Self-healing concrete, carbon nanomaterials, and bricks that change color according to temperature are advanced technologies that could be widely used in the construction industry of the future.
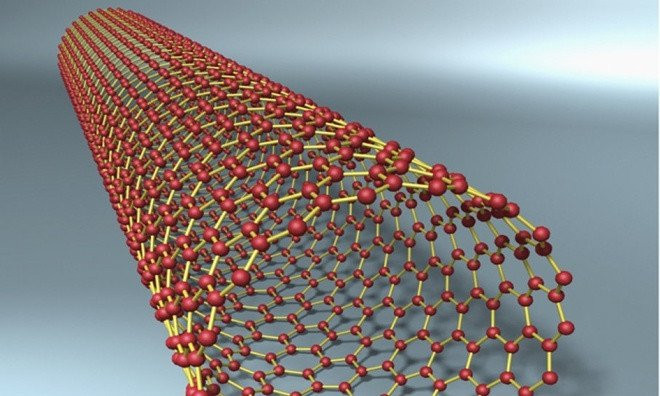 |
| Using electron beam lithography, scientists can now fabricate carbon tubes just one nanometer thick. Carbon nanotubes have a higher strength-to-weight ratio than any other material on Earth, and can be stretched millions of times beyond their original thickness. Carbon nanotubes are so light and strong that they can be mixed into other building materials such as metal, concrete, wood, and glass to increase their density and strength. (Image: Corbis). |
 |
| In 2015, Lafarge Tarmac, a British building materials company, introduced a permeable concrete called Topmix that can absorb 4,000 liters of water in a minute. It is designed with a super-absorbent coating, allowing water to penetrate the surface quickly and avoid stagnation. Permeable concrete not only helps to deal with flooding, but also reduces the heat generated by asphalt paving materials in hot weather. For areas prone to flooding, this method can replace conventional concrete and solve the problem effectively. (Photo: Mirror). |
![Aerogel là một vật liệu rắn dạng bọt gần nhẹ như không khí, có khả năng giữ nguyên hình dạng. Aerogel là một vật liệu rắn dạng bọt gần nhẹ như không khí, có khả năng giữ nguyên hình dạng. Nó được tạo ra bằng cách loại bỏ chất lỏng khỏi gel, tất cả những gì còn lại là cấu trúc silica (SiO2) với 90 đến 99% không khí. Aerogel có tính chất siêu cách điện và cách nhiệt. Dù rất nhẹ, Aerogel có thể thể chịu được sức nóng của một bộ đèn hàn hoặc sức nặng của một chiếc ôtô. (Ảnh: NASA).]() |
| Aerogel is a foamy solid material that is nearly as light as air and can hold its shape. It is created by removing the liquid from a gel, leaving behind a silica (SiO2) structure that is 90 to 99 percent air. Aerogels are super insulators and insulators. Despite being so light, aerogels can withstand the heat of a blowtorch or the weight of a car. (Image: NASA) |
![Gạch thủy tinh trang trí có phủ một lớp sơn thay đổi màu sắc theo nhiệt độ trên bề mặt. Công ty Moving Color, Mỹ, sản xuất gạch thủy tinh trang trí có phủ một lớp sơn thay đổi màu sắc theo nhiệt độ trên bề mặt. Ở nhiệt độ phòng gạch có màu đen bóng. Nhưng khi bạn chạm vào những viên gạch hoặc để chúng dưới ánh sáng và nước ấm, viên gạch sẽ xuất hiện nhiều màu sắc như màu lục, màu lam, màu tím óng ánh. (Ảnh: Moving Color Studios).]() |
| Moving Color Company, USA, produces decorative glass tiles with a coating that changes color according to the temperature on the surface. At room temperature, the tiles are glossy black. But when you touch the tiles or leave them under light and warm water, the tiles will appear in many colors such as green, blue, and iridescent purple. (Photo: Moving Color Studios). |
 |
| Inspired by termites, the Self-Organizing Systems Research Group at Harvard University in the US has created small construction robots that can work together in groups. These four-wheeled robots build brick walls by lifting bricks, climbing walls and placing them in the appropriate positions. They have sensors to detect the presence of other robots as well as algorithms to avoid colliding with each other while moving. (Photo: AFP). |
 |
| WinSu, based in Shanghai, China, built a five-story building and a large villa in Jiangsu province using a 150-meter-long, 6-meter-high 3D printer. The walls were printed layer by layer, then assembled to form a complete block. The "ink" is recyclable construction waste such as iron, glass, cement and special additives. This process of using recycled materials can limit carbon emissions. (Photo: Xinhua/REX). |
 |
| In the future, roads could function as chargers for electric vehicles. New Zealand company Halo IPT has successfully created a road pad that can wirelessly charge an electric vehicle parked above. This technology can be installed directly on roads, garages and parking lots, to ensure continuous charging for vehicles. (Photo: Corbis). |
 |
| Every year, humans release about 33 billion tons of greenhouse gas CO2 into the atmosphere, increasing the process of global warming. Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), USA, use a special yeast to convert CO2 into calcium carbonate (CaCO3) used as a building material. A cup of this genetically modified yeast can produce 1 kg of CaCO3 from 0.5 kg of CO2. (Photo: Nazgoz). |
According to Khoahoc.tv














