Who is at risk for kidney stones?
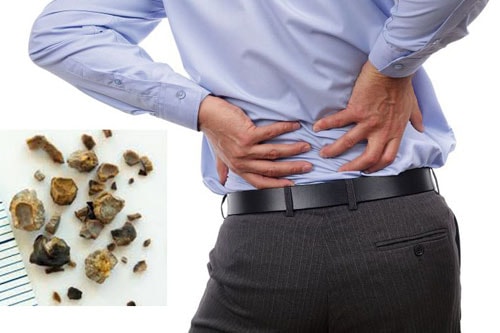
Kidney stones are the deposition of minerals in the kidneys that form stones over time. Stones can rub against the urinary tract, causing back pain and blood in the urine.
Who is at risk for kidney stones?
People who have the habit of holding urine (urinating less), drinking less water or losing a lot of water through sweat. Normally, the amount of urine in 24 hours in adults is about 1.5 liters. When the 24-hour volume is reduced by half, the risk of kidney stones will double.
People who eat a diet high in meat, high in salt, drink a lot of milk, use a lot of vitamins C and D, are exposed to a lot of sunlight, are overweight, obese, or are addicted to alcohol, will have a high risk of getting the disease.
Patients who have to lie immobile for a long time such as spinal injuries, fractures, paralysis, multiple trauma, people with hyperparathyroidism, other diseases that cause urinary obstruction such as prostate tumors, urethral strictures due to trauma or congenital. People with a family history of kidney stones, urinary stones (diseases with genetic factors) will have a higher risk of developing the disease.
 |
Risk of disease related to occupational factors:
Workers who work in hot environments are at high risk of developing kidney stones. This is because excessive sweating reduces the amount of urine excreted by the kidneys.
Workers exposed to cadmium (metal processing workers, paint manufacturers, battery manufacturers, etc.) and other toxic substances are also at high risk of kidney stones.
What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
Pain: Severe pain, pain usually starts from the ureter points, spreads along the ureter path down to the pubic mound, sometimes pain also penetrates the hips, back, sometimes nausea and vomiting. Dull pain, occurs in cases of medium or even large stones but located in the renal pelvis.
Hematuria: This is a common complication of kidney and urinary stones, especially when the stones are moving inside the ureter, causing pain and hematuria.
Painful urination, frequent urination, pus in urine: When there is a urinary tract infection, recurring many times, stones may be passed in urine.
Fever: High fever, chills accompanied by symptoms of hip and back pain, painful urination, frequent urination, and pus in urine are signs of acute pyelonephritis.
Signs of urinary tract obstruction: Intermittent or complete urinary obstruction.
How to prevent kidney stones?
Drink plenty of water to urinate a lot (about 10 cups/day, equivalent to 2.5 liters of water), so the risk of stones recurring is low.
Treatment of urinary diseases such as infections and obstructions should be performed properly by specialists because urinary infections are one of the main causes of stones.
Do not use too much vitamin C, D. A moderate calcium diet, reducing salt, protein and foods high in oxalate, increasing exercise, and reducing obesity will reduce the risk of kidney stones.
Workers in hot conditions must compensate for the amount of water lost through sweat. Depending on each specific case, the amount of water to be replaced is different. On average, after 20 minutes of work, you should take a break to drink water once (even if you do not feel thirsty) for a total of about 1 liter of water per hour of work. Drinking water should be cooled to about 10 - 15 degrees Celsius. In addition, you need to have reasonable working and resting time, avoid holding urine for too long during work time.
People working in contact with toxic substances, in addition to measures to minimize exposure, should have regular health check-ups to detect kidney stones early.
According to VNN
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|

