6 reasons why electric cars cannot replace gasoline and diesel cars
Battery recycling, complex repairs, operating range, and cost are obstacles that prevent electric vehicles from becoming widely popular.
On November 17, at the launch event of Tesla Roadster, the world's fastest accelerating commercial electric car, CEO of the American electric car company Elon Musk said "this is a strong punch" to the traditional gasoline and diesel car industry.
 |
Tesla Roadster, the fastest commercial electric car in the world today. |
The head of Tesla has reason to be confident in his statement. The four-seat electric car Roadster accelerates from 0-97 km/h in 1.9 seconds, has a top speed of 402 km/h, and has a range of 998 km.kmper charge (highway).
While Tesla and other automakers investing in electric and hybrid vehicles have highlighted the many challenges they face in making them, Autoevolution has outlined six issues automakers face as they push to make electric vehicles more popular.
Multinational manufacturing
In the era of globalization, car manufacturers take advantage of supply and labor to move production investment abroad. The purpose is to reduce costs and better meet the different needs in many markets. Electric or hybrid vehicles running on fuel cells face many obstacles from this very approach.
 |
Can electric vehicles with their unique supply requirements be produced in as many factories around the world as traditional cars? |
The first hybrid cars to hit the market used Ni-Mh batteries. The rare metals used to make the batteries were mined from ore mines. They were shipped across the world to where the batteries were made and then shipped to the factories that made the cars.
Today, few manufacturers have the financial resources, factories and technology to produce batteries themselves. Most rely on supplies from specialized companies. Geographical distance affects transportation costs and prices. Where to locate an electric vehicle factory to optimize costs and profits is not an easy problem for manufacturers.
Lithium and rare metals
With the increasing demand of the electric vehicle market and the increasingly high level of science and technology, Li-Ion batteries replace Ni-Mh with the advantages of being able to be charged more times, high energy density and easy to replace. The components used to make batteries contain rare metals, especially Lithium.
 |
Rare earth metals are not cheap in the production of batteries for electric vehicles. |
According to 2015 data from the United States Geological Survey, Australia is the world's largest supplier of lithium. Other countries include Chile, Argentina, China and Zimbabwe.
Like oil, lithium is a finite resource and is becoming increasingly expensive due to the increased demand for electric and hybrid vehicles. As long as the cost of mining and using lithium remains high, electric vehicles will not be as cheap as conventional vehicles.
The problem for electric cars is that lithium is not the only rare metal in batteries. Dysprosium, Lanthanum, Neodymium, Praseodymium are other rare earth metals. They are often found in combination and require high-tech mining, extraction, and storage.
Recycle
Electric vehicles are a future trend that attracts many car manufacturers to participate, but in terms of recycling batteries after use, not many companies show excitement and interest in this market.
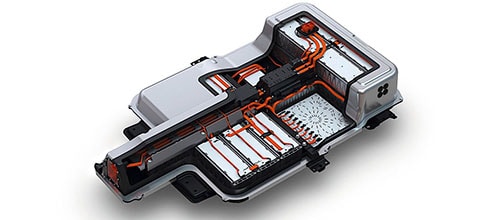 |
Electric car batteries need to be recycled to avoid negative impacts on the environment. |
Toyota is a rare case that has a program to take back old batteries and provide new ones for its products. While most electric cars after being used are sent to the shredder.
The world currently does not have a large enough electric vehicle market to attract companies to invest in recycling batteries from cars.
Repair
Apart from tires or lights, users will find it difficult to repair their own electric vehicles. Even with modern cars today, maintenance or troubleshooting in unexpected situations is an obstacle for many people because of their complexity.
 |
Repairing electric cars is more complicated than repairing gasoline or diesel cars. |
Electric vehicles, like conventional cars, require a high level of reliability. Many people are now wondering what to do if their electric vehicle’s powertrain fails. Repairs can be easily done through a network of dealers or private garages for gasoline and diesel cars, but not necessarily the same for electric vehicles.
Operating range and charging stations
In addition to lowering product prices, manufacturers are racing to expand charging networks and increase the range of electric vehicles. These are the main obstacles to making electric vehicles more popular and convincing customers to give up their habits with traditional cars.
 |
The operating range of electric vehicles is not as wide as that of internal combustion engine vehicles. |
For off-road enthusiasts who want to conquer difficult terrain far from residential areas, electric vehicles are still not a good choice at the moment. Lack of charging stations and the reliability of electric motors are the things that make players wonder.
Renewable Energy
The electricity that powers electric vehicles today is largely derived from non-renewable sources. Solar panels could be a solution, but they are not cheap.
 |
Electric vehicles need time to establish themselves as truly "green" vehicles. |
Hydrogen extraction can be considered as a more optimal method in using clean energy. However, the process of extracting hydrogen from methane releases CO2 which is harmful to the environment. Meanwhile, extracting hydrogen from water currently requires high costs and modern technology. Scientists are working hard to change this.
According to VNE
| RELATED NEWS |
|---|








