The Future of Human-Machine Interface Technology in Asia-Pacific
As the Asia-Pacific region is witnessing an explosion of technology and innovation, human-machine interface (HMI) technology is increasingly becoming a core element, driving the development of many industries.
With the rapid development of technology, the future of HMI technology in Asia Pacific promises to be even more groundbreaking. From applications in healthcare, where artificial intelligence (AI) helps doctors diagnose diseases more accurately, to smart factories with robots collaborating with humans, or smart cities using extended reality (XR) to create immersive experiences, HMI will continue to reshape our future.

Developing smart, intuitive and easy-to-use HMIs will be key to unlocking the full potential of technology and reshaping the way humans interact with machines. The global HMI market is witnessing explosive growth, from $5.8 billion in 2023 to an impressive $11.37 billion by 2030, indicating an increasing demand for intelligent and flexible interfaces.
What is HMI technology?
HMI is a technology that allows operators to interact with machines or systems more easily. In the industrial world, HMI acts as a bridge between operators and industrial machines, allowing control, monitoring, and visualization of data to optimize production processes.
HMIs contribute to productivity by providing intuitive interfaces that streamline operations, reduce human error, and speed up task completion. With features such as customizable dashboards and predictive analytics that provide quick access to critical information and real-time control, HMIs empower operators to make informed decisions quickly and optimize production processes.
How are technology trends shaping the future of HMI?
Asia-Pacific countries are taking a leading role in shaping the future of HMI through groundbreaking concepts such as Society 5.0 and Industry 5.0. Japan, with its Society 5.0 vision, is leading the way in building a super-smart society where AI, IoT and robotics come together to solve social problems and create human-centric solutions.
Industry 5.0 takes human-machine collaboration to the next level, especially in manufacturing. Robots and humans work together, leveraging each other’s strengths, with the precision and speed of machines complementing human creativity and problem-solving abilities.
Industry 5.0 is a huge leap forward from Industry 4.0, placing people at the center and focusing on sustainability. Rather than focusing solely on automation and efficiency, Industry 5.0 encourages collaboration between humans and machines, leveraging artificial intelligence and robotics to improve the quality of life of workers and create a more flexible working environment.
While Society 5.0, a Japanese initiative, aims for a super-smart society that connects cyberspace and physical space to address social issues holistically, Industry 5.0 focuses specifically on transforming the manufacturing industry. Both are human-centric and aim for a sustainable future, but Industry 5.0 is a key part of realizing the vision of Society 5.0.
Healthcare in Asia Pacific is undergoing a revolution thanks to the rapid advancements in AI and robotics. Surgical robots not only increase precision but also reduce errors, while telepresence robots open the door to remote medical services, providing better access to healthcare for those living in remote areas. Japan and South Korea are leading the way in the application of robotic technology in healthcare, creating fundamental changes in the way we care for our health.
In the healthcare sector, Asia-Pacific is undergoing a major transformation due to advances in AI and robotics. Robots are assisting in surgeries, providing precision that reduces human error, while telepresence robots enable remote healthcare services, making diagnosis and treatment more accessible to remote and underserved populations. Countries like Japan and South Korea are particularly advanced in incorporating robots into their healthcare systems, revolutionizing patient care and medical practices.
AI is revolutionizing HMIs in the region, delivering highly personalized experiences. AI algorithms enable machines to learn and adapt to individual user preferences, creating more intuitive and relevant interfaces. From everyday tech devices to smart cities, personalization is becoming the new norm.
In countries like China and Singapore, where smart city initiatives are gaining momentum, this trend is expected to spur the development of more responsive consumer technologies and public services.
AI-powered personalization is one of the most transformative trends, allowing HMIs to adapt to user behavior, providing predictive and personalized experiences. China-based Baidu's AI-powered DuerOS platform, used in smart speakers and home appliances, enables intuitive voice interactions.
Another important trend is the rise of touchless and gesture-based interfaces, fueled by the COVID-19 pandemic. These interfaces are becoming popular in industries such as automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics.
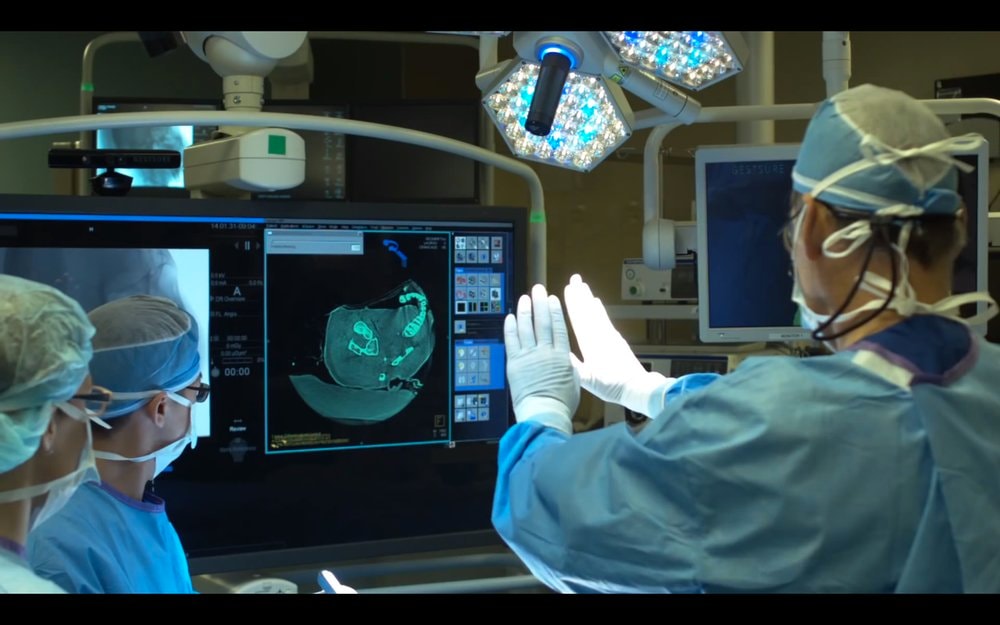
In Japan, Fujitsu has developed gesture control systems for operating rooms that allow surgeons to interact with medical images without touching surfaces, reducing the risk of contamination. Additionally, voice-activated HMIs are transforming consumer electronics, with Samsung’s Bixby assistant leading the way in integrating voice commands into smartphones, TVs and home appliances across the region.
Advanced technologies like brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and biometric emotion recognition are pushing the boundaries of human-machine interactions. BCIs, like Neuralink’s neural signal technology, allow users to control machines directly with their minds, opening up new possibilities for people with disabilities.
In addition, the emergence of driver emotion recognition technology developed by the US technology company Affectiva to monitor the driver's stress and fatigue levels to adjust settings and improve safety. Notably, the global biometric systems market size is expected to increase from 42.9 billion USD in 2022 to 82.9 billion USD in 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.1%.
Additionally, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies are also revolutionizing HMIs by creating immersive environments for industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and education. Boeing's AR-enabled HMI, used in aircraft assembly, reduced error rates by 50% and assembly times by 25%.
The harmonious combination of voice, touch, gestures and intuitive interface has created a comprehensive and seamless user experience. Xiaomi's smart home ecosystem, supported by the platform artificial intelligence of things (AIoT), has taken full advantage of these interaction methods, providing users with unprecedented convenience and flexibility.
As these technologies evolve, HMIs will continue to deliver more adaptive, contextually aware, and immersive experiences across many industries.
What role does 5G technology play in the future of HMI development?
The combination of AI and 5G technology is expected to serve as the backbone for the future of HMI. The speed and low latency provided by 5G networks enable real-time interactions, making advanced applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery possible.
China is leading these advances, with companies like Huawei developing 5G-enabled AI applications, including remote surgical systems that allow for real-time operations over long distances. These initiatives are part of China’s broader AI and 5G strategy, which is revolutionizing smart factories and manufacturing through advanced robotics and automation, enabling faster and more precise production.
In South Korea, mobile carriers SK Telecom and KT Corporation are pushing the boundaries of AI and 5G, particularly in smart cities and transportation. SK Telecom’s AI-powered 5G systems for autonomous vehicles enable real-time communication between vehicles and their environments, enhancing safety and traffic management. At the national level, Korea’s Digital New Deal is building a comprehensive AI-based 5G infrastructure, enabling real-time HMI applications across industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and smart grids.

Photo: Internet
Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative is another example of how AI and 5G are being used to enhance HMIs in public services and urban infrastructure. In partnership with Singtel, the government is using 5G networks to power AI-enabled smart transportation systems, autonomous vehicles, and telemedicine, enabling real-time interactions that improve efficiency and safety.
The powerful combination of AI and 5G technology is revolutionizing the future of HMI across Asia Pacific, opening up new possibilities for industries and enhancing user experiences.
Challenges in implementing advanced HMI
Despite the many benefits, developing advanced HMIs in the Asia-Pacific region also poses significant challenges, particularly in balancing convenience with issues of ethics, privacy and accountability.
For example, AI systems like those in self-driving cars or healthcare robots raise difficult questions about liability. Who is responsible when these systems cause errors or accidents? This is one of the major challenges facing the industry.
Particularly worrying is the fact that AI interfaces collect large amounts of user data, raising serious privacy issues. User consent, data security, and the risk of misuse of personal information become top concerns, especially in the context of increasingly widespread surveillance systems.
Another key challenge is the technology gap and infrastructure disparities across the region. While technologically advanced countries such as Japan, South Korea, and China are leading the way in adopting robotics and AI, other developing countries are lagging behind due to inadequate infrastructure. Lack of access to high-speed internet and modern hardware in some areas slows the adoption of next-generation HMIs, creating a digital divide in the region.





