The 'culprit' is less noticed but has a high risk of causing stroke
Besides common risk factors of stroke such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, etc., some lesser-known and often overlooked risk factors are silent threats in the development of stroke.
1. Hidden risks that are rarely noticed cause stroke
-Migraine headache:Studies have shown that people who suffer from migraines are at increased risk of ischemic stroke. Managing migraines and seeking medical advice is essential for those at risk.
- Air pollution:Has a profound impact on cardiovascular health. Small particles and pollutants can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation and atherosclerosis, ultimately increasing the risk of stroke.
-Depression and chronic stress:Mental health is an integral factor in stroke risk. Depression and chronic stress can lead to all of the well-established stroke risk factors.
-Inflammation:Conditions like atherosclerosis, lupus, and people with chronic inflammatory diseases must manage their health and take preventative measures.
Additionally, sleep apnea can lead to a lack of oxygen in the brain, increasing the risk of stroke over time. Disrupted sleep and low oxygen levels can contribute to high blood pressure and other cardiovascular problems.
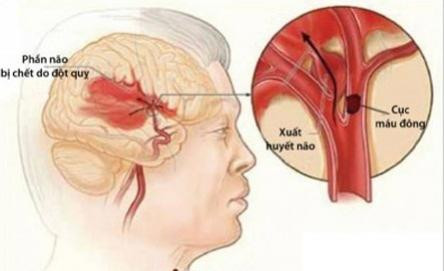
A stroke can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
2. Early signs of stroke can appear at night
A stroke is a potentially fatal medical condition caused by an interruption of blood supply to the brain. This can happen when a blood vessel bursts and bleeds into brain tissue or when a blood vessel becomes blocked in the brain (a blood clot). Brain cells begin to die when blood flow is interrupted, depriving them of oxygen and nutrients.
Some early signs of stroke:Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body;Sudden confusion;Difficulty speaking or understanding speech;Sudden difficulty seeing in one or both eyes;Sudden trouble with walking, balance, or coordination;Sudden severe headache with no known cause;Sudden dizziness;Loss of balance or coordination;Sudden chest pain, upper body pain;Chronic headaches…
Millions of nerve cells die every minute before blood supply is restored. This loss is permanent, so early recognition of symptoms is crucial. Prompt intervention can quickly restore blood flow to the brain and limit brain damage.
3. What to do to prevent stroke?
You can reduce your risk of stroke by making healthy changes. Here are the most important steps you can take to reduce your risk of stroke:Keep blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels normal.If you smoke, quit.If you have heart disease, get treatment..Maintain a healthy weight.Be physically active regularly.Eat healthy…
Making these healthy changes can also help reduce your risk of heart disease and diabetes (risk factors for stroke.).
Reducing sitting time improves glucose control and blood flow, while engaging in physical activity, even light daily activities such as cooking and shopping, also reduces the risk of death and prevents heart disease and stroke./.



.jpg)
-6c936385358262921c0884226b06c05a.jpg)
.jpeg)

