Timely rescue of children with severe traumatic brain injury
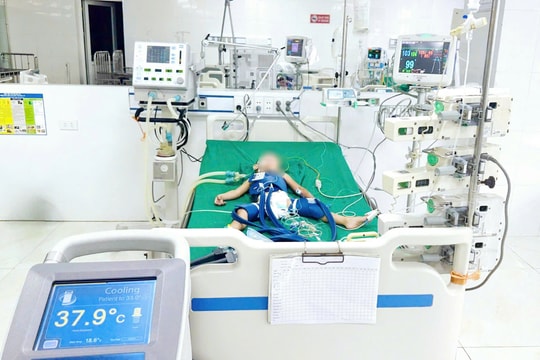
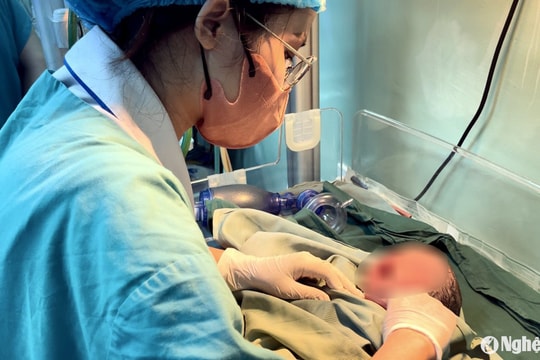
Recently, doctors at Nghe An Obstetrics and Pediatrics Hospital performed emergency surgery and successfully treated an 18-month-old patient with severe traumatic brain injury due to falling down the stairs.
Accordingly, patient D.D.P (18 months old, in Dien Chau district) fell down the stairs from a height of 2m and hit his head on a hard floor. After the fall, the child woke up, cried for a few minutes and then gradually fell into a coma. Quickly, the child was taken by his family to a lower-level hospital for first aid and then transferred to a higher level hospital.Nghe An Obstetrics and Pediatrics HospitalHere, the patient was examined by doctors, performed necessary paraclinical tests and urgently organized an interdisciplinary emergency consultation of Trauma, Orthopedics - Burns, Intensive Care Surgery, Anesthesia and Resuscitation.
.jpg)
CT scan results showed that the patient had multiple skull fractures (frontal, temporal, occipital, and parietal bone fractures), brain tissue contusions, subdural hematoma in the right cerebral hemisphere, and subarachnoid hemorrhage in the right frontal lobe causing herniation of the cerebral acridoid.
The interdisciplinary consultation concluded with the diagnosis: Child was in a coma, traumatic brain injury. Right cerebral hemisphere subdural hematoma, right frontal lobe subarachnoid hemorrhage, right frontotemporal bone fracture, and superior sagittal sinus tear.
The patient was indicated for emergency craniotomy to reduce pressure, remove hematoma and stop bleeding. Entering the surgery, the patient was anesthetized with endotracheal intubation, the team made an inverted question mark incision in the right temporal-frontal parietal region. Then, the surgical team quickly dissected the tissue to expose the skull, observing the fracture of the right temporal-frontal skull through the midline causing a tear in the dura mater and a tear in the superior sagittal sinus that was bleeding heavily. Accompanying this was a lot of brain tissue spilling out, causing hypotension.
The surgeons urgently stopped the bleeding temporarily, expanded the skull to remove about 50ml of subdural hematoma, sutured the venous sinus to stop the bleeding and placed a drain, and created a dura mater. During the surgery, the patient was transfused with 2 units of packed red blood cells, 2 units of fresh frozen plasma... After more than 2 hours of intense surgery, the surgery ended successfully; the patient continued to receive intensive post-operative care and resuscitation at the Department of Surgical Intensive Care.
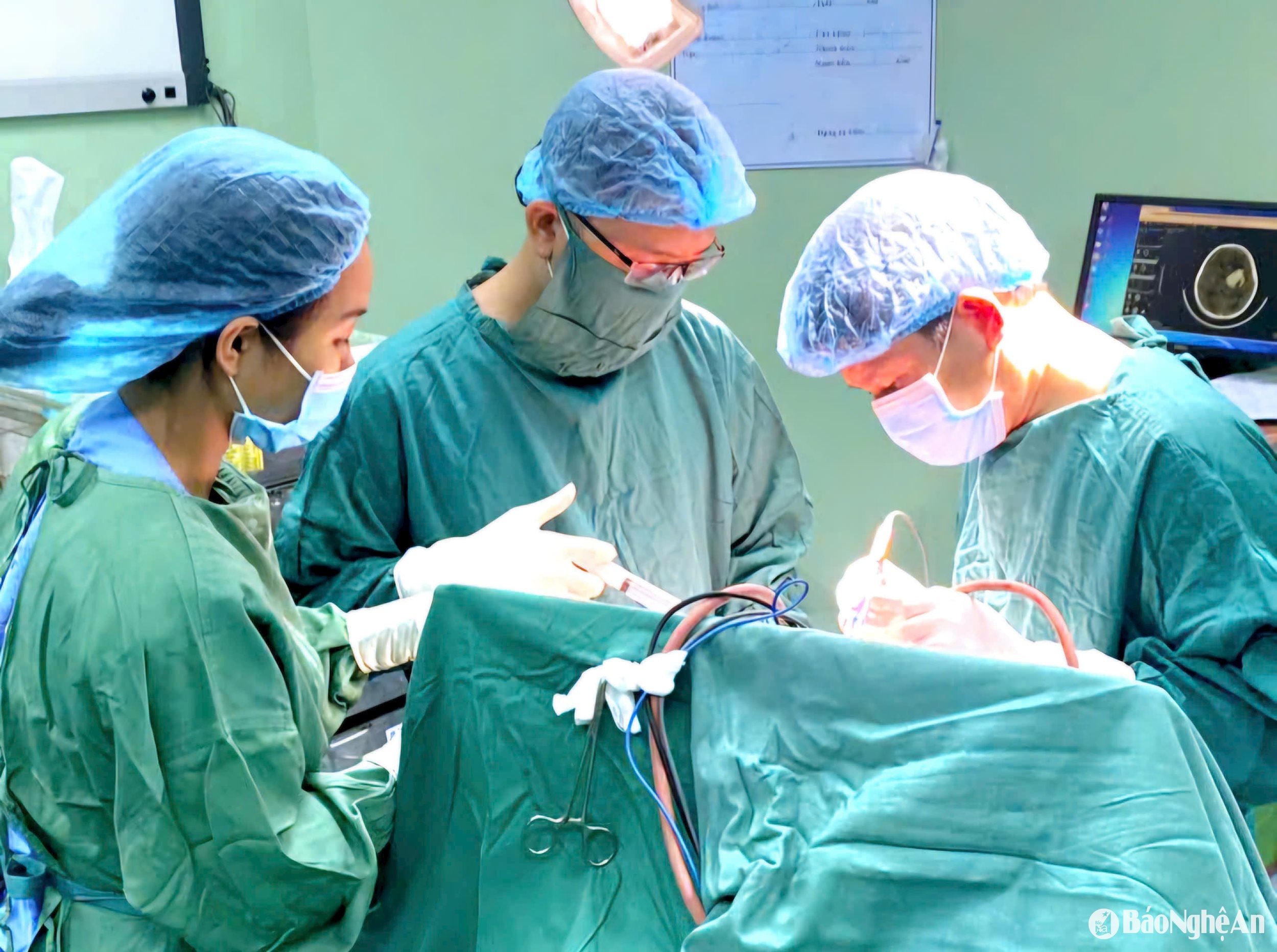
Specialist 2 Phan Van Huy, Deputy Head of the Department of Orthopedic Trauma - Burns, said: Traumatic brain injury is the leading cause of death and disability in children. The venous sinus wound of patient D.D.P. caused acute blood loss, if not treated promptly, the patient could die right on the operating table. In the case of child P., the surgical team performed the fastest surgery, immediately after making an intervention to remove the subdural hematoma, stop bleeding from the torn venous sinus, and limit secondary nerve damage. The success of the surgery came from the close, rhythmic, and precise coordination between the specialties of Orthopedic Trauma, Anesthesia, and Surgical Intensive Care to be able to save the child fromcriticalon the operating table
After 7 days of surgery, the patient was out of danger, conscious and had his endotracheal tube removed. The patient received supportive medical treatment, wound care and monitoring for other complications that may occur after surgery.
Hereby, doctors recommend: The common causes of traumatic brain injury in young children are traffic accidents, domestic accidents (falls due to climbing, heavy objects hitting the head, etc.). Therefore, families and schools need to care and pay attention to children to ensure safety. In case of an unfortunate accident, families need to closely monitor the child's condition, consciousness and unusual symptoms (headache, vomiting, paralysis, etc.). If traumatic brain injury is suspected, the child should be taken immediately to a medical facility for timely examination and treatment./.