How dangerous is Whitmore disease?
(Baonghean.vn) - Treatment is long and costly, so many patients give up. This is also one of the reasons leading to treatment failure and high mortality rate due to Whitmore.
Not uncommon
On the afternoon of September 16, the leader of Nghe An Obstetrics and Pediatrics Hospital said that recently, the hospital has discovered and treated 4 cases of Melioidosis, also known as Whitmore's disease. However, these are not the first cases of this disease. In 2017, we treated one case. Last year, there were 3 cases," the hospital leader told a reporter from Nghe An Newspaper.
These cases were all in the condition of parotid abscesses and inflammation of the parotid gland when they arrived at the hospital. Their condition was already severe because they had been treated at home like mumps. However, when the doctors took pus cultures and did blood tests, they were found to be positive for Whitmore.
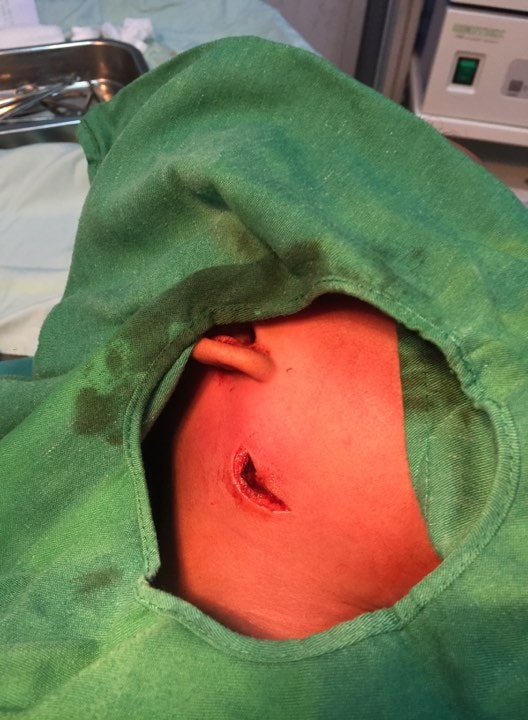 |
| A young patient is being treated at Nghe An Obstetrics and Pediatrics Hospital. |
According to doctors, Whitmore is an infectious disease caused by the Gram-negative bacteria Burkholderia pseudomallei (formerly known as Pseudomonas pseudomallei) that causes blood infection.
The disease has no obvious symptoms and is easily confused with many other diseases, but can cause rapid death. The mortality rate of Whitmore disease can be up to 50% - 60%. Currently, it is the rainy season, a favorable time for Whitmore bacteria to develop.Whitmore bacteria commonly live in mud and water.
The clinical symptoms of the disease are also very vague, diagnosis is very difficult, so it is easily misdiagnosed as pneumonia, soft tissue skin infections, bone and joint infections, bacteremia caused by staphylococcus, streptococcus...
Even if a diagnosis of Whitmore's disease is confirmed, treatment is extremely difficult. Patients usually have to take high doses of intravenous antibiotics continuously for at least 2-4 weeks, followed by maintenance antibiotics for about 3-6 months.
If not treated with the right dose, right regimen and close monitoring, the disease can easily recur, health will gradually deteriorate and death can still occur even after a correct diagnosis.
The treatment is long and expensive, so many patients give up. This is also one of the reasons leading to treatment failure and high mortality rate due to whitmore.
People are usually infected by contact with contaminated soil through skin abrasions, and may also inhale contaminated dust. Infections are common during the rainy season.
Meanwhile, tThe most common symptom of this disease comes from an infection in the lungs, where a pus-filled cavity (pulmonary abscess) can form.The condition can range from mild to severe bronchitis or pneumonia. Patients experience fever, headache, loss of appetite, cough, chest pain, and muscle aches.
In addition, the disease can also manifest as localized infections on the skin (cellulitis) accompanied by fever and muscle pain.Bacteria enter the body through the skin or are inhaled through the respiratory tract, causing inflammation in the central nervous system, parotid glands, bones and joints, causing abscesses in the liver and spleen, genital tract infections, skin infections, and skeletal muscle infections.
The disease can spread from the skin into the blood causing bacteremia, or progress to a chronic form of melioidosis that damages the heart, abdominal aorta, brain, liver, kidneys, joints, and eyes.
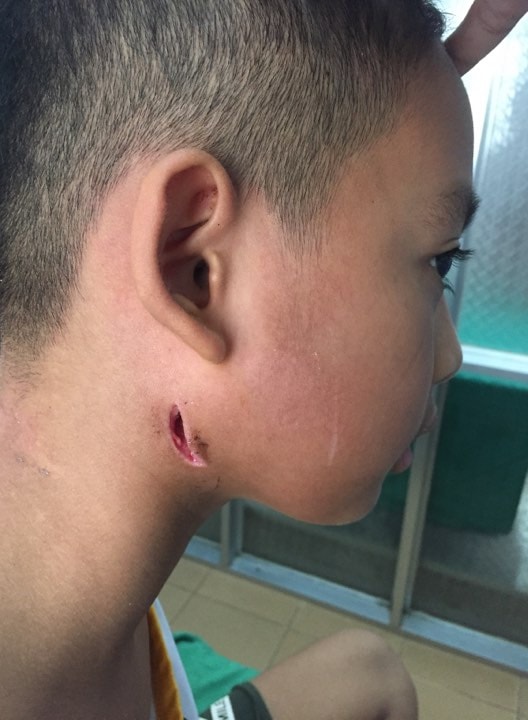 |
| Currently, there is no vaccine or specific method of preventing Whitmore disease. |
How to treat?
Currently, Whitmore disease has no vaccine and no specific prevention method, while the disease is easily transmitted through contact with bacteria carrying the disease through scratched skin, the respiratory tract, or eating and drinking.
Treatment includes antibiotics and surgery depending on the location and severity of the disease.For more severe patients, combination treatment with two of these antibiotics may be required for up to 12 months.
If pulmonary melioidosis is present, and if cultures remain positive after 6 months, lobectomy to remove lung abscesses should be considered.
To prevent this disease, doctors recommend that people who work in contact with soil and water must have protective equipment. If there are scratches on the skin, they need to be treated early and thoroughly.
People with diabetes, lung disease and chronic kidney disease are at risk of contracting this disease with diverse clinical manifestations: high fever, muscle pain, skin infections, muscle abscesses, liver and spleen abscesses, pneumonia... so they need to go to medical facilities for early diagnosis.
In areas where melioidosis is endemic, people with weakened immune systems (such as AIDS, cancer, chemotherapy patients...) should avoid contact with contaminated soil and water, especially in farm areas.









