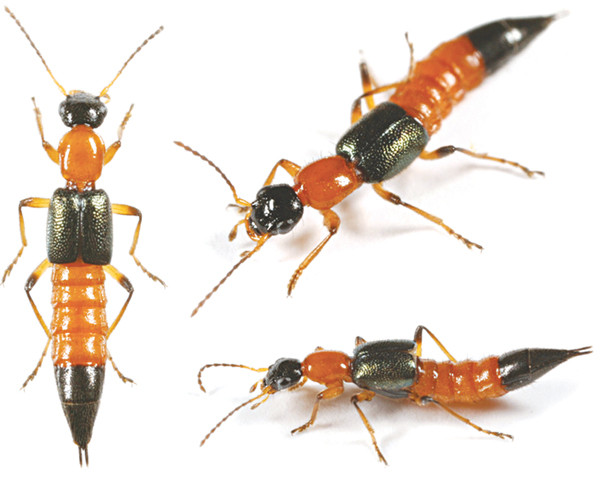
Paederus is a type of insect belonging to the beetle family (Ataphylimidac) with about 1,400 - 20,000 very similar species commonly found are P. literalis, P. fuscipes, P.caligatus and Paederus has a long body, 7 - 10 mm in length, at first glance it looks like an ant, so our people often call it by many different names: wild ants, needle ants, squint ants, rice ants, chin pairs, caged ants, curved-end ants...
This ant has 3 pairs of segmented abdominal legs, one of which is red. It flies and runs very fast. It often lives on the edges of rice fields around stubble, in lawns, near water bodies, vegetable fields, in places under unfinished construction... In the body of the ant, there is Pederin, which causes skin burns, similar to Cantadine in caterpillars and phosphorus in insects.

After days of heavy rain and floods that flooded fields and ponds, ants flew into houses with insects and lights. People working under the lights had insects fall on their necks, faces, and bodies. They accidentally raised their hands to crush the insects, and the Pedirin in the insects stuck to their skin.
Sometimes insects fall into the pool, bathtub or stick to towels or clothes. The patient does not pay attention and rubs the insect, causing blistering dermatitis (there are cases where the patient kills the insect and rubs it on the skin, causing the disease).
Signs of recognition
After contact with insects, the patient feels itching, burning, and heat at the site. After 6 - 12 hours, red, slightly swollen patches appear in streaks, 1 - 5cm in size, 3 - 4mm wide. After 1 - 3 days, red, spotted blisters appear on the skin, then blisters and pus appear.
According to statistics, 100% of cases show signs of redness, swelling and burning sensation at the site; 80% have lesions on the head, neck, face and upper body; 60% have lesions in the morning; 3.82% have swelling and edema of both eyelids. Some cases have symmetrical images that match each other.
Injury progression
Initially, the patient feels pain, slight itching, burning sensation at the skin tightening area, manifested by redness in an area of skin. After 6 - 12 hours, a slightly swollen, red, streaked area forms, on a red background appear large and small blisters with a diameter of 1 - 5mm.
From 1 to 3 days later, blisters and pus blisters appear. At this time, the pain increases and may be accompanied by a feeling of faintness, fever, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and pain in the armpit and groin area corresponding to the injury.
If the injury is near the eyes, both eyes may swell and heal after 5-7 days. In the groin, there may be painful swollen lymph nodes, making it difficult to walk. Blisters and pus blisters develop after 4-5 days, then form a crust and gradually dry. When the crust falls off, it leaves a dark skin mark.
There are cases where the patient has a red spot with small, slightly itchy blisters, the lesions disappear after 3-5 days without forming blisters or pus. During the rainy season, a patient can be infected 2-4 times, in a group there can be 10-12% of people affected, the disease can last 5-20 days.
Principles of injury treatment
If there are only red patches or red spots, the patient only needs to treat at home: use 9% diluted salt water 3-4 times a day to neutralize insect toxins, avoid washing with too much water, avoid scrubbing to cause peeling skin.
If the pain is severe, the patient can go to a specialized dermatology clinic for examination and treatment with specialized medicine for 4-6 days. After treatment, the patient will be cured.
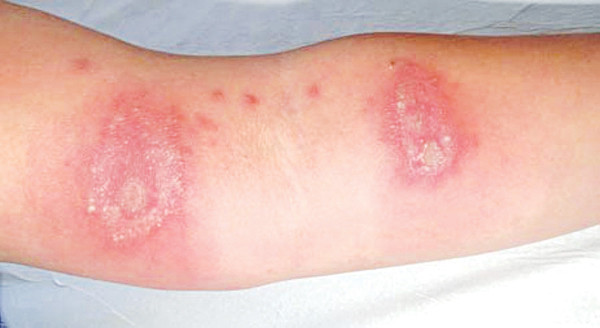
If the infected lesion becomes purulent, use dye solutions: Milian, Methylene Blue, diluted potassium permanganate. After 4-5 days, the lesion will stop being inflamed and the crust will peel off, and antibiotic creams or ointments or corticosteroids will be used. In case of fever with signs of systemic infection, antibiotics can be used in combination with synthetic antihistamines and mild oral corticosteroids.
Disease prevention
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to clear the bushes around the house to avoid the places where insects live. At night, you should close the doors and sleep under a mosquito net. When drying clothes, you should take them in early to avoid insects hiding in them. If you see insects crawling on your skin, you should use paper or blow them away. Do not catch, rub or kill them, causing damage and more contact with the secretions on the skin.
When detecting insects near the living area, close the door or use a very small net to prevent insects from entering the house or room. Before going to bed or before getting dressed, check the bed, blankets, and clothes before using them. If you detect insects on your clothes, do not wear them anymore and wash them.



.jpg)