Musculoskeletal diseases in children need special attention
Parents should not be subjective when their children have persistent knee pain, hip pain or spinal pain.
According to Dr. Pham Quang Thuan, Head of the Department of Internal Medicine, Musculoskeletal, Vietnam Sports Hospital, there are many musculoskeletal diseases in children that parents need to pay special attention to in order to avoid dangerous complications later:
1. Muscle pain, growing bone pain
This is a very common musculoskeletal disease in children, commonly in children from 6 to 12 years old. The disease progresses because the child is overactive or grows too fast, the bones develop slowly and cannot keep up with the development of the muscles. Symptoms of the disease are persistent leg pain and difficulty moving. Children often have pain in the evening after a day of activity.
Children between the ages of 12 and 16 also frequently suffer from Osgood-Schlatter disease, which causes pain and swelling in the tibial tuberosity, just below the kneecap, due to overuse of the joint. The disease causes inflammation of the tibia just below the knee, where the broad ligament attaches. Typical signs include muscle tension, pain, and swelling just below the knee, which is often worse with movement.
If the child has the disease, he or she should stop all physical activities until the knee joint is completely healed. In cases of mild pain, he or she can continue to move but at a lighter level. Osgood-Schlatter disease is only temporary, and the pain will go away after the child's bones stop growing in adulthood.
2. Rheumatism
Rheumatism is common in children 5-15 years old, the disease develops strongly in winter, or every time the weather changes.
The disease usually begins with acute pharyngitis, fever and sore throat. After 7-10 days, the patient may have high fever, fatigue, paleness, swelling, redness and pain in large joints such as the shoulder and hip joints... lasting about 5-7 days and then recovering, leaving no sequelae.
Once acute rheumatic fever is diagnosed, the child must receive prophylactic treatment to prevent recurrence and avoid cardiovascular damage.
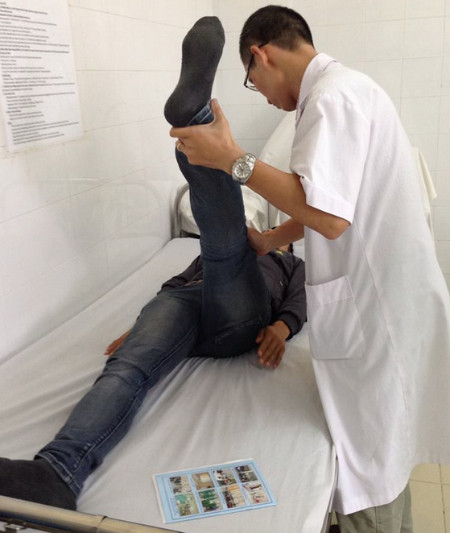 |
| Dr. Pham Quang Thuan examines the patient's musculoskeletal condition. |
3. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head
This disease can occur at any age and is the most common cause of hip joint disease.
The mechanism of femoral head necrosis is often due to lack of blood supply after displaced femoral neck fracture or hip dislocation; vascular occlusion due to hip dislocation, increased pressure in the bone, poisoning... In addition, favorable factors that cause the disease to progress include long-term use of steroids, alcoholism, smoking, chronic liver and kidney disease...
Depending on each case, doctors will prescribe medication, electrical stimulation, or perform decompression drilling, bone grafting, and axis correction osteotomy... When the disease is in the late stages, doctors will have to replace the artificial hip joint to help the patient relieve pain, improve hip function, and walk and move well.
4. Ankylosing spondylitis
Children from 8 to 15 years old are very susceptible to this disease. Symptoms of the disease are back pain, stiff back, limited movement, difficulty walking. The patient has fever, weight loss, fatigue. When the disease is obvious, the lumbar spine hurts a lot, the pain is often worse at night, the spine is stiff, especially in the early morning when waking up.
When seeing these symptoms in children, you should take them to an orthopedic specialist so that the doctor can prescribe a treatment plan as soon as possible. If the disease progresses over time, there may be accompanying internal organ damage. After a period of time, the entire spinal column will no longer be able to move, the patient may have a hunchback, scoliosis, cannot stand up straight, cannot squat. The disease can also cause complications such as respiratory failure, chronic heart failure, pulmonary tuberculosis, and paralysis of the lower limbs.
In the early stages of the disease, doctors may prescribe medication combined with physical therapy to minimize the impact on the movement of the spine and joints. When the disease has developed too severely, in addition to medical treatment and physical therapy, surgery is a measure that can improve the function and appearance of the patient.
5. Spinal deformity (school)
Often occurs in school-age children. The cause may be due to the child wearing a backpack that is too heavy, sitting in the wrong posture...
Symptoms of the disease are easy to detect such as walking to one side, sitting crookedly, and frequent back pain.
Parents should pay attention to their children's sitting posture and not let them carry too many heavy loads on their shoulders to avoid spinal deformities, which can lead to bad posture later on. Children with spinal deformities may need to wear a spinal brace to regain a straight back.
According to Vnexpress






