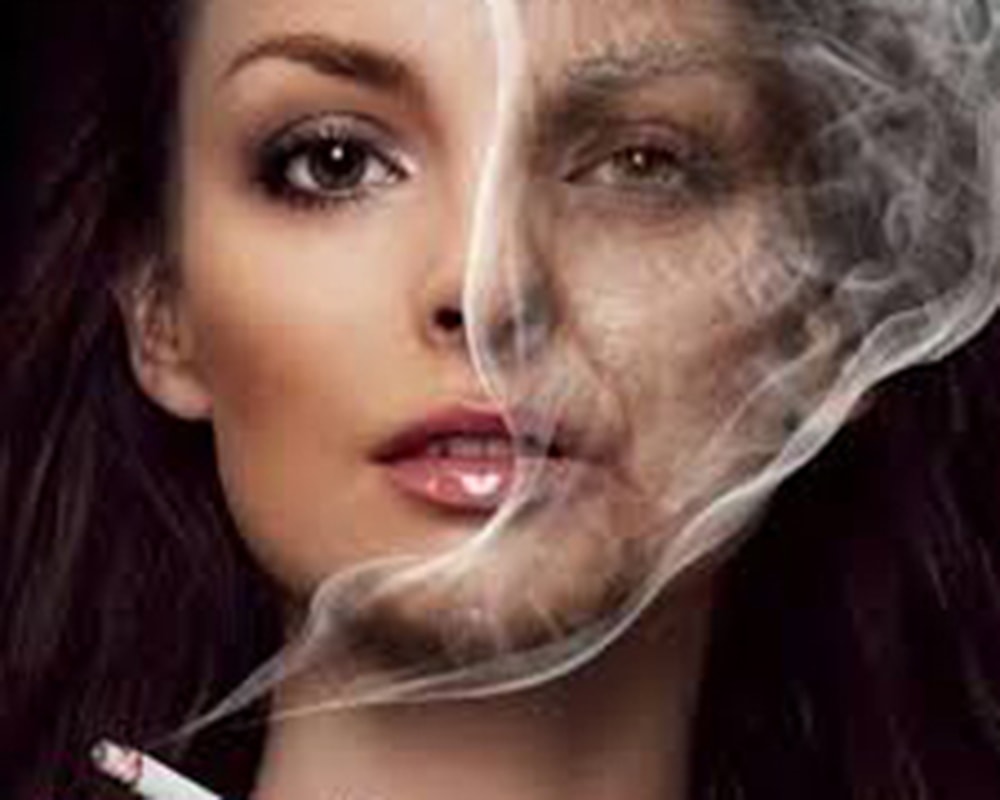
Smoking seriously damages the skin.
Smoking causes facial wrinkles to appear sooner than sun exposure.
Smoking increases skin aging
“Crow’s feet” around the eyes and vertical lines around the mouth known as “smoker’s wrinkles” can appear early. Because smoking damages blood vessels, slowing down microcirculation to the skin, causing poor skin circulation; reduces collagen and causes changes in the skin’s elastic fibers; heat fromcigarettecauses mild facial burns; reduces skin moisture.
Therefore, the face of a smoker will show symptoms such as: many large and small wrinkles, shrunken skin, pale, yellow, gray.

Increased risk of lupus erythematosus
Over the past few years research has shown an increased risk of discoid lupus erythematosus in peoplesmoketenfold increase. One hypothesis is that it increases autoimmune activity by activating B and T lymphocytes. Treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus with Hydroxychloroquine and other drugs is less effective in smoking.
Smoking slows wound healing
Smoking increases the risk of wound infection, graft failure, blood clot formation, and tissue death, including in skin trauma or surgical wounds. The causes may be related to: Decreased collagen synthesis; Vasoconstriction and lack of oxygen to skin cells; Stagnant growth of new blood vessels in the wound.
Psoriasis
Studies show that psoriasis tends to be more widespread and severe in smokers, especially if they also have metabolic syndrome. Pustular psoriasis of the palms/plants is much more common in smokers. This is a cell-mediated immune disease. Smoking is thought to increase the risk of developing psoriasis by affecting the immune system.
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa occurs more frequently in smokers. These abscesses occur in the armpits, under the breasts, and in the groin area. Like common acne, hair follicles become blocked, then become inflamed and form abscesses. Nicotine increases the production of a chemical called acetylcholine around the hair follicles, which promotes overgrowth of the upper part of the follicle and thus causes the blockage.
Smoking increases the risk of skin cancer
Comparing smokers and non-smokers, the risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin was found to be doubled.
Increased severity of viral infections
Including genital warts and virus-related cancers such as cervical, vulvar, and penile cancers.