Successfully designed robotic arm for surgery and remote mine clearance
After designing and testing, perfecting the control algorithms, the actual test results of the robotic arm were very impressive.
The Department of Science and Technology (DOST) of Ho Chi Minh City has accepted the project "Research on design and manufacture of a robot model that copies motion and force feedback" led by MSc. Nguyen Ngoc Diep, lecturer at the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Ho Chi Minh City University of Industry.
Robot arm problems
One of the important contents in the acceptance session of the topic is the ability to remotely control this robot arm. Or in other words, how to synchronize the "feeling" of the secondary robot arm (slave, directly interacting with the object) with the primary arm (master, controlled by the person).
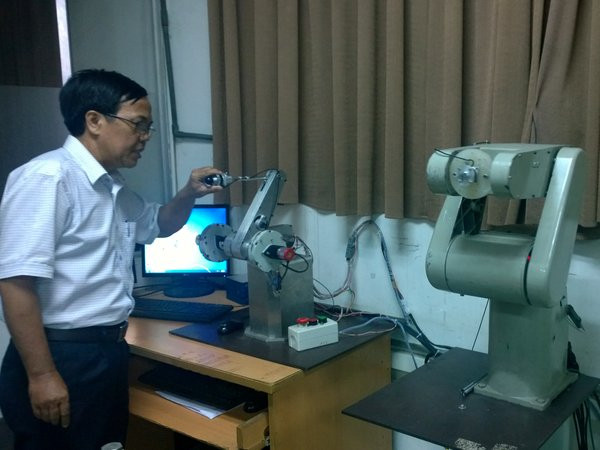 |
| Robot arm problems |
Remote control is an indispensable part of Industry 4.0. Accordingly, workers or engineers do not need to directly interact with the production line but can be dozens or hundreds of meters away to control the equipment.
The purpose of this, in addition to saving costs and travel time, also contributes to minimizing risks for producers if the working environment is highly hazardous (contains toxins, radiation, unsafe labor safety...).
Nowadays, remote control has been applied in many fields such as remote surgery, mine clearance engineering... and even controlling robots to research Mars.
However, to be able to control the remote accurately, to operate as desired by the operator is not a simple matter. If the operator does not know that the slave arm is overloaded and continues to command to press down, it can cause damage to the slave arm.
Besides, signal delay, moment deviation, prestress... must all be at the lowest level.
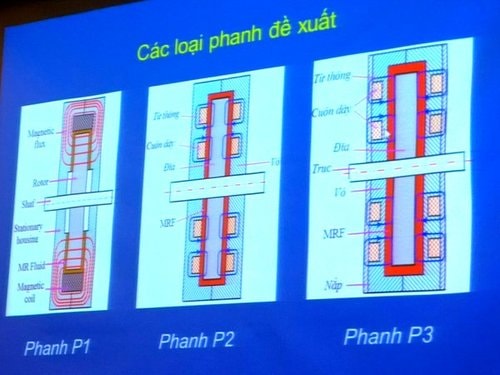 |
| Structure of 3 MRF brake models by Master Diep. |
To solve the above problems, a braking system used to control the movement of each arm is the answer. This is also the main content of the research topic that Master Diep set out to solve - to research, design and manufacture a suitable type of brake to be used as a robotic arm.
The braking solution that MSc. Diep chose is called MRF. MRF (Magnetorheological fluid) is a special type of liquid whose viscosity changes when there is a change in the magnetic field passing through it. At a sufficient magnetic field strength, MRF almost solidifies and can be used as a brake for mechanical parts.
According to the proposal of Master Diep, there are 3 MRF brake models that can be used to make robotic arms including P1, P2 and P3 brakes. In which, P1 has a magnetic coil located at the top of the brake disc, P2 has a coil placed inside the 2 sides of the disc, P3 has a coil placed outside the 2 sides of the disc.
 |
| P2 and P3 brakes have the best performance, meeting the design target (> 10 Nm). |
The results of computer simulation as well as the experiment of Master Diep show that although the P1 brake is light, it has the lowest efficiency (Nm). The 2 models P2 and P3 are heavier but have efficiency that meets actual needs.
One thing to note is that although the P2 brake has the best performance/weight ratio, because the coil is inside, it will be more complicated to repair and maintain. Therefore, MSc. Diep chose the P3 brake because it balances cost and performance.
Design and manufacture
Choosing the brake is only the first part of the problem. The next problem is how to design the robot arm, what material to choose, angle sensor, moment sensor, control chip... MSc. Diep said that the master-slave robot arm system is a 3-degree-of-freedom system (3 rotation axes), with a maximum load of 2.5 kg. In which, the slave arm has an operating range of axis 1 angle from 0 - 270°, axis 2 angle from 0 - 100° and axis 3 angle from 0 - 180°, maximum reach of 0.7 meters, maximum speed at the end point of 0.5 m/s.
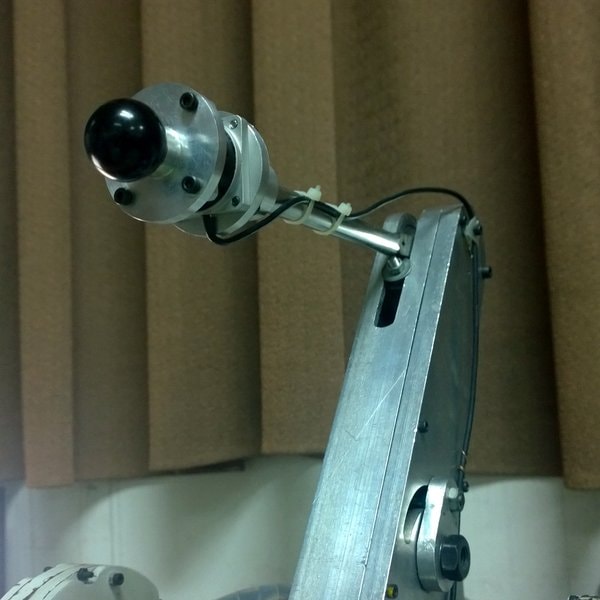
To save costs, the master arm was reused from the "body" of the Fanuc LR 100i arm. The MSc said that only the master shell was "reused", the remaining components (sensors, brakes, encoders) were all designed and newly installed by the research team.
 |
| Structure of slave robot arm by MSc. Diep |
Finally, a "translator" control system is needed for the two arms to "understand each other". The system is proposed by the research group of Master Diep, including 3 LBJ-096-2000 angle measuring encoders, 2 OMD 30EF 3-dimensional force sensors and 3 AZM 350 torque sensors. The system also has 3 brake control devices, 3 HC-KFS 23 motors as AC servo motors and NI PCI 6289, 6225 control cards to measure input/output signals at each arm.
Impressive results
After designing and testing, perfecting the control algorithms, the actual test results of the robotic arm were very impressive.
The project acceptance council of the Department of Science and Technology witnessed with their own eyes the almost trouble-free operation of the pair of arms above.
 |
 |
The movements controlled by the slave arm are reproduced exactly on the master arm. Testing of the "feel" of tension is also carried out with simulated springs mounted in all three horizontal, vertical and diagonal directions.
It can be said that Master Diep's group has completely succeeded in creating a third-order robotic arm in force feedback.
 |
| Force feedback experiments in all three directions horizontal, vertical and diagonal gave good results. |
In a further goal, MSc. Diep proposed that the Department of Science and Technology allow the group to increase the number of degrees of freedom to level 5 (DOF), allowing the arm to perform more complex operations.
The team also hopes to receive more investment to apply smarter algorithms, add active feedback, combine MRF with pneumatic feedback devices, to further enhance the applicability, especially in the medical field, which requires the ability to simulate the feeling of the patient's skin almost realistically.
According to Discovery
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|