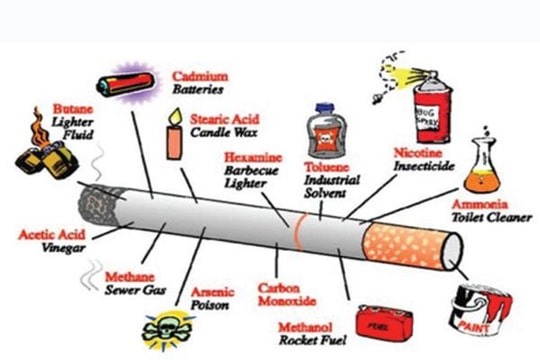
Smoking is a cause of many cardiovascular diseases.
Of all the causes of heart disease, smoking is one of the most important and preventable.
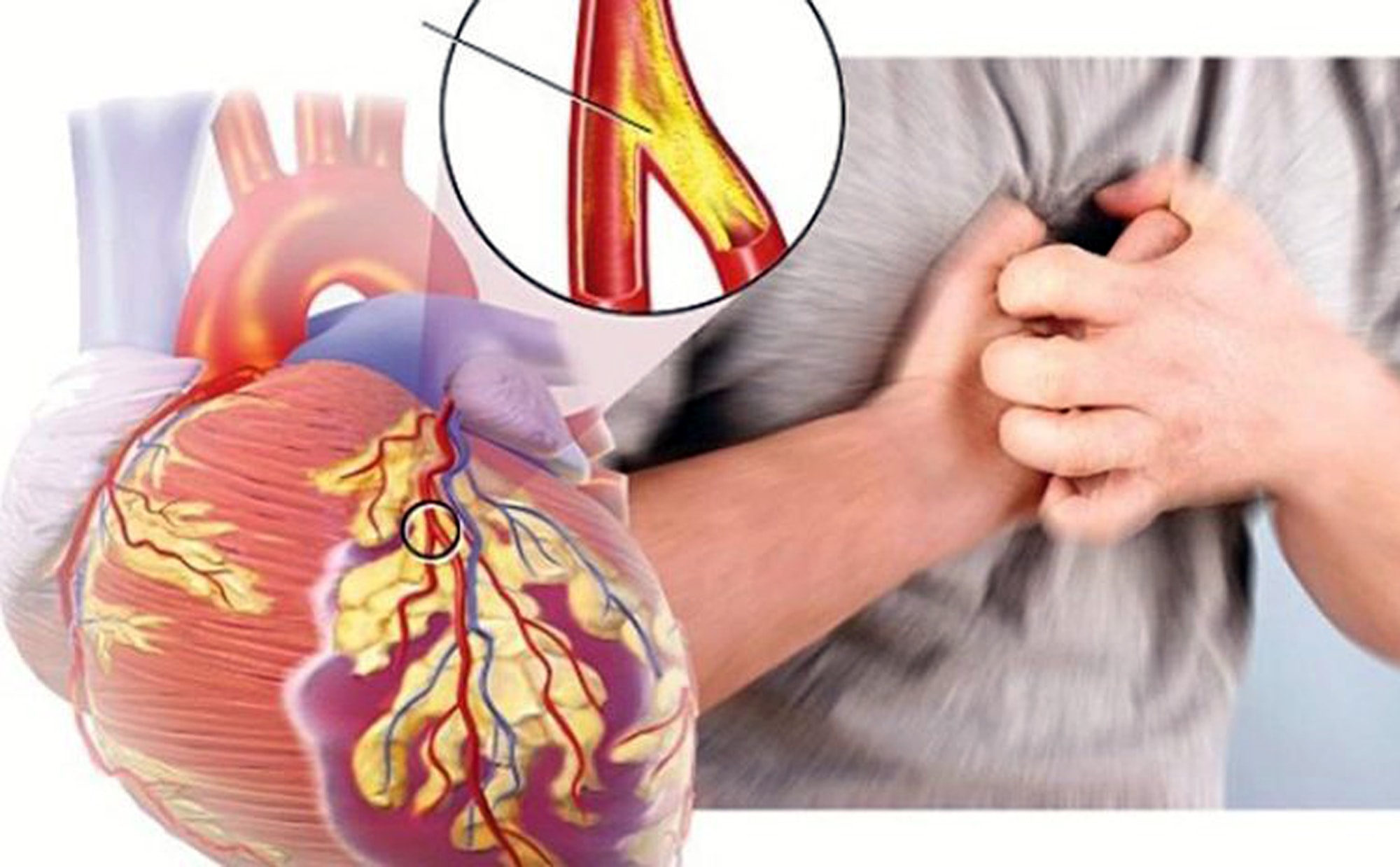
By various mechanisms,smokeis the cause of cardiovascular diseases. First manifested by atherosclerosis, increased blood cell adhesion, increased arrhythmia; reduced oxygen circulation, smokers face these risks more than non-smokers. Among heart diseases, smokers have the highest risk of high blood pressure, coronary heart disease, chest pain, arrhythmia and heart attack.
High blood pressure
Within minutes of smoking, the heart rate begins to increase. The heart rate can increase by as much as 30% and return to normal within 10 minutes of smoking. In response to this stimulation, blood vessels constrict, forcing the heart to work harder to circulate oxygen. Repeated smoking not only increases blood pressure but also changes blood pressure. When blood pressure increases, this phenomenon itself causes heart disease and, more dangerously, high blood pressure leads to serious effects on the heart.
Coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease accounts for more than half of all heart disease caused by smoking. Smoking is a risk factor for developing atherosclerosis, which leads to heart disease. Atherosclerosis is caused by the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries that block and narrow the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. The buildup reduces blood flow and can increase blood pressure. Smoking affects several other parts of the heart, so even a few cigarettes a day will increase your risk significantly.
A study of nurses found that those who smoked four cigarettes a day had a 2.5 times higher risk of coronary artery disease. Heart disease risk is a combination of high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Overall, smokers have a 2 to 4 times higher risk of heart disease and a 70% higher risk of dying from it than non-smokers.
Angina and heart attack
Angina pectoris, also known as ischemia, is a condition caused by a reduction in blood supply to the heart. Long-term smoking damages the lining of blood vessels, leading to chronic constriction of blood vessels. Affected blood vessels are more likely to form plaque. Plaque creates conditions for blood clots to form and block arteries, causing heart attacks. If the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen during contraction, part of the heart muscle can become paralyzed, resulting in a "heart attack". Long-term smokers will suffer from angina and heart attacks at a higher rate than non-smokers. Smokers not only suffer from heart attacks more than non-smokers, but they also suffer from heart attacks that occur earlier and repeatedly in their lives. It is estimated that smoking increases the risk of heart attack recurrence in a year by 6.3 - 12.5% compared to non-smokers.
A study by the Vietnam Heart Institute compared 165 patients who smoked and had a heart attack. All patients had some symptoms of heart attack at the time of the study. The results of the study showed that the risk of myocardial infarction in patients who smoked was higher than that of patients who did not smoke (62.8% and 18.2%, respectively). Increased risks of diabetes and high blood pressure were also found among smokers.
Arrhythmia and sudden death
SmokeSmoking can affect the body's normal functioning by increasing natural chemicals in the body. This can cause arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats. Smokers are at increased risk of developing a dangerous form of arrhythmia called ventriculomegaly and low brain activity. Arrhythmias can increase a person's risk of dying from a heart attack.
Aortic aneurysm
Smokers have a higher risk of developing atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta, the main artery that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. If the aorta becomes weakened by plaques, an aneurysm forms, and the weakened vessel walls can rupture. Smokers are eight times more likely to develop an aneurysm than nonsmokers.
Cardiomyopathy
Heart disease occurs on a large scale, affecting the heart muscle, those who suffer from this disease often have symptoms of severe fatigue and shortness of breath. Heart transplant is necessary for survival because the weakened heart loses its ability to perform its functions. Many studies have found that the risk of heart muscle disease is greater in smokers than in non-smokers.